
Unit 1 friendship
Participants: 靳燕,黄洋,董妮娅,仝亚军,李桂秀,吴晓,邹舍龙
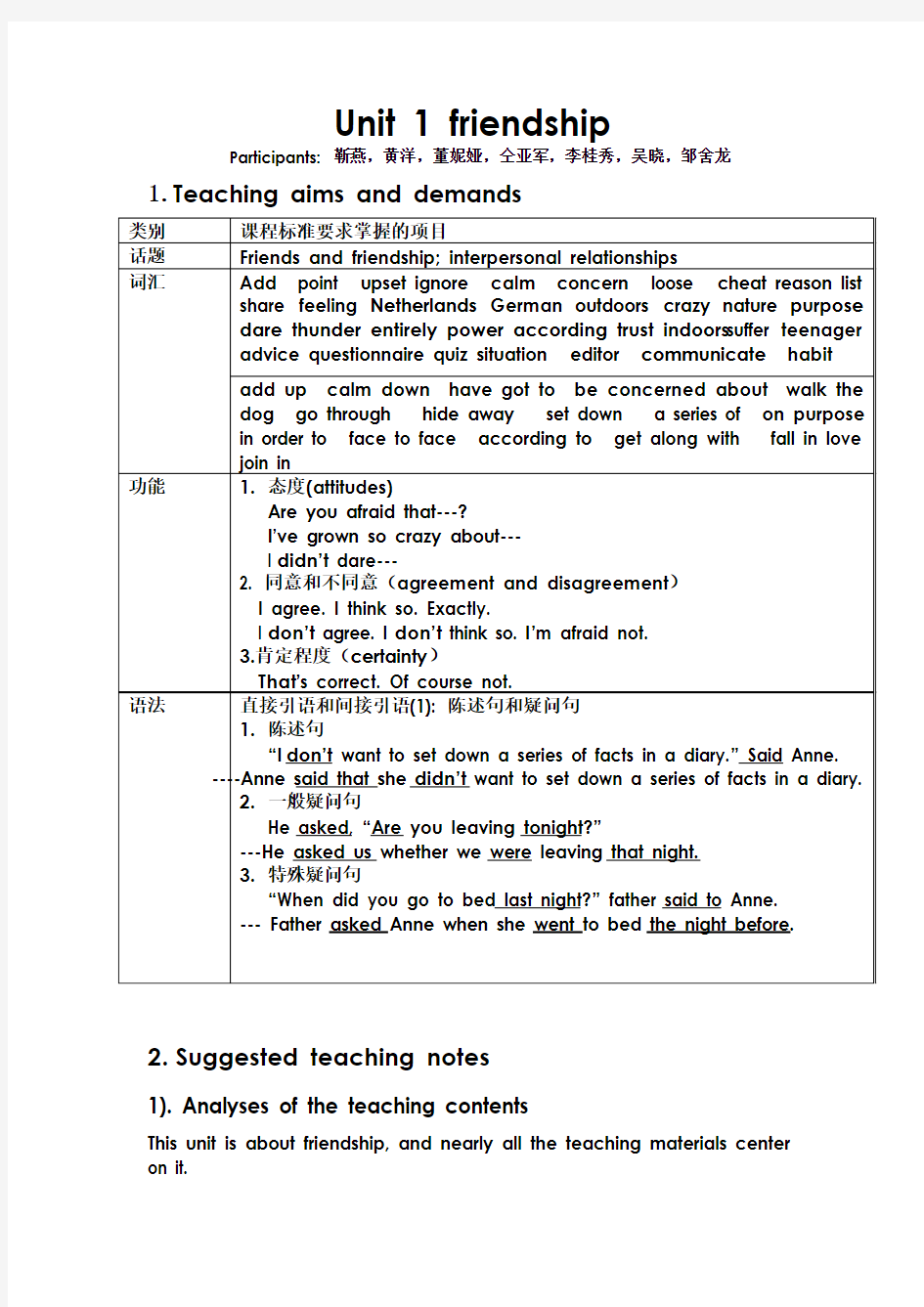
1.Teaching aims and demands
2.Suggested teaching notes
1). Analyses of the teaching contents
This unit is about friendship, and nearly all the teaching materials center on it.
Warming up---The questionnaire leads students to think and talk about friendship, get to know the problems between friends
and seek solutions, which makes preparations for the
further teaching in topics, background and vocabulary. Pre-reading---The questions prompt students to think critically about
friends and friendship in reality, alerting them to the fact
that besides people, a diary can be a friend, too. Reading--- The diary by theJewish girl Anne gave a glimpse of her life during her family’s shelter in Amsterdam from the German
Nazis’ killing in world war 2. she treats the diary as her best
friend, and in it reveals her longing for a normal life and
close contact with nature, which helps her get through the
days.
Comprehending---It helps students further understand the text by doing
multiple choices, questions and answers, and
matching.
Learning about language---It teaches the important expressions and
structures and grammar: direct and indirect
speeches.
Using language---The two letters, listening, questionnaire design, letter
writing and fun writing prepares students to further
talk about friendship, especially the problems with
misunderstanding, and unfriendliness, thus
strengthening students’ abilities to practice
language, discover, and solve problems. Summing up---It summarizes the whole contents of this unit from the
aspects of topics, vocabulary and grammar.
Learning tip--- This part encourages students to form the habit of writing
a diary.
Integrating skills--- The text introduces the way Hawaiians express
friendship, to get students to realize the cultural
differences in the values of friendship in addition
its importance in all cultures.
2) Making of the teaching plan
This unit centers on friends and friendship, exploring different types of friendship with particular attention to that one can develop with oneself, i.e., the comfort and support one seeks from an imaginary friend. Students are expected to come to be truly aware of the qualities and conducts that make a good friend, display and develop the ability to cope with misunderstanding, conflicts and problems related to friendship, and give advice on it. The concept that even an ordinary thing can be a friend should break down the traditional belief in the
interpersonal nature of friendship. Also, the comparison of similarities dissimilarities in friendship comprehension between the East and the West leads students to know better the values of friendship in Westerns’eyes. All in all, this unit promises to unveil the true essence of friendship and helps students to lead a more friendly and harmonious life. Thus, based on the theme, contents and teaching objectives, the whole
3. Teaching plans for each period
Period 1 Warming-up and Speaking
1. Teaching objectives:
1) Target language
I (don’t) think…… I (don’t) think so. I (don’t) agree.
I believe……That’s correct. In my opinion, ……
2) Ability goals
a.Describe your friends in English
b.Figure out the problems between friends and then find different
ways to solve the problems.
