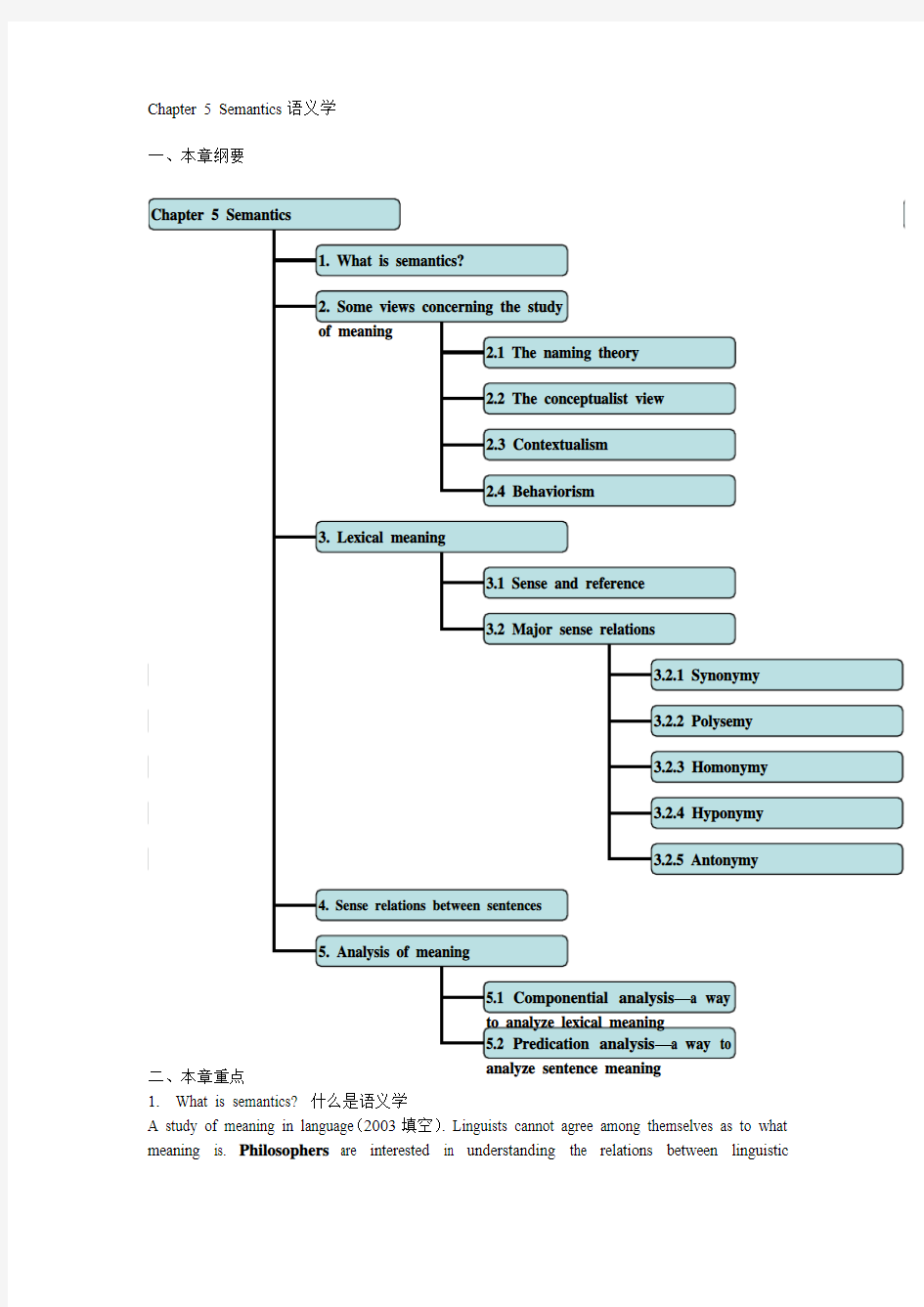

Chapter 5 Semantics语义学
一、本章纲要
二、本章重点
1.What is semantics? 什么是语义学
A study of meaning in language(2003填空). Linguists cannot agree among themselves as to what meaning is. Philosophers are interested in understanding the relations between linguistic
expressions and the phenomena in the real word they refer to and in evaluating the conditions of truth and falsehood of such expressions. Psychologists focus their interest on understanding the human mind through language.
2.Some views concerning the study of meaning
2.1 The naming theory命名论(2005单选;2007名词解释)
It is one of the oldest notions concerning meaning, and also a very primitive one, proposed by Greek scholar Plato. According to his theory, the linguistic form of symbols, in other words, the words used in a language are taken to be labels of the objects they stand for. So words are just names or labels for things. 命名论是最原始的语义理论,由古希腊学者柏拉图提出。该理论把词看作是该词所指事物的名称或标记。
The limitation: 1) applicable to nouns only; 2) within the category of nouns, there are nouns which denote things that do not exist or abstract notions. 这一理论的缺点是显而易见:首先,这一理论似乎只适用于名词,即使在名词类中,一些名词指的显然是世界中根本不存在的事物,有些是指一些抽象的概念,所以它们也就无所谓是指称事物的标记;其次,动词、形容词和副词那些显然不是事物的标记的词。
2.2 The conceptualist view意念论(2008名词解释)
In the interpretation of meaning, a linguistic form and what it refers to are linked through the mediation of concepts in the mind (no direct links). 意念论认为词汇与该词汇所指的事物之间的关系不是直接的,而是间接的,其中介是存在于人的头脑中的意念或概念,词汇通过意念来指称事物,意念便是词汇的意义。
This theory avoids many of the problems the naming theory has met, but it also raises a completely new problem of its own: what is precisely the link between the symbol and the concept?
