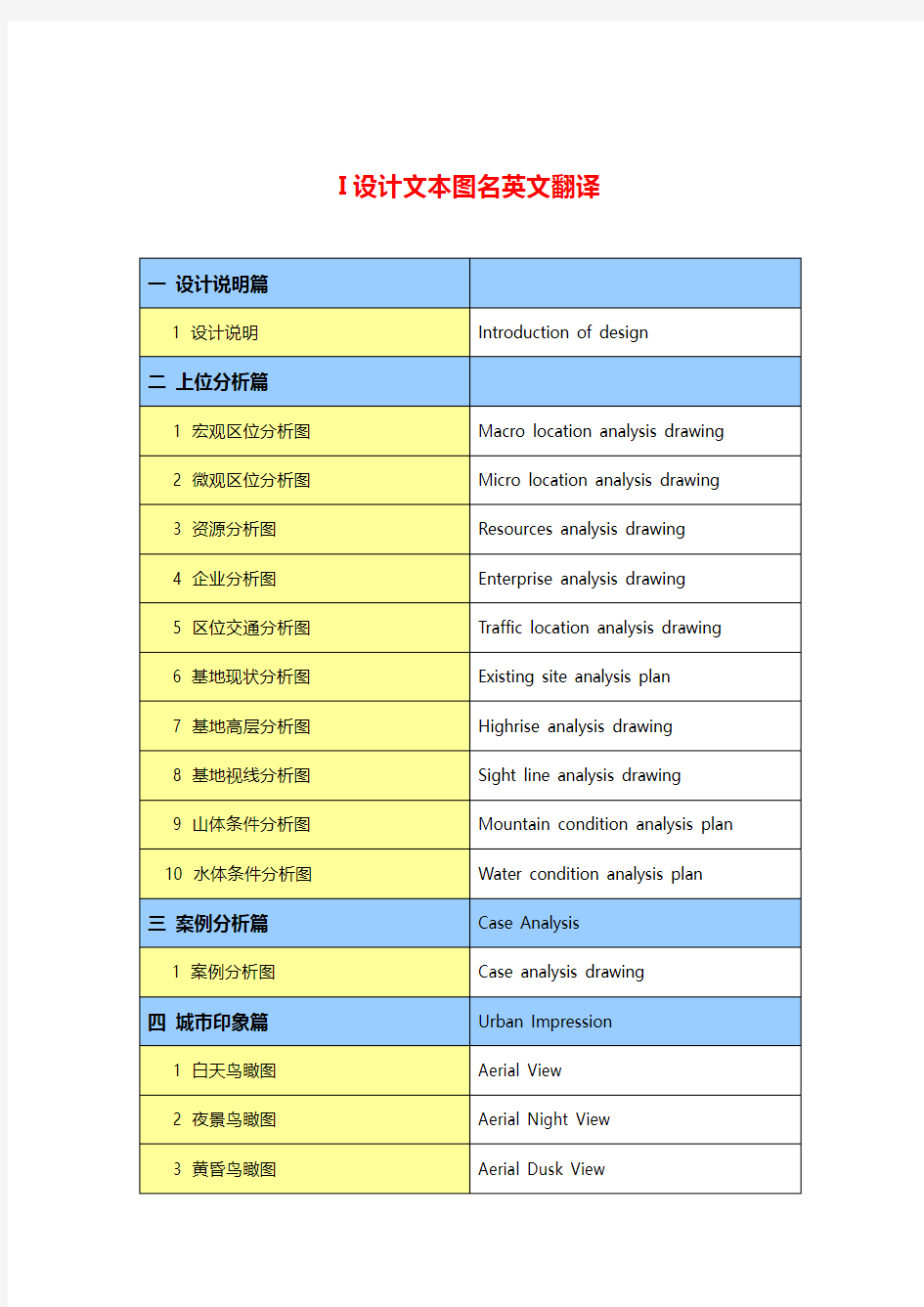
I设计文本图名英文翻译
一设计说明篇
1 设计说明Introduction of design
二上位分析篇
1 宏观区位分析图Macro location analysis drawing
2 微观区位分析图Micro location analysis drawing
3 资源分析图Resources analysis drawing
4 企业分析图Enterprise analysis drawing
5 区位交通分析图Traffic location analysis drawing
6 基地现状分析图Existing site analysis plan
7 基地高层分析图Highrise analysis drawing
8 基地视线分析图Sight line analysis drawing
9 山体条件分析图Mountain condition analysis plan
10 水体条件分析图Water condition analysis plan
三案例分析篇Case Analysis
1 案例分析图Case analysis drawing
四城市印象篇Urban Impression
1 白天鸟瞰图Aerial View
2 夜景鸟瞰图Aerial Night View
3 黄昏鸟瞰图Aerial Dusk View
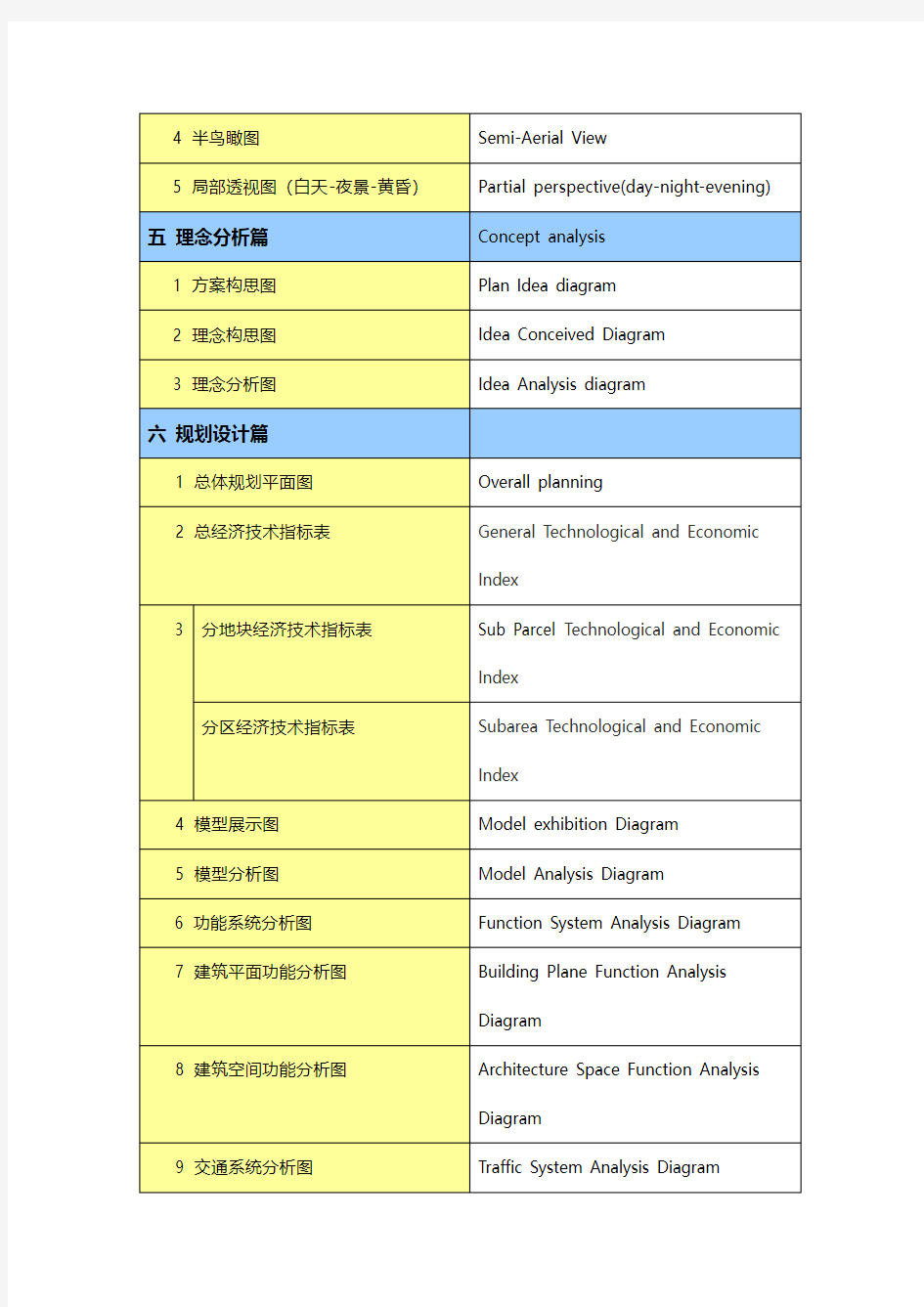
4 半鸟瞰图Semi-Aerial View
5 局部透视图(白天-夜景-黄昏)Partial perspective(day-night-evening) 五理念分析篇Concept analysis
1 方案构思图Plan Idea diagram
2 理念构思图Idea Conceived Diagram
3 理念分析图Idea Analysis diagram
六规划设计篇
1 总体规划平面图Overall planning
2 总经济技术指标表General Technological and Economic
Index
3 分地块经济技术指标表Sub Parcel Technological and Economic
Index
分区经济技术指标表Subarea Technological and Economic
Index
4 模型展示图Model exhibition Diagram
5 模型分析图Model Analysis Diagram
6 功能系统分析图Function System Analysis Diagram
7 建筑平面功能分析图Building Plane Function Analysis
Diagram
8 建筑空间功能分析图Architecture Space Function Analysis
Diagram
9 交通系统分析图Traffic System Analysis Diagram
10 道路系统分析图Road System Analysis Diagram
11 水路系统分析图Water way system Analysis Diagram
12 结构系统分析图Structure System Analysis Diagram
13 空间结构分析图Space Structure Analysis Diagram
14 空间系统分析图Space Structure Analysis Diagram
15 开发系统分析图Development system Analysis Diagram
16 开发强度示意图Development Intensity Diagram
17 消防系统分析图Fire protection system Analysis
Diagram
18 景观系统分析图Landscape system Analysis Diagram
19 空间景观分析图Space Sequence Analysis Diagram
20 绿化系统分析图Afforestation system Analysis Diagram
21 日照系统分析图Sunshine system Analysis Diagram
22 竖向设计分析图Vertical elevation Analysis Plan
23 视线系统分析图Sight System Analysis Plan
24 地块价值分析图District Value Diagram
25 地块价值挖掘分析图
26 天际线分析图Skyline Analysis Diagram
27 灯光系统分析图Lighting System Analysis Diagram
七建筑设计篇
1 首层建筑平面图Ground floor plan
2 夹层建筑平面图Mezzanine plan
3 二层建筑平面图Second floor plan
4 三层建筑平面图Third floor plan
5 地下一层平面图Plan for Basement Floor
6 地下二层平面图2nd Basement plan
7 地下三层平面图3rd Basement plan
8 防火分区图Fire Compartmentation Diagram
9 建筑立面图Building Elevation drawing
10 建筑剖面图Building Section
11 户型平面图Layout plan
12 材料运用示意图Material Exertion Diagram
八建筑意向篇
1 户型意向图Housing intention
2 建筑意向图Architectural intention
九景观意向篇
1景观意向图Landscape intention
十空间意向篇
1 空间意向图Space intention
十一场景意向篇
1 场景意向图Scene intention
* 对于不明确制图图纸的情况,请参考文件最后的图纸导航。
II英文扩展
1引言:preface 目录:catalog 扉页:head page 结语:conclusion 图例:legend
2水:water 海:sea 湖:lake 中央水景:central waterscape 绿化:planting 中央景观绿化:central greening design of landscape 组团绿化:? 绿化隔离带:greenbelt 景观带:landscape belt 庭院:courtyard 中央庭院:central courtyard 采光天井:light court 中庭上空:? 空中花园:hanging garden 屋顶花园:roof garden 别墅花园:Villa garden
3主入口:main entrance 次入口:secondary entrance 车行出入口:garage gateway地下车库:underground garage 地下车库车行出入口:underground garage gateway 消防通道:fire exit 隐形消防通道:? 停车场:parking lot 消防区:fire protection district