3)Learning ability goals
a.To encourage students to think and talk about friends and
friendship by using some phrases and structures.
b.To learn to solve problems that may occur between friends.
c. To cultivate the students to form the good habit of learning English in
Senior Middle School.
2. Teaching important points:
https://www.doczj.com/doc/a89820883.html,e the given adjectives and sentence structures to describe
one of your friends.
b.Learn to evaluate friends and friendship.
3. Teaching difficult points:
a.Work together with partners and describe one of your good
friends.
b.Discuss with partners and find out ways to solve the problems.
4. Teaching methods
a.Task-based teaching and learning
b.Cooperative learning
c.Discussion
5. Teaching aids:
CAI
6. Teaching procedures and ways:
Step 1 Lead-in and Warming-up
Before the lesson, the teacher can arouse the students’ interests by showing a video of Auld Lang Syne .
At the beginning of the first class, we can get the students to talk about their summer holidays. The students can talk freely as they like.
1.How did you spend your summer holidays? How did you
feel? What did you do in your summer holidays? What did
you do in your spare time?
2.What do you think of our new school? Do you like it? Could
you say something about it?
3.Do you like making friends? How do get in touch with your
friends? Do you have many friends? Where are they now?
Do you have any old friends in our school? Have you made
any new friends in our class?
Step 2 Think it over
1. Give a brief description of one of your friends. The following
phrases and structures may be helpful:
His/Her name is ……
He /She is …… years old.
He /She likes …… and dislikes ……
He /She enjoys …… and hates……
He /She is very kind/friendly/……
When /Where we got to know each other.
2. What types of friendship do you have? Please tick them out.
Then fill in the blanks.
girl friends boy friends pen friends
long -distance friends friends of the same age
e-friends (friends over the internet) friends across generations
unusual friends like animals, books……
1).______ is /are most important to you.
2). You spend most of your free time with ____.
3). You will share your secrets with _____.
4). When in trouble, you will first turn to _____.
Step 3 Make a survey
1. List some qualities of a good friend or your ideal friend. Have the students get into groups of four to find out what each has listed.
Tell your partner your standards of good friends by using the following structure:
I think a good friend should (not) be……
In my opinion, a good friend is someone who……
1.Have a member of each group report on what their lists have in
common and list them on the board.
2.Ask the class whether or not they agree with all the qualities listed.
3.Then have the students do the survey in the textbook.
4.Have the students score their survey according to the scoring sheet
on page 8.
5.The teacher ask some students how many points they got for the
survey and assess their values of friendship:
★4~7 points: You are not a good friend. You either neglect your friend’s needs or just do what he/she wants you to do. You should think more about what a good friend needs to do.
★8~12 points: You are a good friend but you sometimes let your friendship become too important, or you fail to show enough concern for your friend’s needs and feelings. Try to strike a balance between your friend’s needs and your own responsibilities.
★ 13+ points: You are an excellent friend who recognizes that to be a good friend you need balance your needs and your friend’s. Well done. (You may also show your students the results above and let themselves self-reflect upon their own values of friendship)
Step 4 Talking and sharing( work in pairs)
1. If your best friend does something wrong, what will you do?
Try to use the following phrases:
I (don’t) think…… I (don’t) think so.
I (don’t) agree. I believe……
That’s correct. In my opinion,……
2. What is a friend?
A British newspaper once offered a prize for the best definition(定义) of a friend. If you were the editior, choose the best one from the following entries(条目), and explain why.
One who understands my silence.
A friend in need is a friend indeed.
Friends are just the people who share your happiness and sorrow. When you look at your watch at 4 am, but still know you can call
them and wake them up, and they’ll still want to talk to you ,that’s friendship.
To have a friend, you need to be a good friend.
Step 5 Group work (output)
The teacher can give each group one of these questions below to talk about. Then let the class share their ideas. It’s better to stimulate the students to express their own opinions about these questions.
1.Do you think it is a good idea to borrow money from your friend?
Why and Why not?
2. What factors may cause the breakdown of a good friendship?
3. What can be your unusual friend besides human beings? And why?
Step 6 homework
1.Write down a short passage about your ideas /the factors/your
unusual friends.
2.Prepare for the new lesson.
Period 2 Reading “Anne’s Best F riend”
1. Teaching objectives:
1) To develop the students’ reading ability, learn to use some readi ng strategies such as guessing, key sentences, skimming and so on;
2). To get the students to realize the importance of friends and friendship, and to tell true friends from false friends;
3). To grasp some useful words and expressions in this passage, such as on purpose, be crazy about etc.;
4). To learn the writing style of this passage.
2. Teaching method: Task-based teaching
3). Teaching procedure:
Step 1.Pre-reading
1. Please enjoy three pieces of music and find out what they are about.
2 .Why do you think friends are important to you?
3. What do you think a good friend should be like? List the good qualities
a good friend should have .
4. Have you ever considered making friends with animals, plants or even an object? Why or why not?
Step 2.Reading
1. Try to guess what Anne’s friend is and what the passage is about by reading the title and having a quick at the pictures in this passage without reading it.
2. Skimming the first two paragraphs to confirm your guessing.
1) What was Anne’s best friend? W hy did she make friends with it?
2) Did she have any other true friends then? Why?
3) What is the difference between Anne’s diary and those of most people?
4) Do you keep a diary? What do you think most people set down in their diaries?
5) We are going to read one of Anne’s diaries .but before reading ,can you tell me what the diary is about with the help of one key sentence in the 2nd paragraph?
3. Reading of Anne’s diary
How she felt in the hiding place
Two examples to show her feelings then
Step 3.Post-reading
1.What would you miss most if you went into hiding like Anne and her family? Give your reasons.
2.Group work
Work in groups to decide what you would do if your family were going to be killed just because they did something the Emperor did not like.
Where would you plan to hide?
How would you arrange to get food given to you every day?
What would you do to pass the time?
------
3. Discovering useful words and expressions
Complete the following sentences, using words and expressions from Reading
1) She has grown _______ about computer games.
2) Was it an accident or did David do it on _______?
3) From the beginning ,Paul made it clear that he would be ______ (完全地)in control.
4) He used to work _______ even in the middle of winter.
5) Just the _______ of more food made her feel sick.
6) You had better have a _________ talk with him.
7) Born in a poor family, the manager _________ lots of hardships in his childhood.
8) A diary is often kept to ________ what happens in people’s daily lives.
Step 4.Talking about friends and friendship
1.There are many proverbs about friends and friendship. Choose the one you agree with and explain why, then choose one you disagree with and explain why.
A friend in need is a friend indeed.
Friends are like wine; the older, the better.
A friend to all is a friend to none.
The same man cannot be both friend and flatterer(阿谀奉承者).
False friends are worse than open enemies.
Walking with a friend in the dark is better than walking alone in the light.