Ogden和Richards所提出的语义三角理论就是对这一理论的最好解释。
(直线表示两者之间有直接联系,虚线表示两者之间无直接联系。)
这一理论的主要缺点是人们并不清楚符号与概念或意念之间到底有什么精确的联系。有的学者认为这种联系是一种心理活动过程.但问题是人们在遇到一个命名标记时,事实上,人们并不需要看到它们在脑海里形成的意象。
2.3 Contextualism (语境论)(2004判断)
Contextualism is based on the presumption that one can derive meaning from or reduce (归纳)
meaning to observable contexts. Two kinds of context are recognized: the situational context and the linguistic context. 语境论认为语言的意义来自语境,取决于语境。语境一般分为:情景语境和语言语境。
Every utterance occurs in a particular spatiotemporal situation (时空情景), of which the main components include, apart from the place and time of the utterance, the speaker and the hearer, the actions they are performing at the time, the various objects and events which exist in the situation. The linguistic context, known as co-text, is concerned with the probability of a word?s co-occurrence or collocation with another word, which forms part of the …meaning? of the word, i.e. its collocative meaning. It is also concerned with the part of text that precedes and follows a particular utterance. 情景语包括时空环境,交际的参与者,当时的行为活动,环境中的相关物体等。语言语境包括词之间的共现或搭配。这种共现和搭配构成了这个词的语义的一部分。例如在black hair(黑发)和black coffee(不加牛奶的清咖啡)中,black词义的不同是它的搭配不同所致。语言语境也包括一个特定话语的上下文。
“By regarding words as acts, events, habits, we limit our inquiry to what is objective in the group life of our fellows” and “We shall know a word by the company it keeps”- British John Firth “Language should be treated as a mode of action, not an instrument of reflection.”–Malinowski “For a large class of cases …the meaning of a word is its use in the language” - Wittgenstein
2.4 Behaviorism行为主义论
Behaviorists like Bloomfield attempted to define the meaning of a language form as “the situation in which the speaker utters it and the response it calls forth in the hearer”, which is somehow close to contextualism and linked with psychological interest. Bloomfield以行为主义心理学为基础提出了语义的行为主义论。Bloomfield 认为语义存在于情景中,存在于说话人所说的话在听话人身上引起的反应的情景之中。
Jill Jack
S - - - - r………………….s - - - R (stimulus, response)
3.Lexical meaning词汇意义
3.1 Sense and reference意义和所指
Sense is concerned with the inherent meaning of the linguistic form. It is the collection of all the features of the linguistic form; it is abstract and de-contextualized.(2001名词解释;2004填空;2007判断)
Reference means what a linguistic form refers to in the real, physical word; it deals with the relationship between the linguistic element and the non-linguistic word of experience. (2001,35名词解释;2004,15填空)
Obviously, linguistic forms with the same sense may have different references in different situation. On the other hand, linguistic forms with the same reference might differ in sense, such as “morning star” and “evening star”. (**)(2001,判断)
意义和所指是词汇意义的两个侧面,彼此既有联系,又有差异。意义(sense)是词汇抽象的、内在的、独立于语境之外而存在的意义。这种意义通常是词典编撰人员所关心的。例如:"boy"在字典中被定义为" a male child, till puberty or young manhood. "这里,“男孩”并不指任何现
实世界中具体的男孩,任何一种具有定义特征的人都可称为“男孩”。
所指是词汇在特定的语境中所指称的具体事物。它是关于语言与非语言的客观世界之间的关系。例如:“The boy is crying.”在这个例子中,“boy”一定是有所指的,特指一个交际活动中交际者都知道的那个“男孩”。这就是在这个特定的交际情景中“男孩”的所指。
意义(sense)相同的词在不同语境中所指可能会不同,例如:
I saw a boy at the gate yesterday.
I saw a man beating a boy in front of the house.
另一种情况是词的所指意义可能相同,但是意义却不同,例如:morning star 和evening star 意义是不同的,但是所指是相同的,都指“金星”。
3.2 Major sense relations主要的意义关系
3.2.1 Synonymy同义现象
Synonymy refers to the sameness or close similarity of meaning. Words that are close in meaning are called synonyms. English is rich in synonyms for historical reasons. Because of their different origins between native words and borrowed (loan) words, there are often subtle differences between these synonyms. Synonyms that are mutually substitutable under all circumstances are called complete synonyms, which are rare. As per the way they differ, they can be in 5 types:
同义现象指意义的相同或相近现象。由于历史的原因,大量的外来词加入本族语,使得英语中富含同义词。在任何语境中都可以相互替代的绝对同义词十分罕见。绝大多数同义词之间存在着语义上的微妙差异。同义词通常分为五类:
1)Dialectal synonyms – synonyms which are used in different regional dialects (e.g. BE, AmE)
方言同义词
方言同义词是指在语义上相同或相近的词,但是用在不同的方言之中,如:
British English American English
Picture Movie
Ill Sick
Engine Motor
Post Mail
即使在美国英语或英国英语内部也存在方言同义词。(2004,单选)
2)Stylistic synonyms – synonyms which differ in style (or degree of formality) 文体同义词
在文体或使用正式程度上相异的同义词是文体同义词。例如:
begin commence
ask, question, interrogate
fear, terror, trepidation
gee-gee, horse, steed
3)Synonyms that differ in their emotive or evaluative meaning表情意义或评价意义相异的同
义词
The emotion of the user indicates the attitude or bias of the user toward what he is talking about.
有些同义词有着相同的所指意义,但是表达了不同的情感。例如“small” 和“little”是同义词,但是“small”是中性词,不含有情感语义色彩,而“little”却蕴涵浓厚的情感色彩,是比较:
Poor little boy!