4广场:square 购物广场:plaza 商业:commerce 商务:business 商业步行街:Commercial Pedestrian Street 商业区:shopping centre 金融中心:financial centre 服务中心:service centre 管理中心:management center 物业管理处:Property Management Office 接待中心:reception center
reception hall 会议中心:conference center 展示中心:Exhibition Center
5公园:park 湿地公园:Wetland Park. 生态公园:Eco-park 水上乐园:water park 游乐园:amusement park 摩天轮:ferris wheel 木栈道: wooden trestle 亲水栈道:亲水平台:play pool 眺望亭:gazebo 游船码头:marina 岛屿:island 小路:path
6规划设计:planning design 建筑设计:architectural design 景观设计:landscape design 总图规划:master planning 效果图:rendering 单体设计:Individual Building Design 项目规划:project planning 周边坏境:surroundings
7流线:streamline 会议:meeting 交流:communicate 舒适:comfort 局部小气候:local climate 科技:technology 生态:ecology 休闲:leisure
时尚:fashion 大气:classy 效率:efficiency 绿化节能:Green energy saving 高端:high-end 现代感:sense of modernity 速度:speed 原生态:ecosystem 展示:exhibit
空气清新:fresh air 健康:health 独一无二:reception room 创意无限:视野开阔:open view 互动性:interactive 教育性:instructive 乐趣:fun
8大堂:lobby 酒店:hotel 五星级酒店:Five-star Hotel 套房:suite 标准房:Standard room 会议室:meeting room 储藏室:store room 接待室:reception room 休息室:Restroom 娱乐室:rumpus room 棋牌室:Chess & Poker Room 走廊通道:游泳馆:Natatorium 游泳池:Swimming pool 展览馆:Exhibition hall 博物馆:Museum 艺术馆:Art gallery 餐厅:Restaurant 咖啡室:cafe 门室:办公:office 会所:Club
9景观主轴:景观次轴:生态核心轴:
III图纸导航
一设计说明篇
1 设计说明
*来源于稳健棉花博物馆单体建筑设计二上位分析篇
1 宏观区位分析图
*来源于李渡烟花博览园概念规划设计
2 微观区位分析图
*来源于李渡烟花博览园概念规划设计3 资源分析图
*来源于宜都青林寺谜语村概念规划设计4 企业分析图
*来源于稳健棉花博物馆单体建筑设计5 区位交通分析图
6 基地现状分析图
*来源于金色农谷青少年教育实践基地概念规划设计
7 基地高层分析图
*来源于江西修水陈门五杰纪念公园概念规划设计8 基地视线分析图
9 山体条件分析图
10 水体条件分析图
*来源于宜都青林寺谜语村概念规划设计三案例分析篇
1 案例分析图
*来源于新浜汽车城概念规划设计四城市印象篇
1 白天鸟瞰图
2 夜景鸟瞰图
3 黄昏鸟瞰图
4 半鸟瞰图
5 局部透视图(白天-夜景-黄昏)
丽水市水阁中心小学规划建筑设计方案设计说明 第一章建筑设计 一、工程概况 丽水市水阁中心小学校址位于丽水市经济开发区内,基地西距开发区中心大道30米,南距北三路112米,东临东一路。基地南北长约202米,东西宽约200米,总用地面积40047平方米,地块形状方整,地势平坦,是一块理想的建校用地。水阁中心小学规划建设36个班,可容纳1620名在校生。方案力求把水阁中心小学设计成环境优美、设备齐全、高档次、高品位的一流校园。 二、设计依据 1.《丽水市水阁中心小学设计方案招标邀请书》 2.《城市普通中小学校校舍建设标准》 3.《中小学校建筑设计规范》 4.《浙江省教育厅关于实施“浙江省万校标准化建设工程”的通知》 5.国家及地方政府颁布的相关规范、规定和标准。 三、校园总体规划布局 1、设计构思 本设计崇尚、尊重自然环境,力求创造生态校园,体现园林式校园的特点,以现代的手法、现代的构思和现代的材料来营造一个现代的绿色园林校园,营造出一种优异的校园环境。设计认同中国传统文化,特别强调对中国园林及院落式建筑布局的认知和审美——即强调人与自然的和谐共存,视“自然”为人类生存的母体,精神的家园,同时赋予其时代的内容和表现方式。 ·引入周边山体自然景观,整体融入区域地景,形成天人合一的校园生态环境。 ·以绿色校园为构思骨架与灵魂,动静分离,疏密有致,相互渗透的功能分区。 ·层次分明的校园主次道路形成高效便捷的路网结构。 2、规划结构及功能分区 设计以主环路为骨架,相关功能区周边布置形成自由生动的规划结构:其主要构成为江南园林式及院落式的布局理念与手法,来对校园进行区块划分和功能定位。 整个校区分成四个大区块,其中东面临近东一路处设一个校前区,为学校入口广场。围绕校
禹宏·启城住宅小区项目方案设计 第一章建筑设计 一、设计依据 1、建设单位提供的数字化四线坐标及现状地形图 2、建设项目规划意见书和勘测红线图 3、《城市居住区规划设计规范》(GB50180-93 2002版) 4、《民用建筑设计通则》(GB50352-2005) 5、《住宅设计规范》(GB50096-2011) 6、《住宅建筑规范》(GB50368-2005) 7、《高层民用建筑设计防火规范》GB50045-95(2005年版) 8、《建筑设计防火规范》GB50016-2006 9、《汽车库建筑设计规范》(JGJ100-98) 10、《汽车库、修车库、停车场设计防火规范》(GB50067-97) 11、《夏热冬冷地区居住建筑节能设计标准》(JGJ134-2010) 12、《公共建筑节能设计标准》(GB50189-2005) 13、《城市道路和建筑物无障碍设计规范》(JGJ50-2001) 14、现行的《蚌埠市城市规划管理技术规定》 15、《建设项目日照分析技术管理规则(试行)》(2005版) 16、《建筑工程面积计算规范》GBT/50353-2005 17、与本项目相关的国家、地方颁布的法律、法规、规范和技术标准。 二、项目概况 1、项目区位 本项目地块位于安徽省蚌埠市,东临中学西路,西接西外环路,南临健康路,北接禹王西路。交通十分便利,接近城西新城区中心,本小区和拟建的医院、第二中学,都在半径600米的距离之内。地理位置优越,随着相应市政配套的日益完善,本区域将成为蚌埠市未来又一高档商住圈。 2、用地性质及规模 项目地块规划为居住和商业用地,总用地面积约80838.0㎡,规划总建筑面积209983平方米,地上建筑面积约19.39万平方米。 3、地形地貌 地块用地呈长方形,当前为闲置用地,现状地块内有堆土,东西两边略有高差,总体地势南低北高。 4、规划要求 ■容积率 地块容积率要求≤2.4 ■建筑密度 地块1建筑密度:26% (出让要求不大于26%)
