
2013年同等学力英语语法专项复习:复合从句
一、总述
根据从句在句中担任成分的不同,可将其分为名词性从句、形容词性从句和副词性从句。
名词性从句包括主语从句、表语从句、宾语从句和同位语从句。引导名词性从句的关联词有:
单纯连接词:that, whether, if (此类连接词在从句中不充当句法成分)。
疑问代词:who, whoever, whichever, what, whatever (此类词在名词性从句中充当一定的句法成分)。疑问副词:when, where, why, how (此类副词在句中充当句法成分)。
二、重点考点
1. 名词性从句
名词性从句包括主语从句、表语从句、宾语从句和同位语从句。引导这些名词性从句的关联词包括:从属连词that 、if、whether ;连接代词who 、whoever 、whom 、whomever 、which 、whichever 、what 、whatever 、whose ;连接副词where 、when 、why 、how 。其中,从属连词只起连接作用,在从句中不充当任何句法成分,而连接代词和连接副词则既起连接作用,又在从句中充当一定的成分。例如:
That Owen should have married his cousin is not at all surprising.
The fact is that he didn’t go to the dinner party.
I don’t know if he will attend the meeting.
Have you heard the news that Mary is going to marry Tom?
A. 在含有主语从句的复合句中,为保持句子平衡,常用it 作形式主语,而将真正的主语从句放在句末。例如:It’s well-known that water is indispensable to life.
B. 为保持句子平衡,that 引导的宾语从句也常用it 代替,而将真正的宾语从句置于主句句末。这常常出现在主句有形容词或分词作宾语补足语的情况下。例如:
He made it quite clear that he preferred to live here.
C. 从属连词whether 和if 都作“是否??”解,但if 不可引导主语从句和表语从句。
whether 可与or (not) 连用,而if 不可以。例如:
I don’t know whether (if) she is at home. Whether she comes or not makes no difference.
D. that 和what 引导名词性从句的区别:that 在从句中不充当成分,而what 在从句
中充当一定的成分,如主语、表语、宾语等。that 可省略,what 则不可省。例如:
He always means what he says. She suggested (that) he do it at once.
E. 同位语从句大多由从属连词that 引导,常跟在下列名词后面,如fact、idea 、opinion 、news 、hope 、belief 等。同位语从句一般用来解释说明这些名词的具体含义和内容。that 不可省略。例如:
We are familiar with the idea that all matter consists of atoms.
The news that we are invited to the conference is very encouraging.
2. 定语从句
引导定语从句的关联词包括:(1) 关系代词:that, which, whose, who, whom, as; (2) 关系副词:when, where, why 。关系代词和关系副词在定语中都充当一定的句法成分,关系代词在从句中充当动词的宾语时,一般可省去。
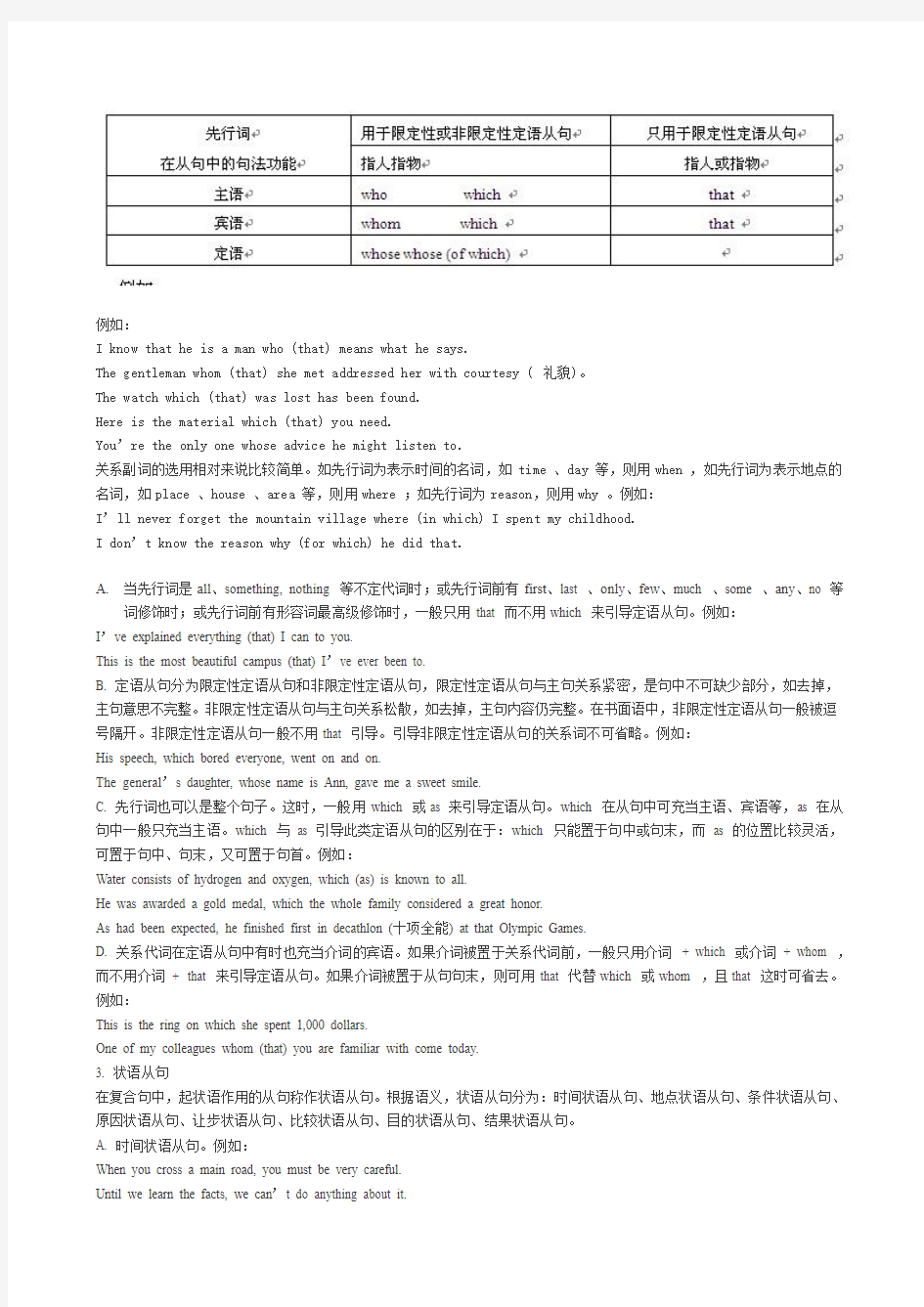
关系代词的选用比较复杂,它受下列条件的制约:(1) 先行词是指人还是指物;(2) 关系代词在从句中的句法功能;(3) 定语从句是限定性的还是非限定性的。关系代词的选用情况见下表:
例如:
I know that he is a man who (that) means what he says.
The gentleman whom (that) she met addressed her with courtesy ( 礼貌)。
The watch which (that) was lost has been found.
Here is the material which (that) you need.
You’re the only one whose advice he might listen to.
关系副词的选用相对来说比较简单。如先行词为表示时间的名词,如time 、day 等,则用when ,如先行词为表示地点的名词,如place 、house 、area 等,则用where ;如先行词为reason,则用why 。例如:
I’ll never forget the mountain village where (in which) I spent my childhood.
I don’t know the reason why (for which) he did that.
A.当先行词是all、something, nothing 等不定代词时;或先行词前有first、last 、only、few、much 、some 、any、no 等
词修饰时;或先行词前有形容词最高级修饰时,一般只用that 而不用which 来引导定语从句。例如:
I’ve explained everything (that) I can to you.
This is the most beautiful campus (that) I’ve ever been to.