* Poor small boy! (不自然)
4)Collocational synonyms搭配同义词
有些词是同义词,但是搭配不同,如:a flock of, a pack of, a herd of a swarm of , a school of,它们搭配如下:
A flock of sheep
A pack of wolves
A herd of cows
A swarm of bees
A school of whales
5)Semantically different synonyms, e.g. amaze, astound; escape, flee语义相异的同义词
一些同义词在语义上略有差异,例如rage, fury, indignation 在语义上与anger相近,但是rage暗含“情感的失控”; fury是这几个词中语义强度最强的词,暗含“情感的失控到了几乎疯狂的程度”;indignation暗含“由于道义上的原因引起的愤怒。”
3.2.2 Polysemy多义现象
Polysemy refers to the fact that the same one word have more than one meaning. A word having more than one meaning is called a polysemic word. (primary meaning →new meaning) 多义现象是指同一个词有一个以上的意义。以neck为例,它的意思有:
(1) that part of an animal which joins the head to the body
(2) the part of a garment that goes around the neck
(3) a narrow stretch of land
(4) a strait
(5) the lower part of a capital
从历史的角度看,多义现象是词义的发展的结果。
3.2.3 Homonymy同音同形异义关系
(2002单选;2005名词解释)Homonymy refers to the phenomenon that words having different meanings have the same form, i.e. different words are identical in sound or spelling, or in both. When two words are identical in sound, they are called homophones. When two are identical in spelling, they are homographs. (2008,单选)
When two are identical in both sound and spelling, they are complete homonyms. On how to differentiate same polysemic word (related meanings) and two complete homonyms (meaning
quite different), we refer to etymology of words in question. (2006,判断)
3.2.4 Hyponymy上下义关系
(2003名词解释)Hyponymy refers to the sense relation between a more general, more inclusive word and a more specific word.
(2002填空)The word which is more general in meaning is called the superordinate, and the words which are more specific in meaning are called its hyponyms.
(2006名词解释)Hyponyms of the same superordinate are cohyponyms to each other.
3.2.5 Antonymy反义关系
Antonymy refers to the oppositeness of meaning. Such words are called antonyms.
1)Gradable antonyms可分等级的反义词
Some antonyms are gradable because there are often intermediate forms between.
2)Complementary antonyms(互补性反义词)(2001填空;2007名词解释)
Being complementary to each other, the denial of one implies the assertion of the other.
3)Relational opposites关系反义词
Pairs of words that exhibit the reversal of a relationship between the two terms.
4.Sense relation between sentences
1)X is synonymous with Y (if X is true, Y is true, and if X is false, Y is false)同义关系
2)X is inconsistent with Y (if X is true, Y is false, and if X is false, Y is true)语义对立(2006填空)
3)X entails Y (Y is an entailment of X)Y是X的蕴含(2003单选)
Entailment is a relation of inclusion. If X entails Y, the meaning of X is included in Y):
(1)If X is true, Y is necessarily true.
(2)If X is false, Y maybe true and false
(3)If Y is false, X is false
e.g. X: He has been to France; Y: He has been to Europe.
4)X presupposes Y. (Y is a presupposition of X) (Y是X的预设)
(1)If X is true, Y must be true
(2)If X is false, Y is still true.
(3)If Y is true, X is either true or false.
(4)If Y is false, non truth value can be said about X
e.g. X: John?s bike need repairing; Y: John has a bike.
5)X is a contradiction (invariably false) X自相矛盾
e.g. My unmarried sister is married to a bachelor.
6)X is semantically anomalous (语义变异)(absurd as it presupposes a contradiction):
e.g. The table has bad intentions.
5.Analysis of meaning意义分析
5.1 Componential analysis – a way to analyze lexical meaning语义成分分析(2004,42问答)
Componential analysis is a way proposed by structural semanticists to analyze word meaning (2007填空).
(2005填空) This approach is based on the belief that the meaning of a word can be divided into meaning components, which are called semantic features.
Plus and minus signs are used to indicate whether a certain semantic feature is present or absent in the meaning of a word, and these feature symbols are usually written in capitalized letters.
For example, the word “man”is analyzed as consisting of semantic features of +HUMAN, +ADULT, +ANIMATE, +MALE. One advantage is to show how the words are related in meaning. It is senseless to analyze the meaning of every word by dividing it into its meaning components.
5.2 Predication analysis – a way to analyze sentence meaning述谓结构分析
1)The meaning of a sentence is not the sum total of the meanings of all its components.
2)There are two aspects in sentence meaning: grammatical meaning(grammaticality, grammatical well-formedness) and semantic meaning(governed by selectional restrictions, which are constraints on what lexical items can go with what others).
在分析句子的意义之前,有两点应该明确:
1)一个句子的意义并不是它所有组成部分意义的总和。一个句子的意义不能通过把组成它的所有单词的意义的相加来得出。
2)句子的意义包含两个方面:语法意义(grammatical meaning)和语义(semantic meaning)。一个句子的语法意义是指它的语法性。
The grammatical meaning of a sentence refers to its grammaticality, i.e., its grammatical well-formedness. The grammaticality of a sentence is governed by grammatical rules of the language. (2008名词解释)一个句子的语义是否可接受受选择性限制规则的支配。语法性受语言的语法规则的支配。
(2007单选)选择性限制规则是对词的结合或搭配进行限制的规则,以确保语义的可接受性。符合语法的句子并不一定就是语义可接受的句子。例如:
*The brown concept jumps sympathetically.
Some sentences may be grammatically well-formed, i.e., they comply perfectly with the grammatical rules of the language, yet they may not be semantically meaningful. The reason is that they contain words which are not supposed to go together, thus violating the selectional restrictions.