本科毕业设计 外文文献及译文 文献、资料题目:Designing Against Fire Of Building 文献、资料来源:国道数据库 文献、资料发表(出版)日期:2008.3.25 院(部):土木工程学院 专业:土木工程 班级:土木辅修091 姓名:武建伟 学号:2008121008 指导教师:周学军、李相云 翻译日期: 20012.6.1
外文文献: Designing Against Fire Of Buliding John Lynch ABSTRACT: This paper considers the design of buildings for fire safety. It is found that fire and the associ- ated effects on buildings is significantly different to other forms of loading such as gravity live loads, wind and earthquakes and their respective effects on the building structure. Fire events are derived from the human activities within buildings or from the malfunction of mechanical and electrical equipment provided within buildings to achieve a serviceable environment. It is therefore possible to directly influence the rate of fire starts within buildings by changing human behaviour, improved maintenance and improved design of mechanical and electrical systems. Furthermore, should a fire develops, it is possible to directly influence the resulting fire severity by the incorporation of fire safety systems such as sprinklers and to provide measures within the building to enable safer egress from the building. The ability to influence the rate of fire starts and the resulting fire severity is unique to the consideration of fire within buildings since other loads such as wind and earthquakes are directly a function of nature. The possible approaches for designing a building for fire safety are presented using an example of a multi-storey building constructed over a railway line. The design of both the transfer structure supporting the building over the railway and the levels above the transfer structure are considered in the context of current regulatory requirements. The principles and assumptions associ- ated with various approaches are discussed. 1 INTRODUCTION Other papers presented in this series consider the design of buildings for gravity loads, wind and earthquakes.The design of buildings against such load effects is to a large extent covered by engineering based standards referenced by the building regulations. This is not the case, to nearly the same extent, in the
专业资料 学院: 专业:土木工程 姓名: 学号: 外文出处:Structural Systems to resist (用外文写) Lateral loads 附件:1.外文资料翻译译文;2.外文原文。
附件1:外文资料翻译译文 抗侧向荷载的结构体系 常用的结构体系 若已测出荷载量达数千万磅重,那么在高层建筑设计中就没有多少可以进行极其复杂的构思余地了。确实,较好的高层建筑普遍具有构思简单、表现明晰的特点。 这并不是说没有进行宏观构思的余地。实际上,正是因为有了这种宏观的构思,新奇的高层建筑体系才得以发展,可能更重要的是:几年以前才出现的一些新概念在今天的技术中已经变得平常了。 如果忽略一些与建筑材料密切相关的概念不谈,高层建筑里最为常用的结构体系便可分为如下几类: 1.抗弯矩框架。 2.支撑框架,包括偏心支撑框架。 3.剪力墙,包括钢板剪力墙。 4.筒中框架。 5.筒中筒结构。 6.核心交互结构。 7. 框格体系或束筒体系。 特别是由于最近趋向于更复杂的建筑形式,同时也需要增加刚度以抵抗几力和地震力,大多数高层建筑都具有由框架、支撑构架、剪力墙和相关体系相结合而构成的体系。而且,就较高的建筑物而言,大多数都是由交互式构件组成三维陈列。 将这些构件结合起来的方法正是高层建筑设计方法的本质。其结合方式需要在考虑环境、功能和费用后再发展,以便提供促使建筑发展达到新高度的有效结构。这并
不是说富于想象力的结构设计就能够创造出伟大建筑。正相反,有许多例优美的建筑仅得到结构工程师适当的支持就被创造出来了,然而,如果没有天赋甚厚的建筑师的创造力的指导,那么,得以发展的就只能是好的结构,并非是伟大的建筑。无论如何,要想创造出高层建筑真正非凡的设计,两者都需要最好的。 虽然在文献中通常可以见到有关这七种体系的全面性讨论,但是在这里还值得进一步讨论。设计方法的本质贯穿于整个讨论。设计方法的本质贯穿于整个讨论中。 抗弯矩框架 抗弯矩框架也许是低,中高度的建筑中常用的体系,它具有线性水平构件和垂直构件在接头处基本刚接之特点。这种框架用作独立的体系,或者和其他体系结合起来使用,以便提供所需要水平荷载抵抗力。对于较高的高层建筑,可能会发现该本系不宜作为独立体系,这是因为在侧向力的作用下难以调动足够的刚度。 我们可以利用STRESS,STRUDL 或者其他大量合适的计算机程序进行结构分析。所谓的门架法分析或悬臂法分析在当今的技术中无一席之地,由于柱梁节点固有柔性,并且由于初步设计应该力求突出体系的弱点,所以在初析中使用框架的中心距尺寸设计是司空惯的。当然,在设计的后期阶段,实际地评价结点的变形很有必要。 支撑框架 支撑框架实际上刚度比抗弯矩框架强,在高层建筑中也得到更广泛的应用。这种体系以其结点处铰接或则接的线性水平构件、垂直构件和斜撑构件而具特色,它通常与其他体系共同用于较高的建筑,并且作为一种独立的体系用在低、中高度的建筑中。