B. 定语从句分为限定性定语从句和非限定性定语从句,限定性定语从句与主句关系紧密,是句中不可缺少部分,如去掉,主句意思不完整。非限定性定语从句与主句关系松散,如去掉,主句内容仍完整。在书面语中,非限定性定语从句一般被逗号隔开。非限定性定语从句一般不用that 引导。引导非限定性定语从句的关系词不可省略。例如:
His speech, which bored everyone, went on and on.
The general’s daughter, whose name is Ann, gave me a sweet smile.
C. 先行词也可以是整个句子。这时,一般用which 或as 来引导定语从句。which 在从句中可充当主语、宾语等,as 在从句中一般只充当主语。which 与as 引导此类定语从句的区别在于:which 只能置于句中或句末,而as 的位置比较灵活,可置于句中、句末,又可置于句首。例如:
Water consists of hydrogen and oxygen, which (as) is known to all.
He was awarded a gold medal, which the whole family considered a great honor.
As had been expected, he finished first in decathlon (十项全能) at that Olympic Games.
D. 关系代词在定语从句中有时也充当介词的宾语。如果介词被置于关系代词前,一般只用介词+ which 或介词+ whom ,而不用介词+ that 来引导定语从句。如果介词被置于从句句末,则可用that 代替which 或whom ,且that 这时可省去。例如:
This is the ring on which she spent 1,000 dollars.
One of my colleagues whom (that) you are familiar with come today.
3. 状语从句
在复合句中,起状语作用的从句称作状语从句。根据语义,状语从句分为:时间状语从句、地点状语从句、条件状语从句、原因状语从句、让步状语从句、比较状语从句、目的状语从句、结果状语从句。
A. 时间状语从句。例如:
When you cross a main road, you must be very careful.
(1) when、as、while 引导时间状语从句时都可以表示主句的动作与从句的动作同时发生,即同时性。它们的区别在于:when 和as 引导的状语从句中的动作可以是延续性的,也可以是非延续性的,即瞬时性;while 引导的状语从句中的动作只能是延续的动作或状态。当主句和从句中的动作均为延续性动作时,一般用while,而不用when 或as。当表示两个同时发展、变化的情况下,一般用as, 作“随着??”解。例如:
When she comes, I shall tell her to wait for you.
As she got older, she got wiser.
While Peter was reading, his wife was cooking.
(2) 有些副词和一些表示时间的名词词组也可用作从属连词,引导时间状语从句。如:instantly, immediately, directly, the day, every time, the minute, the second, the moment 等。例如:
Immediately he arrived, he started describing us what had happened.
The day he returned home, his grandpa was already dead.
B. 条件状语从句
引导条件状语从句的从属连词有:if, unless, as (so), only if (只要)。例如:
If you don’t come on time, we’ll start out without you.
As (so) long as you keep on trying, you’ll certainly succeed.
除了以上提到的从属连词外,还有其他的一些词或词组也可引导条件状语从句。例如:providing that, provided, supposing that, suppose that, on condition that, in case 等。例如:
Provided (that) he wins the support of the minority groups, he will be able to win the election.
C. 原因状语从句引导原因状语从句的从属连词有:because, since, as, now (that), in that, considering
that 等。例如:
Since the speaker can’t come, we’ll have to cancel the meeting.
in that 和now (that) 的用法:in that 引导的从句对主句进行解释或说明,意思是:在??方面,在于??;因为。now (that) 表示既然。例如:
Theory is valuable in that it can provide a direction for practice.
Now (that) the weather has improved, let’s go out for a picnic.
D. 让步状语从句
引导让步状语从句的从属连词有:though, although, even if (even though), as, no matter,despite the fact that, in spite of the fact that, while。例如:
Tom always enjoys swimming, even though the weather is rough.
Despite the fact that there exist national differences, certain funny situations have a universal appeal.
一些疑问词在词尾加上ever 后,也可引导让步状语从句,相当于no matter + 疑问词。这些词包括:whatever, wherever, whenever, whoever, however 。例如:
Whatever he says, don’t believe him.
Whoever you are, you must obey the traffic regulations.
E. 目的状语从句引导目的状语从句的从属连词有:so that, in order that, lest, in case, for fear that 。例如:They climbed to the top of the building in order that they could get a bird’s-eye view of the city.
Ask her to hurry up with these letters so that I can sign them.
so that 和in order that 的区别:so that 更常用,in order that 更正式。so that 引导的从句一般置于句末,而in order that 引导的从句既可置于句首,又可置于句末。例如:
In order that the grass and flowers could bloom again, it was necessary that the rocks should be removed.
She got up early so that she could catch the first bus.
F. 结果状语从句
结果状语从句一般由下列连词引导:so that、so…that、such…that。例如:
He overslept, (so) that he was late for work.
They got such a fright that they dropped the bag and ran away.
It was so cold that we had to cancel the game.
It’s such a good chance that we mustn’t miss it.
(2) so that 既可引导目的状语从句,也可引导结果状语从句。so that 引导目的状语从句时,一般从句动词前会出现can (could) 、may (might) 、shall (should), 而so that 引导的结果状语从句表示客观事实,不会出现上述词语。引导结果状语从句的so that 前常有逗号,表示强调。so that 引导的目的状语从句可置于句首,而so that 引导的结果状语从句只能置于句末。例如:
He left early so that he could catch the train.
他早早动身,以便能赶上车。(目的)
He left early, so that he caught the train.
他早早动身,赶上了火车。(结果)
G. 方式状语从句
引导方式状语从句的从属连词有as、as if (though)、the way、how。例如:
He made some changes as you had suggested.
She was behaving as if (though) she hadn’t grown up.
三、例题
1. It was not such a good meal ______ she had expected.
A. as
B. what
C. than
D. like
2. ______ I admit that the problems are difficult, I don’t agree that they can’t be solved.
A. Suppose
B. Because
C. While
D. Until
3. ______ little you may like it, old age comes to most of us.
A. So
B. Since
C. However
D. Despite
4. She didn’t break the bad news to her mother ______ that she might break down.
A. so
B. for fear
C. in order
D. because
5. I’d like to warn you ______ was said here must be kept secret.
A. whatever
B. that
C. whom
D. which
6. I don’t care ______.
A. if or not he will win
B. whether or if he will win
C. whether he will not win
D. whether he will win or lose
7. She was late again, ______ was annoying.
A. what
B. who
C. that
D. which
8. The reason ______ I’m writing is to tell you about my examination results.
A. because
B. as
C. why
D. for
9. The tree, the branches ______ are almost bare, is a very old one.
A. whose
B. in which
C. of which
D. which
10. He will never forget the days ______ he spent with his grandma.
A. that
B. when
C. where
D. on which
11. Advertising is distinguished from other forms of communication ______ the advertiser
pays for the message to be delivered.
A. in that
B. in which
C. in order that
D. on the way
12. An old friend from abroad, ______ I was expecting to stay with me, telephoned from the airport.
A. that
B. which
C. whom
D. who
13. ______ I had done it, I knew I had made a mistake.
A. Direct
B. Directly
C. Moment
D. Constant
14. ______ a month ago, we had neither instruments nor a director.
A. Till
B. For
C. Until
D. To
A. because
B. which
C. that
D. where
16. ______ the formation of the sun, the planets, and other stars began with the condensation of an interstellar gas cloud.
A. Believing that
B. To believe that
C. The belief that
D. It is believed that
17. ______ is obvious.