(2002,35名词解释) Proposed by British G. Leech, the basic unit in semantic analysis of a sentence is called predication, which is the abstraction of the meaning of a sentence. A predication consists of argument(s)(论元) (logical participant and generally identical with the nominal element) and predicate (谓语) (something that is said about an argument or it states the logical relation linking the arguments). Grammatical form of a sentence does not affect its semantic predication. Predicate is the main element.述谓分析是由Leech提出的一种分析句子语义的手段。句子由主语、谓语构成,是语法分析的基本单位。述谓是句子语义分析的基本单位,是句子的抽象语义内容。述谓是由论元(argument)和谓词(predicate)构成。一个论元是一个述谓的逻辑参与者,与一个句子中的一个或数个名词性成分大体一致。一个谓词是关于论元的陈述,或说明一个句子的论元间的逻辑关系。例如: He jumped. 是由论元He和谓词jump构成,写作:HE(JUMP)。由于句子的语法形式不影响述谓,所以以下句子具有同样的述谓HE( JUMP).:
He jumps.
He is jumping.
He will jump.
He has been jumping.
Did he jump?
According to the number of arguments contained in a predication, predications may be classified into: two-place predication (containing two arguments), one-place argument (one) and no-place argument (no argument). 根据一个述谓中所包含的论元的数目可以把述谓结构分为一位述谓结构(含一个论元)、二位述谓结构(含两个论元)和空位述谓结构(不含论元)
Children like sweets. ( two-place predication) 写作:CHILDREN, SWEET(LIKE)
John is ill. (one-place predication) 写作:JOHN(BE ILL)
It is hot.(no-place predication) 写作:(BE HOT)
“It is hot”是关于气象方面的话。由于it没有独立于谓词之外的意义,很难说it表达成分是论元。It的意义很容易预测,人们不会提出一个回答是it的问题,如:
What is hot? * It! 所以,”It is hot.”是空位述谓结构。
在述谓结构中,谓词是主要成分,因为它包含了时态、形态等,也可以说它制约着论元,因为它决定了论元的数量和性质。成分分析和述谓分析结合起来可以帮助我们来描述句子的大部分意义。
三、本章历年试题
I. Directions: Read each of the following statements carefully. Decide which one of the four
choices best completes the statement and put the letter A, B, C, or D in the brackets.
(2%×10=20%)
5. Predication analysis is a way to analyze _______ meaning.
A. phoneme
B. word
C. phrase
D. sentence
5. The phenomenon that words having different meanings have the same form is called ______.
A. polysemy
B. hyponymy
C. antonymy
D. homonymy
5. “I bought some roses” __________ “I bought some flowers”.
A. entails
B. presupposes
C. is inconsistent with
D. is synonymous with
5. Synonyms are classified into several kinds. The kind to which“girl”and“lass” belong is called
( ) synonyms.
A. stylistic
B. dialectal
C. emotive
D. collocational
5. The naming theory was proposed by .
A. the Greek scholar Plato
B.
C.K. Ogden and I.A. Richards
C. the British linguist J. Firth
D. the American linguist L. Bloomfield 5.Antonyms are divided into several kinds .Which of the following is NOT a kind of antonyms?
()
A.complementary B.relational C.superordinate D.gradable
6.In terms of predication analysis , the utterance“ Is it going to snow this afternoon?” is a______________()
A.one-place predication B.two-place predication
C.three-place predication D.no-place predication
5. Whether a sentence is semantically meaningful is governed by rules called _______________.
A. selectional restrictions
B. grammatical rules
C. phrase structure rules
D. phonological rules
5. The words stationary and stationery are identical in sound, but different in spelling and meaning. They are _______.( )
A. complete homonyms
B. homographs
C. hyponyms
D. homophones
II. Directions: Fill in the blank in each of the following statements with one word, the first letter of which is already given as a clue. Note that you are to fill in ONE word only, and you are not allowed to change the letter given. (1% ×10=10%)
15. Componential analysis is based on the belief that the meaning of a word can be dissected into meaning components, called s features.
15. C analysis is based upon the belief that the meaning of a word can be divided into meaning components.
15. Pairs of words that exhibit the reversal of a relationship between the two items are called r_______ opposites.
15. R is what a linguistic form refers to in the real world; it is a matter of the relationship between form and the reality.
15. The study of the linguistic meaning of words, phrases, and sentences is called s . 15. That the denial of one member of two words implies the assertion of the other is the characteristic of c________ antonyms.
15. In terms of truth condition, if X is true, Y is false, and if X is false, Y is true. The relationship between X and Y is i_________________
16. Hyponymy is the relationship which obtains between specific and general lexical items. The word that is more general in meaning is called _s________.
III. Directions: Judge whether each of the following statements is true or false. Put a T for true or F for false in the brackets in front of each statement. If you think a statement is false, you must explain why you think so and then give the correct version. (2%×10=20%)
25. ( ) A grammatically well-formed sentence is always semantically well-formed.
( )25. Linguistic forms having the same sense may have different references in different situations while linguistic forms with the same reference always have the same sense.
25. ( ) The predication analysis of a sentence only applies to statements and interrogative forms.
25. ( ) Sense and reference are of the same thing in meaning study.
25. ( ) The conceptualist view of meaning holds that there is no direct link between a symbol and reference, i.e. between language and thought.
25. ( ) The important criteria to distinguish polysemy from homonymy are the etymology of
the words in question and the closeness of the relationship between the meanings in question. 25. ( ) The contextualist view of meaning holds that meaning should be studied in terms of the situational context and linguistic context.
25. ( )The same semantic feature occurs in one part of speech only. For example, "female" occurs only in nouns such as "mother", "woman" "girl" "tigress" and so on but not in other parts of speech.
IV. Directions: Explain the following terms, using one or two examples for illustration. (3% ×10=30%)
35. reference
36. semantic triangle
37. grammatical meaning
34. co-hyponyms
35. predication
35. homonymy
35. grammaticality
35. recursiveness
36. the naming theory
https://www.doczj.com/doc/af1528859.html,plementary antonyms
V. Directions: Answer the following questions. (10%×2=20%)
42. Explain and give examples to show in what way componential analysis is similar to the analysis of phonemes into distinctive features.
42.Explain what is sense and what is reference with examples.