(一)、基本规定 一、文本制做应采用统一格式,一般为A 3。" 二、建筑方案设计文件编排顺序: 1 .封面: 标明项目名称、编制日期、建设单位及设计单位名称。 2、菲页: 设计单位资质章、设计人员签名、设计单位企业法人营业执照(复印件)和工程设计证书(复印件)等。 3.设计文件目录 4 .设计说明 5 .设计图纸: 总平面图(或用地规划图)、方案一建筑效果图及建筑设计图(平、立、剖)、方案二建筑效果图及建筑设计图(平、立、剖)。其它方案顺延。 6 .技术分析图: 根据项目特点提供相应的功能分析图、交通分析图、环境绿化景观分析图、日照分析图、内部流线分析图等 三、所有图纸和图板都应按比例绘制或制作。图板应注明建设单位、设计单位、工程名称和图名。 四、文字说明部分应采用WORD文挡格式。 (二)、设计说明内容要求 一、设计依据和设计要求
二、建筑设计说明: 建筑构思说明,概述场地现状和周边环境;规划场地内原有建筑的利用和保护,古树、名木、植被保护方案;道路布置、交通分析、停车场地设置、消防措施等。 建筑平面布局交通组织和功能分析;建筑的空间构成及立面设计;当地形较复杂时应做竖向设计说明; 三、主要技术经济指标 第二区 建筑设计方案要求 关于建筑设计方案文本要求 1.封面 要求: 必须注明建设项目、建设单位、设计单位、方案完成日期,并加盖建设单位公章及设计单位资质章。 2.方案设计说明及指标明细表 要求: 说明书按照规划、建筑、绿化、供电、供水、排水、电讯、人防、消防、环保、暖通、节能等顺序;指标明细表需按照申报的建筑设计方案实际设计面积进行核算。 3.现状分析图及照片 要求: 标明建设用地现状自然地形地貌、道路、绿化、工程管线及各类用地内建筑的范围、性质、层数、质量、单位名称,以及规划四至范围影响范围内的建
PA VEMENT PROBLEMS CAUSED BY COLLAPSIBLE SUBGRADES By Sandra L. Houston,1 Associate Member, ASCE (Reviewed by the Highway Division) ABSTRACT: Problem subgrade materials consisting of collapsible soils are com- mon in arid environments, which have climatic conditions and depositional and weathering processes favorable to their formation. Included herein is a discussion of predictive techniques that use commonly available laboratory equipment and testing methods for obtaining reliable estimates of the volume change for these problem soils. A method for predicting relevant stresses and corresponding collapse strains for typical pavement subgrades is presented. Relatively simple methods of evaluating potential volume change, based on results of familiar laboratory tests, are used. INTRODUCTION When a soil is given free access to water, it may decrease in volume, increase in volume, or do nothing. A soil that increases in volume is called a swelling or expansive soil, and a soil that decreases in volume is called a collapsible soil. The amount of volume change that occurs depends on the soil type and structure, the initial soil density, the imposed stress state, and the degree and extent of wetting. Subgrade materials comprised of soils that change volume upon wetting have caused distress to highways since the be- ginning of the professional practice and have cost many millions of dollars in roadway repairs. The prediction of the volume changes that may occur in the field is the first step in making an economic decision for dealing with these problem subgrade materials. Each project will have different design considerations, economic con- straints, and risk factors that will have to be taken into account. However, with a reliable method for making volume change predictions, the best design relative to the subgrade soils becomes a matter of economic comparison, and a much more rational design approach may be made. For example, typical techniques for dealing with expansive clays include: (1) In situ treatments with substances such as lime, cement, or fly-ash; (2) seepage barriers and/ or drainage