2. We have talked about friends and friendship today, can you write one or two sentences to express your understanding of friends and friendship.
Step 5.Homework:
1. Interview a high school student, a businessman, a police officer and a housewife to find out their opinions about friends and friendship. Write a
report to share it with the whole class.
2. Describe one of your best friends following the writing style of this passage.
Ending: Let’s sing this song about friends together
Period3 Grammar
1.Teaching objectives
Learn to use direct speech and indirect speech
2. Teaching important point
Summarize the rules of Direct Speech and Indirect Speech.
3. Teaching difficult point
Learn about the special cases in which the tenses shouldn’t be changed.
4. Teaching methods
Discussing, summarizing and practicing.
5. Teaching procedures
Step1 Lead in
T: In the last lesson, we learned Anne Frank’s story. She is telling her stories to two of her friends—you and Tom. Tom has something wrong with his ea rs,so you have to repeat Anne’s sentences, using indirect speech. Sometimes you explain Tom’s sentences to Anne.
“I have to stay in the hiding place.” said Anne.→
Anne said she had to stay in the hiding place.
“Do you feel sad when you are not able to go outdoors?” Tom asked Anne. →
Tom asked Anne if/whether she felt sad when she was not able to go outdoors.
“I don’t want to set down a series of facts in a diary,” said Anne.→Anne said that she didn’t want to set down a series of facts in a diary. “What do you call your diary?” Tom asked.→
Tom asked what she called her diary.
Ss go on this topic by themselves.
Step2 Grammar
T: Now let’s look at these sentences again. If we want to change Direct Speech into Indirect Speech, what should be changed?
Ss discuss by themselves.
Ss: sentence structures, tenses, pronouns, adverbials of time and place and verbs should be changed.
T: Quite right. Look at the form on the screen. These are the rules.
直接引语变成间接引语时,要注意以下几点:人称变化、时态变化、宾语从句要用陈述句语序。
1.直接引语是陈述句,变成间接引语时,由连词that 引导。例如:
She said, "I am very happy to help you."→
She said that she was very happy to help you.
2. 直接引语是一般/选择疑问句,变成间接引语时,由连词whether或if 引导。例如:
He asked me, "Do you like playing foot ball?"→
He asked me if/whether I liked playing football.
注意:大多数情况下,if和whether 可以互换,但后有or not,或在动词不定式前,或放在介词后作连接词时,一般只用whether。例如:
She asked me whether he could do it or not.
3. 直接引语是特殊疑问句,变成间接引语时,由相应的疑问词who, whom, whose, how, when, why, where 等引导。例如:
My sister asked me, "How do you like the film?"→
My sister asked me how I liked the film.
4. 直接引语是祈使句,变成间接引语时,把动词原形变成动词不定式,并在动词不定式前加tell, ask, order 等的宾语。例如:
The captain ordered, "Be quiet."→
The captain ordered us to be quiet.
注意:此种情况的否定句,在动词不定式前加not。
My teacher asked me, "Don't laugh."→
My teacher asked me not to laugh.
5. 一些注意事项
(1)间接引语一般要用陈述句的语序,即主、谓、宾的顺序。例如:
He asked Lucy, "Where did you go?"→
He asked Lucy where she went.
Tom said, "What do you want, Ann?"→
Tom asked Ann what she wanted.
(2)直接引语是客观事实、普遍真理等,变成间接引语时,时态不变。例如:
They told their son, "The earth goes round the sun."→
They told their son that the earth goes round the sun.
(3)直接引语变间接引语时,指示代词、时间状语、地点状语等要作相应的变化。例如:
He said, "I haven't seen her today."→
He said that he hadn't seen her that day.
注意:如果转述时就在原来的地方,就在说话的当天,就不必改变指示代词、时间状语、地点状语等。
Direct Speech Indirect Speech
Present past
Past past and past perfect
Present perfect past perfect
Past perfect past perfect
Present continuous past continuous
Step3 practice
T: Turn to Page 5. Please change the following direct speech into indirect speech and indirect into direct.
1.“I’m going to hide from the Germans,” Anne said.
2.“I don’t know the address of my new home,” said Anne.
3.“I cannot ask my father because it is not safe to know,” she said.
4.“I had to pack up my things very quickly,” the girl said.
5.“Why did you choose your diary and old letters?” Dad asked her.
6.Mum asked her if/whether she was very hot with so many clothes on.
7.Margot asked her what else she had got.
8.Anne asked her father when they would go back home.
9.Anne asked her sister how she could see her friends.
10.Mother asked Anne why she had gone to bed so late the night
before.
Step4 Correcting mistakes
T analyses the common mistakes Ss have made during the practice. T: Now let’s look at the screen and pay attention to these sentences. Choose the right sentence and tell me why the other one is wrong. Step5 A game
Play a guessing game “who is my secret friend?” One student comes to the front with his partner.
The rest students ask him questions while his partner changes them into indirect speech. In the end, the person who has guessed the right answer can come to the front to take the place of the first student .So the game goes on.
Suggested sentences:
Can your friend speak?
What does he/she wear today?
Is he/she tall or short?
What do you and your friend do in your free time?
Do you quarrel with each other?...
Step6 Homework
Do Exercise1 on Page 42. He re is another page of Anne’s diary. Read it through and then use indirect speech to retell the story.
Period 4 integrating skills “Friendship in Hawaii”
1. Teaching objectives:
To learn about ways of showing friendship in Hawaii and share their opinions on friendship. Because it is a lesson of integrating skills, Ss are also asked to write sentences on friendship.
2. Teaching procedures:
Step1 Lead-in
1. Talk about different ways of showing friendship of minority groups
in China.
2. Compare Chinese ways of showing friendship with Western ways.
And discuss why there is a big difference. Therefore, show the sentence: Every culture has its own ways to show friendship.
3. Ask students if they can think of any place in the world where
Chinese and Western cultures live side by side. They may think of Hongkong, Macao, Singapore. And the teacher will add one more -------Hawaii.
Step2 Fast reading
1. It is said that Hawaii is a place where the East truly meets the west.
Consider how people show their friendship in Hawaii.
Show a picture and find the information from the textbook. ( by giving “leis” to one another.)
Explain what is a “lei”.
2. Read fast and find out more ways to show friendship in Hawaii to fill
in the form.
3. According to the form, ask them to consider what friendship is in
Hawaiians.
Step 3 Careful reading
1.Read the 2nd paragraph carefully and ask “Why do many
different peoples call Hawaii their home?”
( Hawaii is a place where people make one big community from many smaller communities. It means Hawaii has a rich cultural diversity.)