A. That things will improve
B. What things will improve
C. Things will improve
D. If things will improve
18. My idea is ______.
A. that you should take this matter into consideration
B. If you should take this matter into consideration
C. what you should take this matter into consideration
D. which you should take this matter into consideration
19. He put forward the suggestion ______ the matter be brought up at the next meeting.
A. which
B. that
C. what
D. whether
20. The question is ______ we should go or not.
A. whether
B. which
C. that
D. what
21. They discussed ______ they should close the shop.
A. what
B. if
C. whether
D. which
22. Do you think ______ I should attend the meeting?
A. if
B. whether
C. that
D. what
23. Do you doubt ______ I believe you?
A. that
B. which
C. who
D. if
24. Human beings are superior to animals ______ they can use language as a tool to communicate.
A. lest
B. for that
C. in which
D. in that
25. Don’t put off till tomorrow ______ you can do today.
A. that
B. what
C. when
D. what
26. ______ told you to quit smoking is quite right.
A. Whoever
B. Whichever
C. That
D. What
27. What ______ would happen if the director knew you felt that way?
A. do you suppose
B. will you suppose
C. you suppose
D. you would suppose
28. It was quite by accident that Harry discovered that a man ______ was living in London.
A. who he had been friendly with when a student
B. whom he been friendly with when a student
C. whom he had been friendly as a student
D. with whom he had been friendly as a student
29. Dr. Fordhan still talks like the man ______ he was ten years ago.
A. that
B. who
C. what
D. whose
30. He talked brilliantly of the man and the books ______ interested him.
A. what
B. that
C. whom
D. whose
31. The monument is all ______ remains of the ancient city.
A. what
B. that
C. which
D. who
32. The Great Wall is said to be the only man-made thing ______ can be seen from the moon.
A. that
B. which
C. what
D. who
33. Shanghai is one of the most important financial centers ______ I have known.
34. He tried to stand on his hands for minutes, ______ is rather a difficult thing to do.
A. which
B. what
C. that
D. for which
35. The two things ______ they felt very proud were Jim’s gold watch and Della’s hair.
A. about which
B. of which
C. in that
D. for which
36. ______ he realized, I was very useful to him.
A. Which
B. As
C. Although
D. Since
37. We find such shrubs ______ will best stand up to (抵御)hard weather.
A. which
B. as
C. what
D. who
38. We are facing the same problems ______ we did years ago.
A. which
B. as
C. what
D. that
39. Let’s go and have a look at the house ______ roof has been blown off.
A. that
B. that
C. whose
D. which
40. He mentioned a book ______ the title has shipped my memory.
A. of which
B. for which
C. about which
D. in which
41. The reason ______ I’m writing is to tell you about a party on Saturday.
A. because
B. why
C. for
D. as
42. The time will come ______ man can fly to outer space freely.
A. when
B. where
C. whether
D. what
43. This is the place ______ we once lived.
A. what
B. whether
C. where
D. when
44. The policemen went into action ______ they heard the alarm.
A. promptly
B. presently
C. quickly
D. directly
45. We were about to go out ______ it began to rain.
A. when
B. while
C. as
D. since
46. Earthworms occur ______ adequate moisture and food and the necessary soil conditions are found.
A. and
B. whenever
C. however
D. wherever
47. The ship changed its course ______ there was a storm.
A. on the account of
B. due to
C. because of
D. because
48. “Was your sweater expensive?”“______ that it is handmade, the price seems reasonable.”
A. In view of
B. Since
C. Considering
D. Because
49. Take an umbrella ______ it rains.
A. in any case
B. in case
C. because
D. for
50. The pilot had radioed the airport ______ those arrangements could be made.
A. so as that
B. in order that
C. providing
D. as to
A. as
B. what
C. than
D. like
2. ______ I admit that the problems are difficult, I don’t agree that they can’t be solved.
A. Suppose
B. Because
C. While
D. Until
3. ______ little you may like it, old age comes to most of us.
A. So
B. Since
C. However
D. Despite
4. She didn’t break the bad news to her mother ______ that she might break down.
A. so
B. for fear
C. in order
D. because
5. I’d like to warn you ______ was said here must be kept secret.
A. whatever
B. that
C. whom
D. which
6. I don’t care ______.
A. if or not he will win
B. whether or if he will win
7. She was late again, ______ was annoying.
A. what
B. who
C. that
D. which
8. The reason ______ I’m writing is to tell you about my examination results.
A. because
B. as
C. why
D. for
9. The tree, the branches ______ are almost bare, is a very old one.
A. whose
B. in which
C. of which
D. which
10. He will never forget the days ______ he spent with his grandma.
A. that
B. when
C. where
D. on which
11. Advertising is distinguished from other forms of communication ______ the advertiser
pays for the message to be delivered.
A. in that
B. in which
C. in order that
D. on the way
12. An old friend from abroad, ______ I was expecting to stay with me, telephoned from the airport.
A. that
B. which
C. whom
D. who
13. ______ I had done it, I knew I had made a mistake.
A. Direct
B. Directly
C. Moment
D. Constant
14. ______ a month ago, we had neither instruments nor a director.
A. Till
B. For
C. Until
D. To
15. I’m going to spend the winter vacation in Shanghai, ______ I have relatives.
A. because
B. which
C. that
D. where
16. ______ the formation of the sun, the planets, and other stars began with the condensation of an interstellar gas cloud.
A. Believing that
B. To believe that
C. The belief that
D. It is believed that
17. ______ is obvious.
A. That things will improve
B. What things will improve
C. Things will improve
D. If things will improve
18. My idea is ______.
A. that you should take this matter into consideration
B. If you should take this matter into consideration
C. what you should take this matter into consideration
D. which you should take this matter into consideration
19. He put forward the suggestion ______ the matter be brought up at the next meeting.
A. which
B. that
C. what
D. whether
20. The question is ______ we should go or not.
A. whether
B. which
C. that
D. what
21. They discussed ______ they should close the shop.
A. what
B. if
C. whether
D. which
22. Do you think ______ I should attend the meeting?
A. if
B. whether
C. that
D. what
23. Do you doubt ______ I believe you?
A. that
B. which
C. who
D. if
24. Human beings are superior to animals ______ they can use language as a tool to communicate.
A. lest
B. for that
C. in which
D. in that
25. Don’t put off till tomorrow ______ you can do today.
A. that
B. what
C. when
D. what
26. ______ told you to quit smoking is quite right.
27. What ______ would happen if the director knew you felt that way?
A. do you suppose
B. will you suppose
C. you suppose
D. you would suppose
28. It was quite by accident that Harry discovered that a man ______ was living in London.
A. who he had been friendly with when a student
B. whom he been friendly with when a student
C. whom he had been friendly as a student
D. with whom he had been friendly as a student
29. Dr. Fordhan still talks like the man ______ he was ten years ago.
A. that
B. who
C. what
D. whose
30. He talked brilliantly of the man and the books ______ interested him.
A. what
B. that
C. whom
D. whose
31. The monument is all ______ remains of the ancient city.
A. what
B. that
C. which
D. who
32. The Great Wall is said to be the only man-made thing ______ can be seen from the moon.
A. that
B. which
C. what
D. who
33. Shanghai is one of the most important financial centers ______ I have known.
A. what
B. that
C. which
D. for which
34. He tried to stand on his hands for minutes, ______ is rather a difficult thing to do.
A. which
B. what
C. that
D. for which
35. The two things ______ they felt very proud were Jim’s gold watch and Della’s hair.
A. about which
B. of which
C. in that
D. for which
36. ______ he realized, I was very useful to him.