systems; or (3) a computing of the serviceability loss and a mod- ification of the design to "accept" the anticipated expansion. In order to make the most economical decision, the amount of volume change (especially non- uniform volume change) must be accurately estimated, and the degree of road roughness evaluated from these data. Similarly, alternative design techniques are available for any roadway problem. The emphasis here will be placed on presenting economical and simple methods for: (1) Determining whether the subgrade materials are collapsible; and (2) estimating the amount of volume change that is likely to occur in the 'Asst. Prof., Ctr. for Advanced Res. in Transp., Arizona State Univ., Tempe, AZ 85287. Note. Discussion open until April 1, 1989. To extend the closing date one month,
[山东]大型体育中心规划及单体设计方案文本 建筑功能:体育馆高度类别:多层建筑 外立面材料:幕墙幕墙面板材料:组合幕墙 结构形式:钢筋混凝土结构钢筋混凝土结构:框架 图纸深度:方案(初设图)项目位置:山东 设计风格:现代风格设计流派:现代 图纸格式:JPG 图纸张数:54 张 用地面积:244609 ㎡容积率:0.26 建筑密度:27 % 绿化率:21.7 % 地上层数:2 层地下室功能:车库 效果图:有 设计理念: 体育中心配套的体育馆,游泳馆结合设置在体育场西侧,与体育场成中心广场。三者形成绕主广场环布的形式。主广场和政府办公用,文化科教用地的景观形成了体育中心总体规划的流线性,突出了主体育场的中心主导性和重要性,也强化了主体育场,中心广场,市政府用地及文化用地的东西向景观轴线。 图纸包含:鸟瞰图,效果图,立面图,剖面图,设计说明,经济技术指标,分析图,示意图等。
{详细内 容}:https://www.doczj.com/doc/9e19000050.html,/tech/detailprof987806JZ.h tm [广东]43层高层商业综合体建筑设计方案文本 建筑功能:商业综合体高度类别:高层建筑 外立面材料:幕墙幕墙面板材料:玻璃幕墙 结构形式:钢筋混凝土结构钢筋混凝土结构:框架 图纸深度:方案(初设图)项目位置:广东 设计风格:现代风格设计流派:artdeco 图纸格式:JPG 图纸张数:149 张 建筑面积:25952.09 ㎡用地面积:38623.56 ㎡ 容积率:8.36 建筑密度:49 %
绿化率:30 % 建筑高度:180 m 地上层数:43 层地下层数:3 层 地下室建筑面积:56565 ㎡地下室功能:车库 效果图:有机动车辆停车位:1561 个 设计理念: 作为现代城市的必不可少的主要出行方式,选择一种交通工具,具有准时,快捷,高速的特征,它的出现从根本上提高了人们对时空的把控能力,缩短了城市内的空间距离。地铁,公交,私家车是对城市空间价值的有效挖掘和利用,分区居住成为可能。城市的服务和价值随着交通脉络的延展的得到更大范围,更快速地流转。 图纸包含:鸟瞰图,效果图,立面图,剖面图,设计说明,经济技术指标,分析图,示意图等。 {详细内 容}:https://www.doczj.com/doc/9e19000050.html,/tech/detailprof987805JZ.h tm
( 二 〇 一 二 年 六 月 外文文献及翻译 题 目: About Buiding on the Structure Design 学生姓名: 学 院:土木工程学院 系 别:建筑工程系 专 业:土木工程(建筑工程方向) 班 级:土木08-4班 指导教师:
英文原文: Building construction concrete crack of prevention and processing Abstract The crack problem of concrete is a widespread existence but again difficult in solve of engineering actual problem, this text carried on a study analysis to a little bit familiar crack problem in the concrete engineering, and aim at concrete the circumstance put forward some prevention, processing measure. Keyword:Concrete crack prevention processing Foreword Concrete's ising 1 kind is anticipate by the freestone bone, cement, water and other mixture but formation of the in addition material of quality brittleness not and all material.Because the concrete construction transform with oneself, control etc. a series problem, harden model of in the concrete existence numerous tiny hole, spirit cave and tiny crack, is exactly because these beginning start blemish of existence just make the concrete present one some not and all the characteristic of quality.The tiny crack is a kind of harmless crack and accept concrete heavy, defend Shen and a little bit other use function not a creation to endanger.But after the concrete be subjected to lotus carry, difference in temperature etc. function, tiny crack would continuously of expand with connect, end formation we can see without the