Step 4 Writing task
1.Show proverbs about friends and friendship. Explain them and
ask Ss to choose some they agree with and some they disagree with and explain why.
2.Discuss with their partner and try to write some similar sentences
to show their opinions on friendship.
Step 5 Homework
Surf the Internet to collect materials like poems, stories about friendship. And share them with your friends.
Period 5 Listening & Writing
1. Teaching objectives
To practise students’ listening ability.
To practise students’ writing skill s of how to offer advice.
To improve students’ ability to help others solve problems.
2. Teaching procedure
(Analysis: Listening and writing are expansion of the topic of the text. Listening is about Lisa’s problem of making a friend with a boy. She asks Miss Wang for advice. Through listening and exercise, students learn how to give advice and the skill of giving advice. And also let them think about the problem of boy’s making friends with girls and girls with boys. And then design a task to ask students to give advice according to the different problems to practise their ability to solve the problems. All of these lay the foundation for the next task writing. In this way, students feel that they have information to put out. And writing makes for the improvement of students’ writing ability, strengthening their
comprehension of friendship.)
Step 1 Lead-in
Do you remember what Ann’s best friend is?
Is it a man or a thing?
Have you seen the film Cast Away?
When Tom is alone on a deserted island, what does he make friends with? ( a volleyball)
Guess what my best friend is? (Say sth. about music, pets or plants.)
So you see a man can make friends with anyone and anything.
Then boys, would you like to make friends with girls? Girls, would you like to make friends with boys?
What kind of girl would you like to make friends with? And what kind of boy would you like to make friends with?
If you see a boy classmate makes a friend with a girl, will you say something about them behind?
(If no, say you are kind. If yes, say you are a gossiper.)
If you are that boy/girl, would you like to be gossiped about?
But here Lisa has such a problem. Read the letter. Lisa is asking you for help. What advice will you give? You are given 2 minutes to discuss in groups and then offer group’s opinions.
Step 2 Listening
Besides you Lisa also asks Miss Wang of Radio for Teenagers for help. What advice does Miss Wang give to Lisa? Let’s listen to wha t she says. Listen for 3 times and do listening exercises.
Step 3 Post-listening
Do you think Miss Wang’s advice is helpful?
Now suppose you are editors of Radio for Teenagers, here are some
problems for you to offer advice.
(Give each group a problem and ask them to write down their advice.)
1.I don’t have enough pocket money.
2.I’m not satisfied with my appearance.
3.My desk mate has lost a reference book, she/he thinks that I’m a
thief.
4.I work hard but I hardly make progress.
5.I want to travel to WuZhen Town with my fiends this weekend, but my
parents don’t allow me to go.
6.I don’t like the way Mr. Li teaches us English, so I’m not interested in
English any longer.
7.My mother has just given birth to my little brother. I’m worried that the
baby will rob me of my parents’ love and even everything.
8.I quarreled with my best friend 3 days ago. Up to now, we haven’t
said a word to each other.
9.I’d like to be monitor, but at the same time I doubt whether I have
such ability.
10.I’m often late for school. The teacher is so angry that he threatens
that if I’m late again, I will be dismissed.
Step 4 Writing
Your advice is good and helpful. All of you are qualified editors. Now I have just received a letter from a lonely boy. Read the letter, what is his problem? What is your advice for him? Write a reply.
Step 5 Homework
Write a story about you and your friend.
数学汇总 第一章 集合与函数概念 教学目的:(1)理解两个集合的并集与交集的的含义,会求两个简单集合的并集与交集; (2)理解在给定集合中一个子集的补集的含义,会求给定子集的补集; (3)能用Venn 图表达集合的关系及运算,体会直观图示对理解抽象概念的作用。 教学重点:集合的交集与并集、补集的概念; 教学难点:集合的交集与并集、补集“是什么”,“为什么”,“怎样做”; 【知识点】 1. 并集 一般地,由所有属于集合A 或属于集合B 的元素所组成的集合,称为集合A 与B 的并集(Union ) 记作:A ∪B 读作:“A 并B ” 即: A ∪B={x|x ∈A ,或x ∈B} Venn 图表示: 说明:两个集合求并集,结果还是一个集合,是由集合A 与B 的所有元素组成的集合(重复元素只看成一个元素)。 说明:连续的(用不等式表示的)实数集合可以用数轴上的一段封闭曲线来表示。 问题:在上图中我们除了研究集合A 与B 的并集外,它们的公共部分(即问号部分)还应是我们所关心的,我们称其为集合A 与B 的交集。 2. 交集 一般地,由属于集合A 且属于集合B 的元素所组成的集合,叫做集合A 与B 的交集(intersection )。 记作:A ∩B 读作:“A 交B ” 即: A ∩B={x|∈A ,且x ∈B} 交集的Venn 图表示 说明:两个集合求交集,结果还是一个集合,是由集合A 与B 的公共元素组成的集合。 拓展:求下列各图中集合A 与B 的并集与交集 A B A(B) A B B A A ∪B B A ?