2016年10月高等教育自学考试全国统一命题考试 语言学概论试卷(课程代码 00541) 第一部分选择题 一、单项选择题(本大题共20小题,每小题l分,共20分) 在每小题列出的四个备选项中只有一个是符合题目要求的,请将其选出并将“答题卡” 的相应代码涂黑。未涂、错涂或多涂均无分。 1.下面各项中,属于汉语北方方言的是 A.广州话 B.福州话 C.重庆话 D.上海话 2.汉语拼音字母b、p、m都是 A.舌尖音 B.唇齿音 C.正齿音 D.双唇音 3.下面各项属于自源文字的是 A.英文字母 B.甲骨文 C.腓尼基字母 D.希腊字母 4.儿童“以词代句语言”出现在 A.单词句阶段 B.语法句阶段 C.简单句阶段 D.复杂句阶段 5.“叶子岀水很高,像亭亭的舞女的裙”一句采用的修辞手法是 A.比拟 B.仿写 C.夸张 D.比喻 6.下面各项中含有轻声音节的是 A.渐渐 B.妈妈 C.声声 D.人人 7.“在家休息”是一个 A.动宾词组 B.主谓词组 C.偏正词组 D.兼语词组 8.不同行业有自己的“行话“行话”属于 A.地域方言 B.社会方言 C.亲属语言 D.混合语言 9.“半两棉花——免弹(谈)”采用的方法是 A.转移欢关 B.语义汉关 C.语音双关 D.替代双关 10.下面各项属于语言符号特点的是 A.约定性 B.自然性 C.固定性 D.想象性 11.一种语言的共同语是在某一个方言的基础上形成的,这种方言叫 A.母方言 B.底层方言 C.基础方言 D.原始方言
12.谈话体属于 A.书面语体 B.宣传语体 C.文学语体 D.口语语体 13.唐太宗名李世民,唐代人便把“世”改为“代'把“民”改成“人”,这是为了 A.避讳 B.图吉利 C.讨口彩 D.自谦 14.中国历史上推行“书同文”措施的是 A.齐桓公 B.秦始皇 C.汉武帝 D.唐玄宗 15.汉语中“罗汉、菩萨、塔、阎罗”等词的出现,是因为 A.儒家学说的兴盛 B.道教的兴起 C.名教的影响 D.佛教的传入 16.“弟弟吃苹果”不能说成“苹果弟弟吃'这是受制于语言符号的 A.组合关系 B.聚合关系C联想关系 D.分类关系 17.音高取决于声波的 A.振幅 B.数量 C.长短 D.频率 18.“这是革命的春天,这是人民的春天,这是科学的春天”,这个句子是 A.反复句 B.顶真句 C.对偶句 D.回环句 19.中国叫“绥远、定远”之类名字的地方,往往当年 A.水草丰美 B.山川秀丽 C.曾发生战乱后被抚平 D.人口特别多 20.—个民族的全体或部分成员放弃使用本民族语言转而使用另一民族语言的现象叫 A.语言混合 B.语言转用 C.克里奥尔 D.双语现象 二、多项选择题(本大题共5小题,每小题2分,共10分) 在每小题列出的五个备选项中至少有两个是符合题目要求的,请将其选出并将“答题卡”的相应代码涂黑。未涂、错涂、多涂或少涂均无分。 21.下面关于语言和民族、国家关系的说法中,正确的有 A.—个民族只能说一种语言 B.—个民族可以说多种语言 C.一个国家只有一种语言 D.—个国家可以有多种语言 E.不同民族可以说同一种语言 22.下面各项中,属于元音的有 A.[a] B.[f] C. [l] D.[o] E.[p] 23.下面各项中属于发散思维的表现形式的有 A.音乐 B.舞蹈 C.绘画 D.推理 E.文学 24.下面各项中彼此有亲属关系的语言有 A.日语 B.葡萄牙语 C.老挝语 D.朝鲜语 E.英语 25.下面各项中,属于借词的有
Chapter 4 Phonology(音位学) 4.1 phonetics and phonology:语音学与音位学的区分 Both phonetics and phonology are concerned with speech.语音学和音位学都士对语音的研究。 定义区别 -Phonetics is a study of the production, perception and physical properties of speech sounds. 语音学是研究语音的生产、感知和物理性质的。 -Phonology studies how speech sounds are combined,organized,and convey meanings in particular languages.研究语音如何在在特定的语言中结合、组织和表达含义。 ---Phonology is language-specific.it is the study of how sounds are organized and used in natural languages.音位学是特定于语言的。它的研究对象是自然语言中的声音是如何组织和使用的。 ---Phonetics is a study of speech sounds while phonology is a study of the sound syst em of a language.语音学是一个研究语音的然后音位学是研究一种语言的声音系统的学科。 4.2 Phonemes,phones and allophones 音位、音子、音位变体 Different languages have different phonological systems.不同的语言有不同的语音系统。 定义: ①Phones are the smallest identifiable phonetic unit or segment found in a stream of speech. 音子就是在连续的发音中可辨认的最小语音单位或片段。 ②Allophones are the phones which represent a phoneme in a language and cannot change word meaning by substituting any of the set for another.音位变体是指代表语言中音位的音子,即使以一个取代另一个也不改变词义。 ③Phonemes are the minimal distinctive units in the sound system of a language.音位是语言系统中最小的独特的单位。 Allophones are the realization of a particular phoneme while phones are the realizatio n of phonemes in general.音位变体是一个特定音素的认知而音子则是一般的音素。 4.3Minimal pairs 最小对立体 The phonologist is concerned with what difference are significant or technically speaki ng, distinctive. Minimal pair---a pair of words which differ from each other by one sound. Three conditions(情况): 1)the two froms are different in meaning意义不同 2)the two forms are different in one sound segment声音片段不同 3)the different sounds occur in the same position of the two words.不同声音发生在两个单词的相同位置 Minimal set: a group of words can satisfy(满足)the three conditions . Minimal pairs help determine phonemes. 最小对立体用来定义音位。 4.4 identifying phonemes 识别音素 4.4.1 contrastive distribution,complementary distribution and free variation 对比分布,互补分布和自由变异 The distribution of a sound refers to the collective environments in which the sound concerned may appear.一个声音的分布是指其有关的声音可能出现的集体环境。 1)contrastive distribution对比分布 If two or more sounds can occur in the same environment and the substitution of on