Original Article Impact of crack width on bond: confined and unconfine d rebar David https://www.doczj.com/doc/9e19000050.html,w1, Denglei Tang2, Thoma s K. C.Molyneaux3 and Rebecca Gravina3 (1)School of the Built Environment, Heriot Watt University, Edinburgh, EH14 4AS, UK (2)VicRoads, Melbourne, VIC, Australia (3)School of Civil, Environmental and Chemical Engineering, RMIT University, Melbourne, VIC, 3000, Australia David W. Law Email: https://www.doczj.com/doc/9e19000050.html,w@https://www.doczj.com/doc/9e19000050.html, Received: 14January2010Accepted: 14Decemb er2010Published online: 23December2010 Abstract This paper reports the results of a research project comp aring the effect of surface crack width and degree of corrosi on on the bond strength of confined and unconfined deforme d 12 and 16mm mild steel reinforcing bars. The corrosion was induced by chloride contamination of the concrete and
Civil engineering Civil engineering is a professional engineering discipline that deals with the design, construction, and maintenance of the physical and naturally built environment, including works like bridges, roads, canals, dams, and buildings.[1][2][3] Civil engineering is the oldest engineering discipline after military engineering,[4] and it was defined to distinguish non-military engineering from military engineering.[5] It is traditionally broken into several sub-disciplines including environmental engineering, geotechnical engineering, structural engineering, transportation engineering, municipal or urban engineering, water resources engineering, materials engineering, coastal engineering,[4] surveying, and construction engineering.[6] Civil engineering takes place on all levels: in the public sector from municipal through to national governments, and in the private sector from individual homeowners through to international companies. History of the civil engineering profession See also: History of structural engineering Engineering has been an aspect of life since the beginnings of human existence. The earliest practices of Civil engineering may have commenced between 4000 and 2000 BC in Ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia (Ancient Iraq) when humans started to abandon a nomadic existence, thus causing a need for the construction of shelter. During this time, transportation became increasingly important leading to the development of the wheel and sailing. Until modern times there was no clear distinction between civil engineering and architecture, and the term engineer and architect were mainly geographical variations referring to the same person, often used interchangeably.[7]The construction of Pyramids in Egypt (circa 2700-2500 BC) might be considered the first instances of large structure constructions. Other ancient historic civil engineering constructions include the Parthenon by Iktinos in Ancient Greece (447-438 BC), the
外文文献及翻译题目:沉埋隧道工程对环境的影响 专业土木工程 学生姓名李鹏 班级BM土木071 学号0751411107 指导教师殷勇