说明:当两个集合没有公共元素时,两个集合的交集是空集,不能说两个集合没有交集 3. 补集 全集:一般地,如果一个集合含有我们所研究问题中所涉及的所有元素,那么就称这个集合为全集(Universe ),通常记作U 。 补集:对于全集U 的一个子集A ,由全集U 中所有不属于集合A 的所有元素组成的集合称为集合A 相对于全集U 的补集(complementary set ),简称为集合A 的补集, 记作:C U A 即:C U A={x|x ∈U 且x ∈A} 补集的Venn 图表示 A U C U A 说明:补集的概念必须要有全集的限制 4. 求集合的并、交、补是集合间的基本运算,运算结果仍然还是集合,区分交集与并集的关键是“且” 与“或”,在处理有关交集与并集的问题时,常常从这两个字眼出发去揭示、挖掘题设条件,结合Venn 图或数轴进而用集合语言表达,增强数形结合的思想方法。 5. 集合基本运算的一些结论: A ∩ B ?A ,A ∩B ?B ,A ∩A=A ,A ∩?=?,A ∩B=B ∩A A ?A ∪B ,B ?A ∪B ,A ∪A=A ,A ∪?=A,A ∪B=B ∪A ( C U A )∪A=U ,(C U A )∩A=? 若A ∩B=A ,则A ?B ,反之也成立 若A ∪B=B ,则A ?B ,反之也成立 若x ∈(A ∩B ),则x ∈A 且x ∈B 若x ∈(A ∪B ),则x ∈A ,或x ∈B ¤例题精讲: 【例1】设集合,{|15},{|39},,()U U R A x x B x x A B A B ==-≤≤=<< 求e. 解:在数轴上表示出集合A 、B ,如右图所示: {|35}A B x x =<≤ , (){|1,9U C A B x x x =<-≥ 或, 【例2】设{|||6}A x Z x =∈≤,{}{}1,2,3,3,4,5,6B C ==,求: (1)()A B C ; (2)()A A B C e. 解:{}6,5,4,3,2,1,0,1,2,3,4,5,6A =------ . (1)又{}3B C = ,∴()A B C = {}3; (2)又{}1,2,3,4,5,6B C = , A B B A -1 3 5 9 x
高中英语必修一教案Unit 1 Friendship
1.Suggested teaching notes 1). Analyses of the teaching contents This unit is about friendship, and nearly all the teaching materials center on it. Warming up---The questionnaire leads students to think and talk about friendship, get to know the problems between friends and seek solutions, which makes preparations for the further teaching in topics, background and vocabulary. Pre-reading---The questions prompt students to think critically about friends and friendship in reality, alerting them to the fact that besides people, a diary can be a friend, too. Reading--- The diary by theJewish girl Anne gave a glimpse of her life during her family’s shelter in Amsterdam from the German Nazis’ killing in world war 2. she treats the diary as her best friend, and in it reveals her longing for a normal life and close contact with nature, which helps her get through the days. Comprehending---It helps students further understand the text by doing multiple choices, questions and answers, and matching. Learning about language---It teaches the important expressions and structures and grammar: direct and indirect speeches. Using language---The two letters, listening, questionnaire design, letter writing and fun writing prepares students to further talk about friendship, especially the problems with misunderstanding, and unfriendliness, thus strengthening students’ abilities to practice language, discover, and solve problems. Summing up---It summarizes the whole contents of this unit from the aspects of topics, vocabulary and grammar. Learning tip--- This part encourages students to form the habit of writing a diary. Integrating skills--- The text introduces the way Hawaiians express friendship, to get students to realize the cultural differences in the values of friendship in addition
高一英语必修一单词表(人教版)Unit 1 1.survey n.调查;测验 2.add up合计 3.upset adj. 心烦意乱的;不安的,不适的 4.ignore v.不理睬;忽视 5.calm vt.&vi.(使)平静;(使)镇定adj.平静的;镇定的;沉着的 6.calm...down(使)平静下来 7.have got to不得不;必须 8.concern vt.(使)担心;涉及;关系到n. 担心;关注;(利害)关系 9.be concerned about关心;挂念 10.walk the dog 遛狗 11.loose adj 松的;松开的 12.vet n.兽医 13.go through经历;经受 14.Amsterdam 阿姆斯特丹(荷兰首都) https://www.doczj.com/doc/a89820883.html,herlands 荷兰(西欧国家) 16.Jewish 犹太人的;犹太族的 17.German 德国的;德国人的;德语的。 18.Nazi n.纳粹党人adj. 纳粹党的 19.set down记下;放下;登记 20.series n.连续,系列 21.a series of一连串的;一系列;一套 22.outdoors adv.在户外;在野外 23.spellbind vt.( spellbound,spellbound)迷住;疑惑 24.on purpose故意 25.in order to为了 26.dusk n.黄昏傍晚 27.at dusk在黄昏时刻 28.thunder vi 打雷雷鸣n. 雷,雷声 29.entire adj. 整个的;完全的;全部的 30.entirely adv. 完全地;全然地;整个地 31.power n.能力;力量;权力。 32.face to face面对面地 33.curtain n.窗帘;门帘;幕布 34.dusty adj 积满灰尘的 35.no longer /not?any longer不再 36.partner n.伙伴.合作者.合伙人 37.settle n.安家;定居;停留vt. 使定居;安排;解决 38.suffer vt. &遭受;忍受经历 39.suffer from遭受;患病 40.loneliness n.孤单寂寞 41.highway n.公路
课题:§1.1 集合 1 2 教材分析:集合概念及其基本理论,称为集合论,是近、现代数学3 的一个重要的基础。许多重要的数学分支,都是建立在集合理论的基4 础上。此外,集合理论的应用也变得更加广泛。 5 课型:新授课 6 课时:1课时 7 教学目标:1.知识与技能 8 (1)通过实例,了解集合的含义,体会元素与集合的理解集合“属9 于”关系; 10 (2)牢记常用的数集及其专用的记号。 11 (3)理解集合中的元素具有确定性、互异性、无序性。 12 (4)能选择自然语言、图形语言、集合语言(列举法或描述13 法)描述不同的问题。 14 2.过程与方法 15 (1)学生经历从集合实例中抽象概括出集合共同特征的过16 程,深入理解集合的含义。 17 (2)学生自己归纳本节所学的知识点。 18 3.情感态度价值观 19 使学生感受学习集合的必要性和重要性,增加学生对数20 学学习的兴趣。
教学重点:集合的概念与表示方法。 教学难点:对待不同问题,表示法的恰当选择。 21 教学过程: 22 一、引入课题 23 军训前学校通知:8月15日8点,高一年段在体育馆集合进行军训动员;试24 问这个通知的对象是全体的高一学生还是个别学生? 25 在这里,集合是我们常用的一个词语,我们感兴趣的是问题中某些特定(是26 高一而不是高二、高三)对象的总体,而不是个别的对象,为此,我们将学习27 一个新的概念——集合(宣布课题),即是一些研究对象的总体。 28 阅读课本P 2-P 3 内容 29 二、新课教学 30 (一)集合的有关概念 31 1.集合理论创始人康托尔称集合为一些确定的、不同的东西的全32 体,人们能意识到这些东西,并且能判断一个给定的东西是否属于这个33 总体。 34 2.一般地,我们把研究对象统称为元素(element),把一些元素35 组成的总体叫做集合(set)(简称为集)。 36 3.关于集合的元素的特征 37
必修一 Unit 1 Friendship 单元要点预览(旨在让同学整体了解本单元要点) Ⅰ.词语辨析(旨在提供完形填空所需材料)
Ⅱ.词性变化(旨在提供语法填空所需材料)
Ⅲ.重点词汇(旨在提供综合运用所需材料) 1. upset adj. 心烦意乱的,不安的;不适的vt. (upset, upset) [典例] 1). Our arrangements for the weekend were upset by her visit. 她一来把我们周末的安排给打乱了。 2). Don't upset yourself -- no harm has been done. 不要难过--并没有造成伤害。 3). He was horribly upset over her illness. 他为她的病而忧心忡忡。 4). The students really upset her. 学生们着实让她烦恼。 [重点用法] be ups et by… 被…… 打乱 upset oneself about sth 为某事烦恼 [练习] 用upset的适当形式填空 1). Is it ______ you, dear? 2). She felt rather ______ on hearing the news. 3). Is it an ______ message? 4). Don’t be ______. It will be OK. 答案: 1). upsetting 2). upset 3). upsetting 4).upset 2. concern v.担忧; 涉及; 关系到 n. 担心,关注;(利害)关系 [典例] 1). The news concerns your brother. 这消息与你兄弟有关。 2). The boy's poor health concerned his parents. 那男孩健康状况不佳,使他的父母亲忧虑。 3). That's no concern of mine. 那不关我的事。 [重点用法] as / so far as … be concerned 关于;至于;就……而言 be concerned about 关心 be concerned at / over sth. 为某事忧虑 be concerned in sth. 牵涉到,与……有关,参与 [练习] 用concern的适当形式填空 1). There is an article that _______ the rise of the prices. 2). The children are rather _____ about their mother’s health. 3). Officials should ______ themselves _______ public affairs.