A. Which
B. As
C. Although
D. Since
37. We find such shrubs ______ will best stand up to (抵御)hard weather.
A. which
B. as
C. what
D. who
38. We are facing the same problems ______ we did years ago.
A. which
B. as
C. what
D. that
39. Let’s go and have a look at the house ______ roof has been blown off.
A. that
B. that
C. whose
D. which
40. He mentioned a book ______ the title has shipped my memory.
A. of which
B. for which
C. about which
D. in which
41. The reason ______ I’m writing is to tell you about a party on Saturday.
A. because
B. why
C. for
D. as
42. The time will come ______ man can fly to outer space freely.
A. when
B. where
C. whether
D. what
43. This is the place ______ we once lived.
A. what
B. whether
C. where
D. when
44. The policemen went into action ______ they heard the alarm.
A. promptly
B. presently
C. quickly
D. directly
45. We were about to go out ______ it began to rain.
A. when
B. while
C. as
D. since
46. Earthworms occur ______ adequate moisture and food and the necessary soil conditions are found.
A. and
B. whenever
C. however
D. wherever
47. The ship changed its course ______ there was a storm.
48. “Was your sweater expensive?”“______ that it is handmade, the price seems reasonable.”
A. In view of
B. Since
C. Considering
D. Because
49. Take an umbrella ______ it rains.
A. in any case
B. in case
C. because
D. for
50. The pilot had radioed the airport ______ those arrangements could be made.
A. so as that
B. in order that
C. providing
D. as to
2. 答案:C
解析:四个选择项都是从属连词,都可引导状语从句。题意:虽然我承认这些问题很难解决,但我不同意这些问题不可解决。
3. 答案:C
解析:解此题时,可将四个选择逐个放入空当处试试哪个最为合适。A 不行, so 如果作为程度副词放到句首,句子要部分倒装。B 排除,D 也排除。despite 是介词,它后面应接名词。C 放入句中正合适,however 引导让步状语从句,相当于no matter how 。
4. 答案:B
解析:从句法上看,D 首先可以排除。A、B、C 均可填入空当处,但从前后意思上判断,只有B 合适。for fear that 作“以免、以防”讲,它引导的从句的动词要求用虚拟式。题意:她没将坏消息透露给母亲,以防她精神崩溃。
5. 答案:A
解析:根据空当后谓语形式可推知:空当后一定有一个从句,而且从句的谓语部分为must be kept secret 。而前面的部分为从句的主语。这部分中又有动词的谓语形式,因此它一定是一个有主语的从句。可排除关系代词who 和which;因空当部分在主语从句中作主语,又可排除that (that 引导名词性从句时在从句中不充当任何成分)。whatever 正合适,它可以引导名词性从句。
6. 答案:D
解析:此题考whether 和if 作为从属连词引导宾语从句的区别。whether 可以和or (not) 连用,而if 不可以。据此,即可做出正确选择D。
7. 答案:D
解析:此题空当前为一个完整的主谓结构,空当后出现动词的谓语形式,四个选择项又无并列连词,因此判定逗号后为一个从句。根据空当前后内容判断,逗号后为一个非限定性定语从句,从句的先行词为整个句子。
8. 答案:C
解析:reason 后接从句,说明具体内容,只用why。因此即可将A、B、D 排除。本题中的why 从句可以被视为一个定语从句,也可被视为是一个同位语从句。
9. 答案:C
解析:根据空当前后内容可推知题意:那棵树枝几乎光秃的树是一棵很老的树。逗号隔开的是一个非限性定语从句,空当处应填关系词。whose 不行,因它一般修饰名词。B、C、D 的区别在于介词。因树枝和树为所属关系,所以选C。the branches of which 也可用whose branches 代替。
10. 答案:B
解析:如先行词为表示时间的名词,如time 、day 等,定语从句应用关系副词when 引导。此题便是一例。
11. 答案:A
解析:in that 可引导原因状语从句,对前面的内容加以解释和说明,可译为“在于”、“因为”。B、C、D 不合题意,均可排除。
12. 答案:C
解析:根据空当前后内容可推知:空当处缺少一个关系代词引导非限定性定语从句,此关系代词指人,在从句中作宾语。A、
B、C、D 中,只有whom 合适。that 不可引导非限定性定语从句,因此C 为正确选择。
13. 答案:B
解析:某些副词也可以用作从属连词,引导时间状语从句,表示“一??就??”。这类副词有:instantly, immediately, directly 。某些表示时间的名词加上定冠词the,也可以起连词的作用,引导时间状语从句,译为“一??就??”,如:the moment, the time, the second 。D 因缺少the, 故排除;A 为形容词,不可引导状语从句。正确选择为B。
解析:此题考not…until 的一种变化形式。注意till 和until 的区别:until 可置于句首,而till 不可置于句首。因此正确选择为C。
15. 答案:D
解析:如先行词为表示地点的名词,其后的定语从句一般用where 引导。从空当前后部分的内容推知,逗号后为一个非限定性定语从句。因先行词表示地点,因此D 为正确选择。
16. 答案:D
解析:that 在引导主语从句时常采用it is + 形容词/名词/分词+ that 从句的句型,即由it 作形式主语,而把主语从句放在句子后半部分。
17. 答案:A
解析:that 引导的主语从句位于句首时,that 不能省略。
18. 答案:A
解析:that 在引导表语从句表示陈述时,that 不能省略。
19. 答案:B
解析:此句中that 引导的是同位语从句,用来补充说明名词suggestion 。需要特别注意的是that 在引导同位语从句及其他名词性从句时,只起单纯的连接作用,不在从句中充当任何成分。它一般置于抽象名词之后,如:belief, conviction doubt, explanation, fact, fear, feeling, guarantee, hope, idea, indication, message, news, opinion, order, proof, rumour, suggestion, thought wish, word 等。
20. 答案:A
解析:此句中whether 用于引导表语从句,并与or not 连用。whether 还可以引导主语从句,宾语从句,同位语从句。if 只能引导宾语从句(不包括介词宾语从句)。
21. 答案:C
解析:尽管if 可引导宾语从句,但在discuss、decide 等动词后通常接whether 引导的宾语从句。
22. 答案:C
解析:do you think 后面不能接whether 或if 从句,而要接that 从句。
23. 答案:D
解析:主句里有doubt (动词形式或名词形式)的否定句、疑问句时,用that 引导名词从句。在其肯定句中用whether 或if 引导名词从句,如:I doubt whether/if he can come.
24. 答案:D
解析:that 引导的从句作介词宾语,常见于in that (在某方面、因为),except that (除了、只是),save that(除了),but that (除了),besides that (除了)结构之中。又如:I can say nothing but that the injured must be sent to hospital at once.