沉埋隧道工程对环境的影响 摘要:一座沉埋隧道对环境的深远影响都与穿过水道的沉放管段有关。隧道对这一地区内地下和地表水的影响在隧道设计和施工方法的选择中起最重要的作用。最近在考虑的一个影响施工的问题是必须为隧道开挖的沟槽有可能出现被污染的泥土。挖出与运送这些泥土至专门装备起来以便接收它们的存放地点的方法是一系列重要新技术和质量控制措施的环境问题。最常见的是在任何建筑工程中都会遇到的环境问题,即噪音、灰尘以及交通阻塞。本文对这些问题以及目前用于解决这些问题的技术和措施作了评述。 关键词:隧道环境 沉埋隧道的特征一座沉埋隧道具有两项基本特征:它是某一地下结构场地的一部分,要在繁忙的交通条件下保证施工,而并不意味这个地区是被充分地利用了的。因此,施工空间是很宝贵的。 它基本上是一预制结构。 最终将安装在河流或运河底部位置的隧道管段是在其它地方以非常接近工厂条件的方式筑造的,这种条件在现场和工地是不大可能达到的。施工规划上的优点和将管段制造与工地准备分开进行在后勤上的优点是显而易见的,还有极易于实现有效的质量控制的优点。 隧道工点在环境上的影响同样也大大少于隧道完全都在现场施工的情况;如像空间的需求和施工运输,这两个问题就大大的缓和。 当然,这些优点的先决条件是有现成的可用于管段制造的适宜工地。它必须满足一系列有关环境影响的条件。在如荷兰这类人口密集的国家里,要找到合适的工地很不容易,而且很显然,一旦选定一可用位置,可多次使用就相当引人。因此,隧道施工的总体规划是一个供讨论的普通主题。 两端的地下结构一座新隧道连结到原来既有的地下结构中去,往往实际上是取代一既有的跨越水域的设施,如轮渡或桥梁。它也可为一既有隧道或桥梁的补充设施。无论决定建造一新隧道的理由如何,它的位置将在很大程度上受到既有地下结构布置的制约,而且其施工设计也要满足现有交通运输只受最小程度干扰的要求。这就意味着设计人员在隧道位置方面很少有选择的机会,因而不得不根据这一既定位置的条件和要求来修改隧道设计。
毕业设计(论文)外文文献翻译 (2011届) 学生姓名夏银虎 学号0405070326 院系工程与技术系 专业土木工程 指导教师于周平 填写日期2010-11-13
1中文翻译 摘要:为了研究连续型拓扑优化理论在实际工程中的应用,该文给出了一种多层钢框架支撑体系连续型拓扑优化设计方法。基于灵敏度分析,探讨了连续体结构在多工况荷载作用下、同时受应力和多位移约束的拓扑优化删除准则。为保证拓扑优化结果的合理性,提出了设计区域平均厚度的概念。在该文给出的优化设计方法中,首先在不考虑位移约束的情况下对无支撑钢框架进行优化设计,然后在有位移约束的条件下采用渐进结构优化算法和删除准则对支撑体系进行连续型拓扑优化设计,并将获得的支撑最优拓扑构形转化成相应的杆件。通过一个3跨12层钢框架支撑体系的拓扑优化设计实例验证了该文给出的钢框架支撑体系连续型拓扑优化设计方法的有效性。 关键词:钢框架;支撑体系;连续型;拓扑优化;渐进结构优化 1.1钢筋混凝土 素混凝土是由水泥、水、细骨料、粗骨料(碎石或;卵石)、空气,通常还有其他外加剂等经过凝固硬化而成。将可塑的混凝土拌合物注入到模板内,并将其捣实,然后进行养护,以加速水泥与水的水化反应,最后获得硬化的混凝土。其最终制成品具有较高的抗压强度和较低的抗拉强度。其抗拉强度约为抗压强度的十分之一。因此,截面的受拉区必须配置抗拉钢筋和抗剪钢筋以增加钢筋混凝土构件中较弱的受拉区的强度。 由于钢筋混凝土截面在均质性上与标准的木材或钢的截面存在着差异,因此,需要对结构设计的基本原理进行修改。将钢筋混凝土这种非均质截面的两种组成部分按一定比例适当布置,可以最好的利用这两种材料。这一要求是可以达到的。因混凝土由配料搅拌成湿拌合物,经过振捣并凝固硬化,可以做成任何一种需要的形状。如果拌制混凝土的各种材料配合比恰当,则混凝土制成品的强度较高,经久耐用,配置钢筋后,可以作为任何结构体系的主要构件。 浇筑混凝土所需要的技术取决于即将浇筑的构件类型,诸如:柱、梁、墙、板、基础,大体积混凝土水坝或者继续延长已浇筑完毕并且已经凝固的混凝土等。对于梁、柱、墙等构件,当模板清理干净后应该在其上涂油,钢筋表面的锈及其他有害物质也应该被清除干净。浇筑基础前,应将坑底土夯实并用水浸湿6英寸,以免土
学院: 专业:土木工程 姓名: 学号: 外文出处: Structural Systems to resist (用外文写) Lateral loads 附件: 1.外文资料翻译译文;2.外文原文。
附件1:外文资料翻译译文 抗侧向荷载的结构体系 常用的结构体系 若已测出荷载量达数千万磅重,那么在高层建筑设计中就没有多少可以进行极其复杂的构思余地了。确实,较好的高层建筑普遍具有构思简单、表现明晰的特点。 这并不是说没有进行宏观构思的余地。实际上,正是因为有了这种宏观的构思,新奇的高层建筑体系才得以发展,可能更重要的是:几年以前才出现的一些新概念在今天的技术中已经变得平常了。 如果忽略一些与建筑材料密切相关的概念不谈,高层建筑里最为常用的结构体系便可分为如下几类: 1.抗弯矩框架。 2.支撑框架,包括偏心支撑框架。 3.剪力墙,包括钢板剪力墙。 4.筒中框架。 5.筒中筒结构。 6.核心交互结构。 7. 框格体系或束筒体系。 特别是由于最近趋向于更复杂的建筑形式,同时也需要增加刚度以抵抗几力和地震力,大多数高层建筑都具有由框架、支撑构架、剪力墙和相关体系相结合而构成的体系。而且,就较高的建筑物而言,大多数都是由交互式构件组成三维陈列。 将这些构件结合起来的方法正是高层建筑设计方法的本质。其结合方式需要在考虑环境、功能和费用后再发展,以便提供促使建筑发展达到新高度的有效结构。这并不是说富于想象力的结构设计就能够创造出伟大建筑。正相反,有许多例优美的建筑仅得到结构工程师适当的支持就被创造出来了,然而,如果没有天赋甚厚的建筑师的创造力的指导,那么,得以发展的就只能是好的结构,并非是伟大的建筑。无论如何,要想创造出高层建筑真正非凡的设计,两者都需要最好的。 虽然在文献中通常可以见到有关这七种体系的全面性讨论,但是在这里还值得进一步讨论。设计方法的本质贯穿于整个讨论。设计方法的本质贯穿于整个讨论中。
XXX项目 住宅建筑方案设计合同 甲方(发包方): 乙方(设计方): 签约日期:年月日
目录 1.设计依据 --------------------------------------------------------- 3 2.项目概况及规划要求 ----------------------------------------------- 3 3.工作范围与工作阶段 ----------------------------------------------- 4 4.甲乙双方义务 ----------------------------------------------------- 6 5.设计进度 --------------------------------------------------------- 9 6.设计费用和付款 -------------------------------------------------- 10 7.知识产权保护和保密义务 ------------------------------------------ 12 8.违约责任 -------------------------------------------------------- 13 9.合同终止 -------------------------------------------------------- 15 10.过程控制与协调 ------------------------------------------------- 15 11.其他 ----------------------------------------------------------- 16附件一:各阶段设计任务书 ------------------------------------------ 18附件二:结构设计限额指标 ------------------------------------------ 19附件三:乙方设计人员名单 ------------------------------------------ 20附件四:廉洁合作协议 ---------------------------------------------- 21