高一年级英语必修一教案 人教版高一年级英语必修一教案 作为一名为他人授业解惑的教育工作者,总不可避免地需要编写教案,借助教案可以提高教学质量,收到预期的教学效果。那么应当如何写教案呢?下面是小编整理的人教版高一年级英语必修一教案,供大家参考借鉴,希望可以帮助到有需要的朋友。 人教版高一年级英语必修一教案1 Step I.Revision Check the homework with the whole class. Step II. Warming up Ask the students to read the instructions and make sure they know what to do, and then have a discussion about the two pictures. T: Today, before we begin our reading, I’d like to ask you a question, “What is the biggest sound you have heard in your life?” S1: The sound of wind that blew in a winter night when I was very young. It sounded like a ghost who was howling.
I was very frightened at that time. S2: The biggest noise was the one that I heard when my neighbor was quarrelling with his wife. Perhaps, they broke their TV set. T: That’s too terrible. S3: The noise when planes take off. S4: The sound of trains. T: Good! I agree that all of them are big sound. But did you once heard the sound that the heaven falls and the earth cracks, in Chinese it is 天崩地裂? Ss: No, we have no chance to hear that. T: If there is a sound like this, what is it? S5: When someone hears something unexpected and terrible. For example, when one of his loved families dies, he will feel this sound. T: Terrific! You are using a literary way to express the sound. S6: When an earthquake happens. T: Great! I have waited for this answer for a long time. Today we’ll learn something about earthquakes. I think most of us have heard of earthquakes. Can you imagine how terrible it is ?
人教版高中英语单词表必修一 Unit 1 单词表 △survey /'s?:vei/ n. 调查;测验 add up 合计 upset :[?p'set] adj. 心烦意乱的;不安的;不适的vt. (upset,upset) 使不安;使心烦 ignore /iɡ'n?:/ vt. 不理睬;忽视 calm /kɑ:m/ vt. & vi. (使)平静;(使)镇定adj. 平静的;镇静的;沉着的 calm (…) down (使)平静下来;(使)镇定下来have got to 不得不;必须 concern /k?n's?:n/ vt. (使)担忧;涉及;关系到 n. 担心;关注;(利害)关系 be concerned about 关心;挂念 walk the dog 遛狗 loose /lu:s/ adj. 松的;松开的 △vet /vet/ n. 兽医go through 经历;经受 △Amsterdam /?mst?'d?m/n. 阿姆斯特丹(荷兰首都) Netherlands /'nee?l?ndz/ n. 荷兰(西欧国家)△Jewish /'d?u(:)i?/ adj. 犹太人的;犹太族的German /'d??:m?n/ adj.德国的;德国人的;德语的 n.德国人;德语 △Nazi /'nɑ:tsi/ n.纳粹党人adj.纳粹党的 set down 记下;放下;登记 series /'si?ri:z/ n. 连续;系列 a series of 一连串的;一系列;一套 △Kitty /'kiti/ n. 基蒂(女名) outdoors /'aut'd?:z/ adv. 在户外;在野外 △spellbind /'spelbaind/ vt. (spellbound, spellbound) 迷住;迷惑 on purpose 故意 in order to 为了……
第一章集合与函数概念 §1.1集合 1.1.1集合的含义与表示(第一课时) 教学目标:1.理解集合的含义。 2.了解元素与集合的表示方法及相互关系。 3.熟记有关数集的专用符号。 4.培养学生认识事物的能力。 教学重点:集合含义 教学难点:集合含义的理解 教学方法:尝试指导法 教学过程: 引入问题 (I)提出问题 问题1:班级有20名男生,16名女生,问班级一共多少人? 问题2:某次运动会上,班级有20人参加田赛,16人参加径赛,问一共多少人参加比赛? 讨论问题:按小组讨论。 归纳总结:问题2已无法用学过的知识加以解释,这是与集合有关的问题,因此需用集合的语言加以描述(板书标题)。 复习问题 x-< 问题3:在小学和初中我们学过哪些集合?(数集,点集)(如自然数的集合,有理数的集合,不等式73的解的集合,到一个定点的距离等于定长的点的集合,到一条线段的两个端点距离相等的点的集合等等)。(II)讲授新课 1.集合含义 通过以上实例,指出: (1)含义:一般地,我们把研究对象统称为元素,把一些元素组成的总体叫做集合(简称为集)。 说明:在初中几何中,点,线,面都是原始的,不定义的概念,同样集合也是原始的,不定义的概念,只可描述,不可定义。 (2)表示方法:集合通常用大括号{ }或大写的拉丁字母A,B,C…表示,而元素用小写的拉丁字母a,b,c…表示。 问题4:由此上述例中集合的元素分别是什么? 2. 集合元素的三个特征
由以上四个问题可知,集合元素具有三个特征: (1) 确定性: 设A 是一个给定的集合,a 是某一具体的对象,则a 或者是A 的元素,或者不是A 的元素,两种情况必有一种而且只有一种成立。 如:“地球上的四大洋”(太平洋,大西洋,印度洋,北冰洋) “中国古代四大发明”(造纸,印刷,火药,指南针)可以构成集合,其元素具有确定性;而“比较大的数”,“平面点P 周围的点”一般不构成集合 元素与集合的关系:(元素与集合的关系有“属于∈”及“不属于?两种) 若a 是集合A 中的元素,则称a 属于集合A ,记作a ∈A ; 若a 不是集合A 的元素,则称a 不属于集合A ,记作a ?A 。 如A={2,4,8,16},则4∈A ,8∈A ,32?A.(请学生填充)。 (2) 互异性:即同一集合中不应重复出现同一元素。 说明:一个给定集合中的元素是指属于这个集合的互不相同的对象.因此,以后提到集合中的两个元素时,一定是指两个不同的元素. 如:方程(x-2)(x-1)2 =0的解集表示为{1,-2 },而不是{ 1,1,-2 } (3)无序性: 即集合中的元素无顺序,可以任意排列,调换. 。 3.常见数集的专用符号 (III )课堂练习 (IV )课时小结 1.集合的含义; 2.集合元素的三个特征中,确定性可用于判定某些对象是否是给定集合的元素,互异性可用于简化集合的表示,无序性可用于判定集合的关系。