25. 答案:B
解析:引导宾语从句及其他名词性从句时,that 和whether 在从句中不充当成分,而what 和when 要充当成分。what 常在从句中充当主语或宾语。该句中what 在从句中作宾语。
26. 答案:A
解析:此句中,用于引导主语从句的连接词指人,而且在从句中作主语。这时的主语从句相当于带有定语从句作后置修饰的名词词组,即:Anyone who told you to quit smoking is right. 有类似用法的连接词还有:what, whatever, whichever, wherever。
27. 答案:A
解析:do you suppose (guess 、believe 、imagine 、say、think) 结构与含有疑问意义的连接代词、连接副词连用时,连接代词、连接副词应置于句首。形容词性从句即定语从句(attributive clause),也称为关系分句(relative clause),依照其与先行词之间的关系可分为限定性定语从句(restrictive attributive clause )和非限定性定语从句(non-restrictive attributive clause)。用于引导定语从句的关系代词有:who, whom, whose, that, which, as ;关系副词有:where, when, why, how。
28. 答案:D
解析:用来指人并在定语从句中作宾语(包括介词宾语和动词宾语)时,通常选择关系代词whom 。
29. 答案:A
解析:关系代词在定语从句中作表语时,通常用that 指人或物,而且常可省略。
解析:先行词是既指人又指物的并列名词词组时,通常用that 引导定语从句为宜。
31. 答案:B
解析:先行词是all 或其他指物的不定代词(如something 、anything 、nothing 、everything )时,通常用that 引导定语从句,先行词是all(指人)或其他指人的不定代词(anybody 、everybody、nobody )时,既可用that ,也可用who 引导定语从句。
32. 答案:A
解析:先行词前有only 、all、any、every 、no、some、one of、last、next 、very 等修饰词,则关系代词用that。
33. 答案:B
解析:先行词带有最高级修饰语或序数词时,关系代词通常用that。
34. 答案:A
解析:先行词指主句的整个意思时,通常用关系代词which 。
35. 答案:B
解析:关系代词在定语从句中作of 的介词宾语,而且介词of 前置时,须用which 引导定语从句。句中的形容词proud 与of 搭配,后跟宾语。
36. 答案:B
解析:as 可作关系代词,引导非限制性定语从句。它的位置比较灵活,可出现在句尾,也可以在句首或句中。which 引导定语从句时位置比较固定,通常位于句尾,而不可以移至句首。
37. 答案:B
解析:as 可在“such…as”、“the same…as ”和“as…as”等结构中作关系代词,引导定语从句。在“such…as”结构中,as 有时用that 替换。
38. 答案:B
解析:the same as 是固定用法。as 在此句中是关系代词。
39. 答案:C
解析:能在定语从句中表示所有关系,作定语用的关系代词是whose (既可指人,也可指物)。
40. 答案:A
解析:除了关系代词whose 可表示所有关系以外,还可借助of which 结构表示所有关系。
41. 答案:B
解析:当先行词是reason 时,用关系副词why 引导定语从句,它在从句中用作状语。
42. 答案:A
解析:当先行词是时间名词,而且关联词在定语从句中作时间状语时,选用关系副词when 引导定语从句。但要特别注意的是,若关联词不在从句中作时间状语,而是作宾语等成分,这时尽管先行词是时间名词,关联词也要选用关系代词,如:This is the day which/that I’ll remember forever.
43. 答案:C
解析:由where 引导的定语从句的先行词通常是表示地点的词,而且where 在定语从句中作地点状语,如关联词在从句中作宾语,则应用which ,如:This is the place which we visited last year.
44. 答案:D
解析:directly 偶尔用作从属连词,意为“一??就??”,用来引导时间状语从句。其他三个选项均为副词。用于引导时间状语从句的从属连词还有:after, as before, since, ever since, till, until, when, whenever, while, whenever, as soon as, no sooner…than, hardly/scarcely/barely…when, immediately, instantly, every time, the moment, the minute 。
45. 答案:A
解析:当主句里有was/were about to do 时,when 引导时间状语从句是递进的含义(此时、那时),表示没有料到的事情。
46. 答案:D
解析:此句空白处需填入一个从属连词,而且从句是表示地点的状语从句,所以选D。可用来引导地点状语从句的从属连词还有where 。
47. 答案:D
considering that。
48. 答案:C
解析:本句中的considering that 可理解为短语连词,表示原因。
49. 答案:B
解析:此句中in case 作从属连词,引导表示目的的状语从句。可引导此类状语从句的连接词还有:that, so that, in order that, for fear that (以免),in case (以防),lest(以免)。
50. 答案:B
解析:in order that 是短语连词,表示目的。
相关阅读:同等学力英语复习资料
同等学力成绩查询
2013年同等学力考试报名
2014年同等学力完型填空讲义 一、考试大纲要求及完型填空考查内容 ?本部分共设10题,每题1分,考试时间为10分钟。本部分在一篇难度适中的短文中设置10个空白,每个空白给出4个备选答案,要求考生 从所给备选答案中选出一个最佳答案,使短文完整。 完型填空主要测验学生的语言综合运用能力,包括基础知识的掌握和运用, 对整个文章逻辑联系的理解,在情景中辨析词义的能力以及词组短语搭配的使用 能力,这是大部分考生认为难度最大的考查项目。归根结底,完型填空的题目就是在基本的语法、词汇考点的基础上,再加上阅读的上下穿梭的逻辑能力,所以说完型填空考题是以一合三的考法。 ?重点考查词汇、逻辑关系 二、考点: 1.语法题 (1)语法的2个考点 考点一从句(重点) 考点二非谓语动词——动词-ing形式和-ed分词(次重点) (2)连词的使用方法(语法衔接题) 2.词汇题 (1)简单的同义词、近义词辨析 (2)语义的衔接技巧 3.固定搭配 三、完形填空答题技巧 1. 重视首句,把握开篇 完形填空一般无标题,首句不留空白,是完整的一句。细读此句可以判断文章体裁,预测全文大意和主旨。读懂首句可以帮助建立正确的思维导向,避免误入歧途,对理解全文起重要的作用。 2. 阅读全文,掌握大意 速读全文要一气呵成,尽管有空格,生词或不明白的地方,仍要快速读下去,不 要急于看选项。一遍读不懂可以再迅速读一遍,直到明了大意(who, when, where, what),掌握梗概,总体把握文章内容,结构,时态,语态变化,情节的展开, 结果的形成,然后答题。 3. 前后照应,灵活答题 (1)择优法 (2)排除法 对于一时难以确定的答案,可按空格位置,从语法结构,上下文意,习惯用法, 词义辨析等方面,对选项逐个分析试填。此时,“瞻前顾后”是必要的:即先读所填句,回顾上一句,兼顾下一句。如果一句中有两处填空,要“双管齐下”,在两处同时试填,然后通读全句,确定答案。 4.识别短语注意搭配
先讲倒装 一.概念: 英语句子通常有两种语序:一种主语在前,谓语在后,称为自然语序,另一种谓语在前,主语在后,称为倒装语序。 二.相关知识点 按“主语+ 谓语”这种顺序排列的句子是陈述语序。如果排列顺序变为“谓语(或谓语一部分)+主语”,就是倒装。 倒装句分为: 完全倒装:整个谓语移至主语前面叫完全倒装。 部分倒装:只把助动词、系动词或情态动词放在主语之前叫部分倒装。 1. 当以there, here, out , in , up , down, away 等副词开头的句子,为了起到强调的作用,可构成倒装句,只把副词放在句首,主语和谓语位置调换,不加助动词。 Our teacher came in. ——>> In came our teacher. 这种倒装要求:主语必须是名词。主语是人称代词时,主语和谓语语序不变。 如 Here it is. A way he went. 这类倒装句式一般只用一般现在时和一般过去时。 Here comes the bus. Out rushed the boys. 2. how, then, just, often 表示时间的副词放在句首,可构成倒装句,只把副词放在句首,主 语和谓语位置调换,不加助动词。 Then came 8 years of the Anti -Japanese W ar. 3. 表地点状语的介词短语放在句首,要用倒装句式,以示强调。这种倒装句也是主谓直接调换位置,不加助动词did, does,do. Under a big tree ___D_____, half asleep. A. did sat a fat man B. a fat man sat C. did a fat man sat D. sat a fat man 4. there放在句首时,要用倒装句式。 在“there + be”结构中的谓语动词有时不用be , 而用表示类似“存在”观念的其他不及物动 词。如:live, stand, come, lie, flow, enter, rise 和appear等。 There came shouts for help from the river. There lies a large wheat field in front of the house. Many years ago there lived an old man in the wooden house. In front of the tower flews a stream. 5. so + 动词+主语 neither/ nor + 动词+主语 表示两人的同样一个情况时,只能表示一件事,即上、下句所使用的动词、时态要一 致。否则要用so it is with… You can ride a bike. So can I . He has been to Beijing. So have I . The first one isn’t good, neither is the second. His uncle is a worker and has been working in the factory for more than ten years. So it is with his aunt. 6. so+ 形容词/副词that 的结构状语从句可以用正常语序表示,也可以把so+形容词/副词放于句首构成倒装。句型如下: so +形容词/副词+be/助动词/情态动词that +从句。 Light travels so fast that it is difficult for us to imagine its speed. = So fast does light travel that it is difficult for us to imagine its speed. So easy was the work that t