2014年10月高等教育自学考试英语(二)试卷 (课程代码00015) 本试卷满分100分,考试时间150分钟。 考生答题注意事项: 1.本卷所有试卷必须在答题卡上作答。答在试卷上无效,试卷空白处和背面均可作草稿纸。 2.第一部分为选择题。必须对应试卷上的题号使用2B铅笔将“答题卡”的相应代码涂黑。 3.第二部分为非选择题。必须注明大、小题号,使用0.5毫M黑色字迹签字笔作答。 4.合理安排答题空间,超出答题区域无效。 第一部分选择题 一、阅读判断(第1—10题,每题1分,共10分) 下面的短文后列出了10个句子,请根据短文的内容对每个句子作出判断:如果该句提供的是正确信息,选择A;如果该句提供的是错误信息,选择B;如果该句的信息文中没有提及,选择C。在答题纸相应位置上将答案选项涂黑。 The Stranger Who Changed My Life It was a sunny morning in the spring of 1966. I was driving a taxi, looking for a customer. While passing New York Hospital, I found a man running down the hospital steps, waving at me. I stopped. The man reached the taxi and jumped in. “The Airport, please,”he said. As always, I wondered about my passenger. Was this man a talker? After a few moments, he started saying, “How do you like driving a taxi?” “It’s OK” I said. “I make a living and meet interesting people sometimes.” “What do you do?” I asked. “I am a doctor at New York Hospital.” Many times during long rides, I’d developed a good relationship with my passengers and received very good advice from them. This time I decided to ask for his help. “Could I ask a favor of you?” He didn’t answer. “I have a son, 15, a good kid. He wants a job this summer. Is it possible that you get one for him?” He still wasn’t talking, and I was starting to feel foolish. Finally, he said, “Well, my students have a summer research project. Maybe he could join in. Have him send me his school record.” He left his address and paid me. It was the last time I ever saw him.
1.Human capacity for language has a genetic basis, but the detail of language have to be taught and learned. 2.Displacement means that language can be used to refer to thing which present or not present, real or imagined matter in the past, present or future or in far-away places. https://www.doczj.com/doc/af1528859.html,nguage is a system considering of two sets of structures, or two levels. https://www.doczj.com/doc/af1528859.html,nguage is a system of arbitrary vocal symbols used for human communication. 5.Chomsky defined competence as the ideal speaker’s knowledge of the rules of his language. 6.Parole refers to the realization of langue in actual use. 7.Modern linguistics gives priority to the spoken from of language. 8.The description of a language as it changes through time is a diachronic study. 9.Psycholinguistic relates the study of language to psychology. 10.Linguistics is generally defined as the scientific study of language. 11.Of the two media of language, speech is more basic than writing. 12.vibration of the vocal cords results in a quality of speech sounds called voicing 13.of all the speech organs , the tongue is the most flexible, and is responsible for varieties of articulation than any other. 14.when the obstruction is partial and the air if forced through a narrow passage in the mouth so as to cause definite local friction at the point ,the speech sound thus produced is a fricative in the production of
2019年10月髙等教育自学考试全国统一命题考试 英语(二)试卷(课程代码:00015) 本试卷共8页,满分100分,考试时间150分钟。 考生答卷前必须将自己的姓名和准考证号写在答题卡上。 必须在答题卡上答题,写在试卷上的答案无效。 第一部分:阅读判断(第1?10题,每题1分,共10分) 下面的短文后列出了10个句子,请根据短文的内容对每个句子作出判断:如果该句提供的是正确信息,选择A;如果该句提供的是错误信息,选择B;如果该句的信息文中没有提及,选择C。在答题卡相应位置上将答案选项涂黑。 To Lease(租赁) or Not to Lease Planning to lease a car because you don't think you can afford to buy? Think again. Leasing can end up being just as expensive as buying. Most people think about leasing because they believe it will cost them less money. They're right-it is cheaper, but only in the short term. For example, if you were to lease anew Subaru Forester, you might pay $300 per month for the car. If you were to buy the same car, you would pay about $400 per month. Over a three-year, you would save $3600-a big savings. But after your lease is over, you have to give the car back. Many people want to lease because they can drive a more expensive car than they might otherwise be able to afford. For example, if you spend $300 monthly on a car, you might be able to lease a new Ford Explorer. For the same price, you might have to buy a used Explorer, or buy a new but much less expensive model. A lease,therefore,allows you to drive the latest models of more expensive cars. However, whatever car you can afford to buy you get to keep it, and it will always have a resell or trade-in(以新旧换)value if you want to upgrade to a new car later. Furthermore, people who lease cars are often shocked by how much they must pay when the lease is over . Most leases limit you to a certain number of miles. If you go over that, you must pay for each mile. As a result, you may end up paying thousands of dollars in mileage(里程) fees. In addition, when you lease ,you have to pay for regular maintenance and repairs to the vehicle. Since you must return the car finally, you are paying to repair someone else's car.