Teaching Plan Unit1 Friendship 教材人教版高中英语必修一 试讲者李瑶单位新疆师范大学 适用年级高中一年级单元第一单元 课题Anne’s Best Friend 课时共五课时,第二课时 ( Reading) 一.教材分析 Analysis of the Teaching Materials This unit is the first unit of the senior English studying which talks about friendship.As for the students, at the beginning of senior school life, making new friends is one of important things for them now,so the topic of this unit is appropriate at the present time. It can easily stimulate students’interests in English learning and help students think how to choose friends and the meaning of the friendship. The reading passage is the center of the unit. It mainly talks about the Anna , a Jewish girl , during the world war II, regarded the diary as her best friend to express her happiness, sorrow and missing to her hometown. 二.学情分析 Analysis of the Students As the students, grade1of senior high school,they have the basic abilities of listening,speaking,reading and writing,but they still need more chances to practice what they have learnt and improve their ability of communicating with others and expressing their ideas fluently and accurately. Meanwhile,it is also necessary to develop their autonomous learning ability and cooperative learning ability, as well cultivate the awareness of cultural differences. 三. 教学目标 Teaching Aims 1.Knowledge Objectives 1.Get students to know the main content of this article. 2.Learn about the formats of a diary. 2.Ability Objectives 1.Develop their reading ability and learn to use some reading strategies such as guessing, key sentences, skimming and so on. 2.Summarize different paragraphs. 3.Emotion Objectives
外研社高一英语必修一 教案 公司内部编号:(GOOD-TMMT-MMUT-UUPTY-UUYY-DTTI-
M o d u l e O n e M y f i r s t d a y a t S e n i o r h i g h Period One Teaching content a)Self-introduction b)Vocabulary and speaking c)Everyday English and function Teaching aims and demands a)have the students to introduce themselves b)have the students to know what you except from them c)have the students get familiar with some words of subjects d)have the students to learn the Everyday English and function Teaching methods a)speaking b)discussing c)pair-work& group-work Teaching steps Step1 Self-introduction (I) This is the first English class in Senior high, you are fresh to the students , so are the students. So it is necessary for you to introduce yourself to the students and get them to introduce them to you and other students , you must stress that the students must introduce them in English. If necessary, you can make an example first.
人教版高一英语必修一语法归纳 以下是小编整理的高一必修一英语人教版语法归纳希望可以帮助大家,把语法进行归纳。 Unit 1 1. 词组: add up 合计 add up to 总计达 add… to…把。。加到。。。里 add to 增加增添扩建 2. calm… down 平静下来 3. have got to 不得不,必须 4. be concerned about / for 关心 5. walk the dog 遛狗 cheat … of 欺骗。。 6. go through 穿过完成用完通过仔细检查 go ahead 同意某人的请求go by 流逝 7. set down 记下 set up 建立 set off 出发引爆 set out to do=set about doing 着手做某事 8. a series of 一系列 9. on purpose 故意地 by accident= chance 偶然地 10. in order to= so as to 为了目的是in order that = so that 11. at dusk 在黄昏 at dawn 在黎明 at midnight 在午夜 at noon 在中午 12. face to face 面对面 13. no longer= not … any longer 不再 14. settle down 安顿下来 suffer from 遭受,患病 15. recover from 恢复 ,痊愈 16. get/ be tired of 对…感到厌烦 17. make a list of 列清单 18. pack… up 装箱打包 19. get along/ on with与…相处,/ 进展 20. fall in love 爱上
高中数学必修一教案全套 Last revision date: 13 December 2020.
『高中数学·必修1』第一章集合与函数概念 课题:§1.1 集合 教材分析:集合概念及其基本理论,称为集合论,是近、现代数学的一个重要的基础,一方面,许多重要的数学分支,都建立在集合理论的基础上。另一方 面,集合论及其所反映的数学思想,在越来越广泛的领域种得到应用。 课型:新授课 教学目标:(1)通过实例,了解集合的含义,体会元素与集合的理解集合“属于” 关系; (2)能选择自然语言、图形语言、集合语言(列举法或描述法)描述不 同的具体问题,感受集合语言的意义和作用; 教学重点:集合的基本概念与表示方法; 教学难点:运用集合的两种常用表示方法——列举法与描述法,正确表示一些简单的集合; 教学过程: 一、引入课题 军训前学校通知:8 月15日8点,高一年段在体育馆集合进行军训动员;试问 这个通知的对象是全体的高一学生还是个别学生? 在这里,集合是我们常用的一个词语,我们感兴趣的是问题中某些特定(是高 一而不是高二、高三)对象的总体,而不是个别的对象,为此,我们将学习一个新 的概念——集合(宣布课题),即是一些研究对象的总体。 阅读课本 P-P内容 二、新课教学 (一)集合的有关概念 1. 集合理论创始人康托尔称集合为一些确定的、不同的东西的全体,人们能 意识到这些东西,并且能判断一个给定的东西是否属于这个总体。 2. 一般地,研究对象统称为元素(element),一些元素组成的总体叫集合(set), 也简称集。 ——————————————第 1 页(共 70页)——————————————
Unit 1 Friendship ? Warming up 1.be good to be good for=do good to be good at 2.following adj. 下面的,下列的 ) the following+n.=the+n.+below ( 形容词修饰名词放在名词之前,介词或者介词短语修饰名词置于其后 ) 3.add v. add...to... add to add up add up to : addition n.in addition=besides +句子 in addition to +n./doing 同类用法联想: because & because of instead & instead of additional adj. 附加的 additionally adv.“而且,其次” “附加给 ..., 除了 ...还有...” 4.分数 score grade point mark (full marks) 5.until 6.with 和...一起,附带着, 用 without 不... within在...内,不出 ... . write with a pen eat with hands/ spoon/chopsticks/knife and fork He left without saying goodbye.