本科毕业设计 外文文献及译文文献、资料题目:Designing Against Fire Of Building 文献、资料来源:国道数据库 文献、资料发表(出版)日期:2008.3.25 院(部):土木工程学院 专业:土木工程 班级:土木辅修091 姓名:xxxx
外文文献: Designing Against Fire Of Buliding xxx ABSTRACT: This paper considers the design of buildings for fire safety. It is found that fire and the associ- ated effects on buildings is significantly different to other forms of loading such as gravity live loads, wind and earthquakes and their respective effects on the building structure. Fire events are derived from the human activities within buildings or from the malfunction of mechanical and electrical equipment provided within buildings to achieve a serviceable environment. It is therefore possible to directly influence the rate of fire starts within buildings by changing human behaviour, improved maintenance and improved design of mechanical and electrical systems. Furthermore, should a fire develops, it is possible to directly influence the resulting fire severity by the incorporation of fire safety systems such as sprinklers and to provide measures within the building to enable safer egress from the building. The ability to influence the rate of fire starts and the resulting fire severity is unique to the consideration of fire within buildings since other loads such as wind and earthquakes are directly a function of nature. The possible approaches for designing a building for fire safety are presented using an example of a multi-storey building constructed over a railway line. The design of both the transfer structure supporting the building over the railway and the levels above the transfer structure are considered in the context of current regulatory requirements. The principles and assumptions associ- ated with various approaches are discussed. 1 INTRODUCTION Other papers presented in this series consider the design of buildings for gravity loads, wind and earthquakes.The design of buildings against such load effects is to a large extent covered by engineering based standards referenced by the building regulations. This is not the case, to nearly the same extent, in the case of fire. Rather, it is building regulations such as the Building Code of Australia (BCA) that directly specify most of the requirements for fire safety of buildings with reference being made to Standards such as AS3600 or AS4100 for methods for determining the fire resistance of structural elements. The purpose of this paper is to consider the design of buildings for fire safety from an engineering perspective (as is currently done for other loads such as wind or earthquakes), whilst at the same time,putting such approaches in the context of the current regulatory requirements.At the outset,it needs to be noted that designing a building for fire safety is far more