2016年10月高等教育自学考试英语(二)真题 第一部分:阅读判断(第1~10题,每题1分,共10分)下面的短文后列出了10个句子,请根据短文的内容对每个句子作出判断:如果该句提供的是正确信息,选择A;如果该句提供的是错误信息,选择B;如果该句的信息文中没有提及,选择C。在答题卡相应位置上将答案选项涂黑。 Being ”Cool” in Middle School A new study shows that gentle and quiet kids in middle school will grow up to rule. Or, they’ll live healthier and more productive lives than the “cool” kids will. The study looked at 13-year-olds who acted old for their age by having “cool”behavior, such as early romantic relationships. They were seen as “cool” and popular kids. But as they grew up, things changed. The study found that these kids tended to have problems with drugs and relationships by their 20s. Their behavior was no longer linked with popularity. Instead, they were thought to be less socially skilled by their peers. Besides, the average “cool”kids, by age 22, did more poorly than the average kids in the study. They had a 45 percent greater rate of problems due to drugs and alcohol. They also had a 22 percent greater rate of criminal behavior. The study also found that these kids failed to develop important life skills. They spent so much time trying to seem cool. They didn’t
历年全国自考语言学概论真题 请考生按规定用笔将所有试题的答案涂、写在答题纸上。 选择题部分 注意事项: 1. 答题前,考生务必将自己的考试课程名称、姓名、准考证号用黑色字迹的签字笔或钢笔填写在答题纸规定的位置上。 2. 每小题选出答案后,用2B铅笔把答题纸上对应题目的答案标号涂黑。如需改动,用橡皮擦干净后,再选涂其他答案标号。不能答在试题卷上。 一、单项选择题(本大题共20小题,每小题1分,共20分) 在每小题列出的四个备选项中只有一个是符合题目要求的,请将其选出并将“答题纸”的相应代码涂黑。错涂、多涂或未涂均无分。 1.下列关于语言符号的表述,不正确的一项是 A.语言符号包括能指和所指 B.语言符号的音和义不可分割 C.语言符号音义关系具有任意性 D.语言符号不能分解和重新组合 2.几万、几十万个词通过排列组合可以产生无限多的句子,这主要是由于语言符号具有 A.离散性 B.强制性 C.可变性 D.任意性 3.下列关于韵律特征的表述,不正确的一项是 A.韵律特征在不同的语言中具有不同的特点 B.韵律特征自身不能单独占据一个时间段落 C.韵律特征从构成要素看是一种对比性特征 D.韵律特征包括“音质特征”和“音段特征” A.同化 B.异化 C.弱化 D.增音
6.下列关于“语”的表述,正确的一项是 A.“语”指的是那些由语素构成的固定词组 B.“语”和“词”在内部构造方面没有分别 C.“语”的结构往往不具有固定性和整体性 D.“语”的结构常常呈现为某种特定的格式 7.英语动词“like(喜欢)”的单数第三人称形式是“likes”,这属于 A.变形构词 B.变性成词C.语汇构词 D.语法构词8.“众人拾柴火焰高”属于 A.惯用语 B.谚语C.歇后语 D.成语9.主要功能是用来“造句”的同一级语法单位是 A.语素和语素组 B.语素组和词C.词和词组 D.词组和句子10.对“很中国”中“中国”一词用法的说明,正确的是 A.仍然是名词 B.变成了形容词 C.名词活用作形容词 D.名词兼形容词11.“你吃点什么吗?”这个句子是 A.一般疑问句 B.特指疑问句C.选择疑问句 D.反问疑问句12.下列词语,属于相对反义词的一组是 A.必然—偶然 B.萧条—繁荣
现代语言学名词解释 现代语言学 一绪论 1 Linguisitics :Linguistics is generally defined as the scientic study of language 2 Phonetics : The study of sounds which are used in linguistics communication is called phonetics.For example,vowels and consonants 3 Phonology” : T he study of how sounds are put together and used in communication is called phonology.For example,phone,phoneme,and allophone. 4 Morphology :The study of the way in which morphemes are arranged to form words is called morphology.For example,boy and “ish”---boyish,teach---teacher. 5 Syntax : The study of how morphemes and words are combined to form sentences is called syntax.For esample,”John like linguistics.” 6 Semantics: The study of meaning in language is called semantics. For example,:The seal could not be found.The zoo keeper became worried.” The seal could not be found,The king became worried.” Here the word seal means different things. 7 Pragmatics: The study of meaning in context of use is called pragmatics.For example, “I do” The word do means d ifferent context. 8 Sociolinguistics: The study of language with reference to society is called sociolinguistics.For example,regional dialects,social variation in language. 9Psycholinguistics: The study of language with reference to workings of mind is called psycholinguistics. 二音系学 1 Phonetics: The study of sounds that are used in linguistic communication is called phonetics. 2 Phonology: The study of how sounds are put together and used in communication is called phonology. 3 Phone: Phone can be simply defined as the speech sounds we use when speaking a language. A phone is a phonetic unit or segement. It does not necessarily distinguish meaning; some do,some don’t. 4 Phoneme: Phonology is concerned with the speech sounds which distinguish meaning. The basic unit in phonology is called phoneme;it is a unit that is of distinctive value. 5 allophone: The different phones which can represent a phoneme in different phonetic environment are called the allophones of that phoneme. 6 Complementary distribution: These two allophones of the same phoneme are
2011年1月广东省高等教育自学考试英语语言学问卷课程代码06422) I.Blank-filling (20%)Fill in the following blanks with a word ,whose initial letter has been given. 1. The 3 branches of phonetics are labeled articulatory phonetics ,auditory phonetics ,and a__________ phonetics. 2. When 2 different forms are identical in every way except for one sound segment which occurs in the same place in the strings ,they are said to be in a m_________ pair . 3. R__________ motivation refers to the fact that learners learn a second language for external purposes . 4. Later Noam Chomsky prefers this innate endowment as UG ,i.e. U_____ Grammar. 5. In "NP → (Deg )A(pp)……", the dots in the rule indicate that other c________ options are available . 6. The articulatory apparatus of human being are contained in 3 important areas :the p______ cavity,the oral cavity ,and the nasal cavity. 7. L________ refers to the abstract linguistic system shared by all the members of a speech community . 8. H________ refers to the sense relation between a more general ,more inclusive word and a more specific word . 9. The description of a language at a given point in time is a s______ study. 