He left with the water running. 分析: saying 前无名词,则是主语发出 saying 的动作; running 前有 water,因此是 water 发出 running 的动作,而不是句子的主语 he。
Unit 1 Friendship I.单元教学目标 II.目标语言
III. 教材分析和教材重组 1. 教材分析 本单元以Friend和Friendship为话题,旨在通过单元教学使学生通过讨论什么是好朋友,什么是真正的友谊,如何交友和保持友谊等问题,使学生树立正确的交友观。并针对日常交友过程中经常遇到的实际问题,指导学生发表自己的见解和看法,通过进一步讨论提供有效的解决方案。并能就此以编辑的身份写出指导信,对相关谚语写出观点明确、论证有力的短文。 1.1 Warming Up以调查问卷的形式,通过对学生在日常交友过程中所遇到的五个问题,展开调查,使学生对是否擅长交友做出评价,激发学生对本单元的中心话题产生兴趣;同时也使教师本单元的授课更具有针对性,从而有效地帮助学生树立正确的交友观。 1.2 Pre-Reading通过四个问题引导学生讨论交友的重要性以及自己心目中好朋友的概念和标准,并使学生认识到不仅人与人,人与物(如日记)也可以成为好朋友。继续探究并树立正确交友观,并为阅读作好了准备。 1.3 Reading讲述第二次世界大战的纳粹统治时期,犹太人Anne一家过着滇沛流漓,与世隔绝的生活。Anne在孤独中只能以日记Kitty 为友,倾诉衷肠,伴其渡过两年的逃亡生涯。控诉了纳粹党的残暴统治给犹太人民带来了深重的灾难,并以日记的形式表达了以主人公Anne为代表的全世界人民憎恨战争渴望和平的共同心愿。学生学习了新的词汇、句型,提高了阅读水平。文中选用了主人公的一篇日记,使学生进一步感受到了挚友的可贵,对主人公内心世界的描写有了更深刻的理解。 1.4 Comprehension 设计了三种题型。其中前两个是考查学生对READING文章细节内容的理解,最后一题是开放性问题,学生可以在更深入理解主人公内心世界的基础上各抒己见,使学生养成勤于思考勇于探究的良好的学习习惯,现时也培养了学生的想象力,进一步提高了阅读水平。 1.5 Learning About Language分词汇和语法两部分。其中,Word study是根据英文释意或在语境中掌握和运用词汇。Grammar是关于直接引语和间接引语的用法训练,包括单句的练习和情景语法练习。
人教版高一英语必修1单词表 Unit 1 1.survey 调查;测验 2.add up 合计 3.upset adj. 心烦意乱的;不安的,不适的 4.ignore不理睬;忽视 5.calm vt.&vi.(使)平静;(使)镇定adj.平静的;镇定的;沉着的calm...down(使)平静下来 6.have got to 不得不;必须 7.concern(使)担心;涉及;关系到n. 担心;关注;(利害)关系 8.be concerned about 关心;挂念 9.walk the dog 溜狗 10.loose adj 松的;松开的 11.vet 兽医 12.go through 经历;经受 13.Amsterdam 阿姆斯特丹(荷兰首都) https://www.doczj.com/doc/a89820883.html,herlands 荷兰(西欧国家) 15.Jewish 犹太人的;犹太族的 16.German 德国的;德国人的;德语的。 17.Nazi 纳粹党人adj. 纳粹党的 18.set down 记下;放下;登记 19.series 连续,系列 a series of 一连串的;一系列;一套 20.outdoors在户外;在野外 21.spellbind 迷住;疑惑 22.on purpose 故意 23.in order to 为了 24.dusk 黄昏傍晚at dusk 在黄昏时刻 25.thunder vi 打雷雷鸣n. 雷,雷声 26.entire adj. 整个的;完全的;全部的 27.entirely adv. 完全地;全然地;整个地 28.power能力;力量;权力。 29.face to face 面对面地 30.curtain 窗帘;门帘;幕布 31.dusty adj 积满灰尘的 32.no longer /not …any longer 不再 33.partner 伙伴.合作者.合伙人 34.settle 安家;定居;停留vt 使定居;安排;解决 35.suffer vt &遭受;忍受经历suffer from 遭受;患病 36.loneliness 孤单寂寞 37.highway公路 38.recover痊愈;恢复 39.get/be tired of 对…厌烦 40.pack捆扎;包装打行李n 小包;包裹pack (sth )up 将(东西)装箱打包
高一年级数学必修一教案 课题:§1.1 集合 教材分析:集合概念及其基本理论,称为集合论,是近、现代数学的一个重要的基础,一方 面,很多重要的数学分支,都建立在集合理论的基础上。另一方面,集合论及其所 反映的数学思想,在越来越广泛的领域种得到应用。 课型:新授课 教学目标:(1)通过实例,了解集合的含义,体会元素与集合的理解集合“属于”关系; (2)能选择自然语言、图形语言、集合语言(列举法或描述法)描述不同的具体 问题,感受集合语言的意义和作用; 教学重点:集合的基本概念与表示方法; 教学难点:使用集合的两种常用表示方法——列举法与描述法,准确表示一些简单的集合;教学过程: 一、引入课题 军训前学校通知:8月15日8点,高一年段在体育馆集合实行军训动员;试问这个通知的对象是全体的高一学生还是个别学生? 在这里,集合是我们常用的一个词语,我们感兴趣的是问题中某些特定(是高一而不是高二、高三)对象的总体,而不是个别的对象,为此,我们将学习一个新的概念——集合(宣布课题),即是一些研究对象的总体。
二、新课教学 (一)集合的相关概念 1. 集合理论创始人康托尔称集合为一些确定的、不同的东西的全体, 人们能意识到这 些东西,并且能判断一个给定的东西是否属于这个总体。 2. 一般地,研究对象统称为元素(element),一些元素组成的总体 叫集合(set),也简 称集。 3. 关于集合的元素的特征 (1)确定性:设A是一个给定的集合,x是某一个具体对象,则或者 是A的元素,或者不是A的元素,两种情况必有一种且只有一种成立。 (2)互异性:一个给定集合中的元素,指属于这个集合的互不相同的 个体(对象),所以,同一集合中不应重复出现同一元素。 (3)集合相等:构成两个集合的元素完全一样 4. 元素与集合的关系; (1)如果a是集合A的元素,就说a属于(belong to)A,记作a∈A (2)如果a不是集合A的元素,就说a不属于(not belong to)A, 记作aA(或a A) 5. 常用数集及其记法 非负整数集(或自然数集),记作N 正整数集,记作N*或N+; 整数集,记作Z 有理数集,记作Q
高中英语必修一教案 Unit 1 Friendship 1.Teaching aims and demands
1.Suggested teaching notes 1). Analyses of the teaching contents This unit is about friendship, and nearly all the teaching materials center on it. Warming up---The questionnaire leads students to think and talk about friendship, get to know the problems between friends and seek solutions, which makes preparations for the further teaching in topics, background and vocabulary. Pre-reading---The questions prompt students to think critically about friends and friendship in reality, alerting them to the fact that besides people, a diary can be a friend, too. Reading--- The diary by the Jewish girl Anne gave a glimpse of her life during her family’s shelter in Amsterdam from the German