高中英语倒装句 倒装句分为全部倒装和部分倒装 1全部倒装全部倒装是只将句子中的谓语动词全部置于主语之前。此结构通常只用于一般现在时和一般过去时。常见的结构有:1)here, there, now, then, thus等副词置于句首, 谓语动词常用be, come, go, lie, run等表示来去或状态的动词。例如:Then came the chairman. 那时总裁来了。Here is your letter. 你的信。 2). up,down,out,away,in , off, ahead放于句首Up jumped the cat and caught the mouse. Ahead sat an old woman. 3)表示地点,时间,方向等的介词短语放在句首时例如:After the head walked a group of workers. 4.“作表语的现在分词/过去分词/形容词+系动词+主语”形式的完全倒装 Seated in the front were the guests. 注意:上述全部倒装的句型结构的主语必须是名词,如果主语是人称代词则不能完全倒装。例如: Here he comes. 他来了。Away they went. 他们走开了。 2部分倒装 部分倒装是指将谓语的一部分如助动词或情态倒装至主语之前。如果句子的谓语没有助动词或情态动词,则需添加助动词do, does或did,并将其置于主语之前。 1. 句首为否定或半否定的词语,如no, not, never, seldom, little, hardly, rarely, scarely, in no way, under no circumstance, at no time决不, not until…等。例如: Never have I seen such a performance. 从未见过如此糟糕的表演。 Nowhere will you find the answer to this question. 无论如何你不会找到这个问题的答案的。 Not until the child fell asleep did the mother leave the room. 母亲一直到孩子入睡后离开房间。 当Not until引出主从复合句,主句倒装,从句不倒装。注意:如否定词不在句首不倒装。例如: The mother didn\'t leave the room until the child fell asleep. 典型例题 1)---Why can\'t I smoke here? ----At no time___ in the meeting-room A. is smoking permitted B.smoking is permitted C. smoking is it permitted D.does smoking permit 2)Not until the early years of the 19th century ___ what heat is. A. man did know B. man know C. didn\'t man know D. did man know 2.Not only…but also前面倒装,后面不倒装 Not only did he refuse the gift, he also severely criticized the sender. 他没有收下礼物,还狠狠批评了送礼的人。 3.Hardly/Scarcely…when, No sooner…than等,要倒装。 Hardly had she gone out when a student came to visit her. No sooner had she gone out than a student came to visit her. 典型例题No sooner___ than it began to rain heavily. A. the game began B.has the game begun C. did the game begin D.had the game begun 4so, neither, nor作部分倒装 so/neither/nor+be/can(should/will/could…..)/do(did/does)+sb表示\"也\"、\"也不\" 的句子要部分倒装。例如: 典型例题---Do you know Jim quarrelled with his brother? ---I don\'t know, _____. A. nor don\'t I care B. nor do I care C. I don\'t care neither D. I don\'t care also 注意:当so引出的句子用以对上文内容加以证实或肯定时,不可用倒装结构。意为\"的确如此\"。例如: Tom asked me to go to play football and so I did. ---It\'s raining hard.---So it is. 5 only在句首后接状语用总分倒装。例如: Only in this way can you learn English well. 只有这样,你才能学好英语。 如果句子为主从复合句,则主句倒装,从句不倒装。例如: Only when he is seriously ill does he ever stay in bed. 病得狠重时,他才卧床休息。 注意:如果only后的词组不是状语,不需倒装。
2013年同等学力英语语法专项复习:虚拟语气 一、总述 虚拟语气(subjunctive mood )用来表示说话人的愿望、请求、意图、建议、怀疑、设想等未能或不可能成为事实的情况,以及在说话人看来实现可能性很小的情况。由于虚拟语气是动词的一种特殊表现形式,因而动词的变化形式体现出虚拟语气所包含的不同含义。虚拟语气用于非真实条件句时的构成如下表所述: 二、重要考点 1. 在非真实条件句中,有时从句的动词所表示的动作和主句的动词所表示的动作并不同时发生,这样的条件句中使用的虚拟式称为混合虚拟式。其构成视具体情况而定。例如: If I had taken my raincoat when I came out this morning, I would not be wet now. If I were you, I wouldn’t have missed the film last night. 2. 引导非真实条件从句的连词if 在正式文体中有时可以省去, were、had、should 等非行为动词这时应提到从句句首。 例如: If I were you, I wouldn’t feel sorry. →Were I you, I wouldn’t feel sorry. 3. 有些句子从表层结构上看是无if 引导的非真实条件句,但从深层意思上看if 是存在的。这种情况下主句动词仍需用虚拟式。这类句子中常出现without (如果没有),but for (要不是),otherwise (否则),but that (若不,后接一从句)等词或词组。例如: But for your help, they couldn’t have succeeded. She wasn’t feeling well. Otherwise,she wouldn’t have left the meeting so early. 4. 在It is + 形容词 + that 从句的句型中,that 引导的主语从句中的谓语动词采用should + 动词原形形式,其中should 常省略。可用于此句型的形容词还有:absurd, advisable, better, best, desirable, (un)fair, fortunate, good, imperative, important, incredible, just, natural, (un) necessary, odd, pleasant, possible, preferable, right, ridiculous, sad, silly, unusual, urgent, vital, wrong 等,表示必要、应该、建议、要求、惊讶、不相信等含义。例如: It’s necessary that we (should) set out at once. It’s proposed that a committee (should) be set up to look into the matter. 5. 具有“提议、建议、请求、命令”等含义的动词所带的从句(包括宾语从句和主语从句)中,谓语动词用should + 动 词原形形式。美国英语多用动词原形,英国英语多用should + 动词原形。有相同用法的动词还有:ask, advise, agree, arrange, beg, command, decide, demand, desire, determine, direct, instruct, insist, intend, maintain, move, order, persuade, pray, propose, recommend, request, require, stipulate, suggest, tell, urge。如: I suggest that we (should) go camping tomorrow. He insisted that our laboratory reports (should) be handed in