10. The study of how speakers of a language use sentences to effect successful communication is called p_________. 11. The structure corresponding to the final syntactic output of the sentence which results from appropriate transformations is called s______ structure. 12. The term d________, first used by Ferguson in 1959,refers to a sociolinguistic situation similar to bilingualism . 13. Learners' independent system of the second language which is of neither the second language is known as i______. 14. The sound [p]in pit is pronounced with a strong puff of air, which is said to be a________. 15. C_______ model states that in word comprehension words are analyzed by hearers from beginning to end. 16. S______ is concerned with the inherent meaning of the linguistic form and is the collection of all the features of the linguistic form . 17. Major lexical categories are Noun, Verb , Adjective , and P___________. 18. S_______ is the sub-field of linguistics that studies the relation between linguistic and society between the uses of language and social structures. 19. P________ is concerned with the progress of language comprehension and production. 20. Linguistics studies not any particular language ,but languages in g____. II. Multiple choice(20%)Choose the best answer to the following items. 21. __refers to the study of the internal structure of words and the rules by which words are formed . A.Syntax B. Etymology C. Lexicology D. Morphology 22. ___ aims to discover how speech sounds in a language form patterns and how these sounds are used to convey meaning in linguistic communication . A. Phonetics B. Phonemics C. Phonology D. Phonotactics 23. Language ___ refers to a natural ability for learning a second language. A. aptitude B. competence C. performance D. attitude 24. ___ is a personal dialect of an individual speaker that combines elements regarding regional ,social, gender, and age variations . A. Idiolect B. Pidgin C. Sociolect D. Creole
2018年4月高等教育自学考试《英语(一)》试题 课程代码:00012 一、阅读判断 Finding Paradise (天堂) and Success in Retirement Ivy Singh and her husband had their retirement all planned out. They wanted to have a place with enough land to grow plants. The couple successfully found a proper place and turned it into a farm called Bollywood Veggies. "We came and had a look and we found paradise. We started Bollywood Veggies there and then," she says. The basic idea of starting the farm was to keep themselves busy in retirement. Mrs. Singh says it was never begun as a business. "We started this as a lifestyle project for retirement." The farm's produce includes beans, cabbage and other crops. Soon, more people found out about the farm. Visitors often asked whether the farm offered any food or drinks. So the couple started a restaurant and a food museum on the farm. As the farm changed from a retirement to a commercial project, Mrs. Singh sought new business opportunities. A key area was growing bananas. Given the popularity of bananas and their use in a range of food products, she saw great potential. The farm uses its crop to make products such as banana chips and bread. Mrs. Singh, driven by the success of the project, now wants to open a retirement home on the farm. She says the farm is a nice place for people who have retired. Mrs. Singh says she does not care much about the profit, because she is getting to live her dream while making a difference to society. 1. Ivy and her husband made a careful plan for retirement. A. True B. False C. Not Given 2. Before retirement, the couple were doing business on plants. A. True B. False C. Not Given 3. The couple started Bollywood Veggies for business purposes. A. True B. False C. Not Given 4. Cabbage was the first vegetable planted on the farm. A. True B. False C. Not Given 5. The couple opened a restaurant close to the farm. A. True B. False C. Not Given 6. Mrs. Singh planted bananas because they were very popular. A. True B. False C. Not Given 7. Visitors to the farm like its banana chips the best. A. True B. False C. Not Given 8. Mrs. Singh built a retirement home on the farm. A. True B. False C. Not Given 9. Mrs. Singh thinks the farm is a good place for retired people.
全国2011年1月高等教育自学考试 现代语言学试题答案及解析点评 (课程代码:00838) I. Directions: Read each of the following statements carefully. Decide which one of the four choices best completes the statement and put the letter A, B, C, or D in the brackets. (2% ×10=20%) 1. C 【解析】句意:语言使用者所知道的语言能力,与我们在实际生活中对语言的产出和理解的具体运用之间存在着区别。因此应当选C。参考书本第7页。 【点评】本题考查语言学中语言能力与语言运用的区别,属重点,应识记。 2. A 【解析】The letter “ch” in the word “church” pronounces /t?/, while the letter “dge” in “judge” pronounces /d?/. /t?/ and /d?/ are all affricates. Affricates means “赛擦音”. 【点评】本题考查英语语音的分类。属概念题,应理解记忆。 3. D 【解析】能够表示如数,时态,级,格这样的语法关系或语法范畴的语素是曲折词缀。曲折词缀——inflectional morpheme 相见书本第52页。 【点评】本题考查形态学中的语素特性,应了解。 4. D 【解析】X-标杆理论中XP可能不仅仅只包含X,它通常包含核心语(head),补语(complement),另外还有指示语(specifier),故选D specifier 详见书本80页。 【点评】本题考查X-标杆理论中XP包含的成分,应了解。 5. C 【解析】意义是词汇内在的,抽象的,游离于语境之外的,是词汇所有特征的集合,而词汇所制成的客观世界中的事物,所指讨论的是语言形式和非语言世界之间的关系。详见书本第96页。 【点评】本题考查意义与所指两个术语的概念,属于常考点,应识记。 6. C 【解析】言外行为是表达说话人意图的行为,是在说话过程中完成的行为。 【点评】本题考查奥斯汀语言实施行为的3种行为中的言外行为。属重点,应牢记。 7. C 【解析】语音系统的变化包括元音的变化,语音的丧失,元音的增加,语音移位。语音的丧失中的尾音脱落(apocope)指词尾语音成分的去除。如name在古英语中发音为/nɑ:ma: /,而在中世纪英语中发音是/nɑ:m? /,再到现代英语中的/neim/, name 的发音在英语发展中词尾的发音脱落掉了。