-高二基础语法专题 虚拟语气基础练习60题 1. The boy acted ____ he had never lived in Canada before. A. as though B. even if C. as D. since 2. ____ to the doctor right away, he might have been alive. A. If he went B. Were he gone C. Should he have gone D. Had he gone 3. If you were older, I ____ you to go there yesterday. A. will allow B. should allow C. would have allowed D. had allowed 4. The secretary suggested that they ____ the men in at once. A. had brought B. should have brought C. brought D. bring 5. I wish I ____ able to tell him all about it last night. A. was B. were C. had been D. should be 6. If we ____ here ten minutes earlier, we ___ the bus. A. arrived/would catch B. arrived/would have caught C. had arrived/had caught D. had arrived/would have caught 7. If I ____ more time, I would have gone with him. A. had B. had had C. have had D. would have 8. He was very busy yesterday, otherwise he ____ to the meeting. A. would come B. came C. would have come D. had come 9. The Jade Emperor ordered that the Monkey King _____ right away. A. would be arrested B. must be arrested C. be arrested D. had to be arrested 10. Jane’s uncle insisted ____ in this hotel any longer. A. not staying B. not to stay C. that he not stay D. staying not 11. Don’t touch the sleeping tiger. If he woke up, he _____ you. A. would come to B. would come at C. would have come toward D. will come to 12. Without electricity human life _____ quite different today. A. is B. will be C. would have been D. would be 13. How I wish I ____ to repair the watch! I only made it worse. A. had tried B. hadn’t tried C. have tried D. didn’t try 14. He demanded that the laboratory report ___ immediately after the experiment was done. A. was written B. be written C. must be written D. would be written 15. The man insisted that he _____ there. A. should send B. would be sent C. sent D. be sent 16. If he had not gone out in the storm _____. A. he will be alive now B. he would be alive now C. he would have been alive now D. he is alive now 17. If it ___ tomorrow, what would we do? A. rains B. were to rain C. would rain D. rain 18. It is required that you ____ at six. A. will arrive B. arrive C. arrived D. would arrive
倒装句 英语句子的主语通常位于谓语动词之前,这种语序被称为正常语序。但有时出于强调或某种特殊的语法结构的需要,需要将谓语动词放在主语之前,这种语序则叫倒装语序。按倒装的形式,倒装可分为两类,一是完全倒装,二是部分倒装。完全倒装是指全部谓语放在主语之前,部分倒装是指只把助动词、情态动词或be动词放在主语之前,谓语的主体部分仍在主语之后。 一、完全倒装 1. 用于there be 句型。 例:There are many students in the classroom. 原句自然顺序是:Many students are there in the classroom. ★2. 表示地点的here和 there位于句首时,其后用完全倒装形式。这类倒装句的谓语通常是动词be和come, go等表示移动或动态的不及物动词,以及stand, lie, live等表示状态的动词(表示存在)。 例:Here comes the bus. 公共汽车来了。 There goes the last train. 最后一班火车开走了。 There stood a desk against the wall. 靠墙放着一张书桌。 注意:若主语为人称代词,则不倒装。如: Here you are. 这就是你要的东西。(给你。) Here it comes. 它来了。 ★3. 表示方向的副词away, down, in, off, out, over, round, up 等位于句首时,其后用完全倒装语序。这类倒装句的谓语通常表示动态的不及物动词。 Out rushed the puppy. 小狗冲了出去。 Away went the girl. 那个女孩走远了。 Down came the rain and up went the umbrellas. 下雨了,伞都撑起来了。 注:若主语为人称代词,则不能用倒装。如: In he comes. 他走了进来。 Down it came. 它掉了下来。 ★4. 表示时间或顺序的副词now, then 等位于句首时,其后用完全倒装语序。这类倒装句的谓语通常表示动态的不及物动词。如:
在职研究生同等学力申硕英语备考经验汇总 一、复习方法篇 1、如何高效增加词汇量 1)不要背书 大部分人背书都是背了后面忘了前面,正襟危坐几个小时,其实记住的单词没几个,为什么?因为人的瞬时记忆力只能记忆5-7个东西,比如你妈妈叫你去买菜,七样以内你能记住,要是十几样你就得用笔记了。因此背书没用,那怎么办?就是分组背,记一组,测试一组,再记下一组。(刘毅的背单词的书就是按照这个原理来设计的) 2)不要用整段时间来背单词 我看过很多人的每日计划,什么几点到几点是背单词时间。这个没用,你花几个小时光背单词,记忆效率绝对很低,脑袋都木掉,合上书一个字也想不起来。一些英语牛人就一个背单词方法——小卡片。每天没事就拿出来看一下,坚持不懈,效果绝对好。 3)在遗忘临界点复习 有个伟大的艾宾浩斯记忆曲线,非常厉害,只要按照那个曲线在遗忘临界点复习,5次复习就可以终身不忘。可以在第1、2、5、15、30、60天把单词再重复看一遍! 4)语境记忆 背单词绝对不能没有例句,中文的一个词你可以对他有很多种解释,英文也一样,如果没有例句帮你体会单词用法,光背词意在真正阅读的时候一定会抓瞎。(刘毅的背单词的书每个单词都有例句) 5)巧用学习工具 现在科技发达,学习工具很多,巧加利用才能事半功倍。我用的是Nokia N73手机,里面有英汉词典,遇到不懂的单词随时用来查,同时也可以把一些单词作为提示有空的时候拿来看。 6)背记单词必须和做真题结合起来 因为单词必须得放到文章中能够认知才叫记住了单词这样单词的记忆会达到事半功倍的效果。传统的每天只是拿着单词书死记硬背是不科学的也是效率最低的。
在单词有了进步之后,你会发现不管是汉译英还是英译汉都不在害怕。但是前提仍然是,多多练习。熟能生巧,翻译多了,跟好的翻译答案对照之后,你会发现好多“的字结构”“使字结构”“无主句”等等之类的句子其实翻译方法是很有章可循的,翻译多了,你会知道什么情况下用被动结构,什么情况下用强调结构,这些能力的前提是必须得多多练习。 2、疯狂做往年的真题并且做后花长时间认真分析 认真做每年的真题,尤其是一些有考验经验的人推荐的真题。争取三天一套,做的时候要卡着时间。做完后要理科对照着正确答案认真分析。做完一套真题可能只需要三个小时的时间,但是做完之后的分析却需要6个小时。所以按照在职学习人的时间来算,三天做一套真题节奏刚好。即便是你做过一遍之后,答案已经背下来了,也仍然要认认真真地做真题,把真题的阅读理解和完形填空作为精读的材料去认真详细地分析每一个句子,攻下你在真题里碰到的每一个生词。 做真题有几大好处,一是通过反复做真题,你可以记住大纲里80%的单词;二是通过反复做真题,你可以熟悉阅读理解完形填空的文章风格和真题出题思路,到考试的时候才不会不适应,尤其是近5年的试题;三是真题的阅读理解其实就是很好很地道的说明文和议论文,熟读之后你会发现里面有好多很精美很地道的句子,拿来用到自己的作文里非常的出彩。三是通过精读真题的阅读理解和完形填空,基本上你第二卷的英译汉已经不成问题了。(第二卷的作文和英译汉通过做真题完全可以搞定了)。 3、针对09新大纲复习对策 今年的英语考试大纲试卷一考试内容与以往相比,去掉了辨识错误部分,保留了会话技能、词汇、阅读理解、综合填空4部分内容。也就是说在考试时间不变的情况下,考试内容减少,试卷难度也就相应降低,对考生而言是好消息。以往,辨错题是试卷中唯一直接考查语法结构题目,新大纲调整后,考生就不需要记忆细小语法知识,更利于考生的英语复习。 专家认为辨识错误部分的5分可能会加到阅读理解部分或词汇部分。根据新大纲中的样题看,2009年英语考试阅读理解部分分值预计会增加,由25分变成30分,题目数量也相应从25个增至30个。同时,新大纲删除500多个旧词增加1220多个新词和50个常用词组。词汇量要求提高预示着今年的英语水平考试难度可能比以往会加大。 面对新大纲词汇量增加的问题,考生可以采用像滚雪球一样的方法记忆。在复习词汇时,首先从掌握大学英语四六级考试要求的词汇入手,每天定时定量地完成背诵内容,第二天,将学过的单词默写几遍,以加深印象。这个阶段大概需要3个月的时间,然后进入背诵考研词汇阶段,考生可选择一本考研核心词汇作为辅助记忆参考书。但是不要认为单词一遍就记住了,记单词的关键是重复记忆。按照记忆曲线,记忆7次一般就差不多记住了,但是还有很少的一部分单词不能记住。他在记完7次以后,把仍然记不住的单词抄在卡片上。正面写着英文单词、词性、音标;背面写着意思、助记法等。
倒装句 倒装的两种考法: 1. 放在单项选择题中,考查考生的倒装语法知识是否熟练掌握; 2. 放在完形填空和阅读理解中,设置理解障碍。 倒装的两种形式: 1. 完全倒装:将整个谓语动词提到主语前。 2. 部分倒装:即半倒装,将谓语的一部分即助动词提到主语前。 一、完全倒装 1】表方位的副词here, there 或out, in, up, down, away, off, over, back等标志词放在句首,句子用完全倒装。 【翻译句子】 (1)车来了。Here comes the bus. (2)铃响了。There goes the bell. (3)孩子们冲出来了。Out rushed the children. (4)那个男孩离开了。Away went the boy. 【疑难】 Here it is. In she came. Away he went. 【疑难剖析】当主语是人称代词时,主谓语序不变。 2】地点状语放在句首且谓语动词为come, live, lie, go, sit, stand等时用完全倒装。【完成例句】 (5)河的南面有一家小工厂。In south of the river lies a small factory. (6)山谷里传来一声喊叫。From the valley came a cry. 3】such, the following等放句首时,句子要完全倒装。 【翻译句子】 (7)Such are the facts. 情况就是如此。 (8)生活就是这样。Such is life. (9)The following is the answer to the question. 这个问题的答案如下。 4】There lie / exist / stand / live +主语+…是there be 句型的变式 【翻译句子】 (10)山顶上有一幢高楼。There is a tall building on the top of the mountain. (11)山顶上耸立着一座古塔。There stands an ancient tower on the top of the mountain. 5】“表语+系动词+主语”的结构。 【例句观察】 Present at the party were Mr. Green and many other guests. 出席晚会的有格林先生,还有一些别的宾客。 Seated on the ground are a group of young men. 坐在地上的是一群年轻人。 【注意】此时,主语较长,可还原为正常语序即:主+系动词+表语。 二、部分倒装
倒装句 概念:用以表示一定句子结构的需要和强调某一句子成分的需要,分为完全倒装和部分倒装。 一.完全倒装:句子中的谓语动词全部置于主语之前。此结构通常只用与一般现在时和一般过去时。 1.以here, there, now, then等副词或out, in, up, down, away等表示运动方向的副词或地点状语置于句首以示强调,句子要全部倒装,谓语动词常用come,go, be, lie,run,rush等。 2.表示地点的介词短语位于句首时 A beautiful lake lies at the foot of the hill At the foot of the hill lies a beautiful lake. 注意:在上述句子中,如果主语为人称代词,则主、谓不需要倒装。 In he came and back he went again. Away he went . 二.部分倒装:be/助动词/情态动词提前到主语的前面。 Is am are was were(be动词)do does did(助动词)can could would may will might(情态动词)等1.only所修饰的副词、介词短语或状语从句放在句首时, 要进行部分倒装. Only then did I realize the importance of learning English. Only after he came back was I able to see him. 注:only修饰主语,仍用自然语序,如:Only socialism can save China. I seldom go to the cinema. 倒装:Seldom do I go to the cinema. 我很少去看电影. I have never seen such a performance. 倒装:Never have I seen such a performance. 我从来没有看过这样的表演. 2.否定副词及介词短语的否定词位于句首时。 高考常考的这类词或词语有:never , not, seldom, hardly, little, nowhere, by no means, in no time等。 3.not until 引导的从句位于句首引起的主句部分倒装 He didn’t finish his homework until his mother came back. 倒装:Not until his mother came back did he finish his homework. 直到他的妈妈回来,他才完成作业。 The mother didn’t leave the room until the child fell asleep. 倒装:Not until the child fell asleep did the mother leave the room. 等到孩子睡着了,妈妈才离开房间. 注意:当Not until引出主从复合句,主句倒装,从句不倒装。 4、as/ though (虽然,尽管)引导的让步状语从句 名词\形容词\副词\分词+as\though+主语+其他 Although I am ugly, I am gentle. 倒装:Ugly as I am, I am gentle. Though he is a child, he has to make a living. 倒装:Child as he is, he has to make a living. 注意:从句的表语是名词,其名词前不加任何冠词
高中英语倒装句语法知识汇总 一.概念: 英语句子通常有两种语序:一种主语在前,谓语在后,称为自然语序,另一种谓语在前,主语在后,称为倒装语序。 二.相关知识点精讲 按“主语+ 谓语” 这种顺序排列的句子是陈述语序。如果排列顺序变为“谓语(或谓语一部分)+主语”,就是倒装。倒装句分为: 完全倒装:整个谓语移至主语前面叫完全倒装。 部分倒装:只把助动词、系动词或情态动词放在主语之前叫部分倒装。 1. 当以there, here, out , in , up , down, away 等副词开头的句子,为了起到强调的作用,可构成倒装句,只把副词放在句首,主语和谓语位置调换,不加助动词。 Our teacher came in. In came our teacher. 这种倒装要求:主语必须是名词。主语是人称代词时,主语和谓语语序不变。 Here it is. Away he went. 这类倒装句式一般只用一般现在时和一般过去时。 Here comes the bus. Out rushed the boys. 2. how, then, just, often 表示时间的副词放在句首,可构成倒装句,只把副词放在句首,主语和谓语位置调换,不加助动词。 Then came 8 years of the Anti Japanese War. 3. 表地点状语的介词短语放在句首,要用倒装句式,以示强调。 这种倒装句也是主谓直接调换位置,不加助动词did, does或do. Under a big tree ________, half asleep. A. did sat a fat man B. a fat man sat C. did a fat man sat D. sat a fat man 4. there放在句首时,要用倒装句式。 在“there + be”结构中的谓语动词有时不用be , 而用表示类似“存在”观念的其他不及物动词。如:live, stand, come, lie, flow, enter, rise 和appear等。 There came shouts for help from the river. There lies a large wheat field in front of the house. Many years ago there lived an old man in the wooden house. In front of the tower flews a stream. 5. so + 动词+主语 neither/ nor + 动词+主语 表示两人的同样一个情况时,只能表示一件事,即上、下句所使用的动词、时态要一致。 否则要用so it is with… You can ride a bike. So can I . He has been to Beijing. So have I . The first one isn’t good, neither is the second. His uncle is a worker and has been working in the factory for more than ten years. So it is with his aunt. 6. so+ 形容词/副词that 的结构状语从句可以用正常语序表示,也可以把so+形容词/副词放于句首构成倒装。句型如下:so +形容词/副词+be/助动词/情态动词that +从句。 Light travels so fast that it is difficult for us to imagine its speed. = So fast does light travel that it is difficult for us to imagine its speed. So easy was the work that they finished it in a few days. 7. done做形容词在句中做表语时,常把表语放在句首,要用倒装句式。 Gone forever are the days when the Chinese people had to use foreign oil. 8. 否定副词not , never, seldom, nowhere, little , rarely 放于句首时要用倒装句式。 We seldom get up at four in the morning. = Seldom do we get up at four in the morning. Not a single word from him could the enemy drag.
同等学力英语语法总结
同等学力英语比较状语从句 常见引导词:as(同级比较), than(不同程度的比较) 特殊引导词:the more … the more … ; just as …, so…; A is to B what /as X is to Y; no … more than; not A so much as B She is as bad-tempered as her mother. 她和她妈一样脾气暴躁。 The house is three times as big as ours. 这所房子是我们的三倍大。 The more you exercise, the healthier you will be. 越锻炼你就越健康。 Food is to men what oil is to machine. 食物之于人,犹如油之于机器。 同等学力英语让步状语从句 引导让步状语从句的连词和词组:although, though(虽然);even if,even though(即使);as,while(尽管);whether…or(不论……还是);whoever,no matter who(无论谁);
whenever, no matter when(无论何时);however,no matter how(无论怎样);whatever,no matter what(无论什么)等。 (1)although和though都表示“虽然”,但although比though正式,更多用于句首;二者都可与yet,still或nevertheless连用,但不能和but连用: He didn’t stop working though(或although)he was ill. 她虽然病了,但未停止工作。 (2)as引导的让步状语从句要用倒装语序,可用though代替,但比though语气强,被倒装的部分能够是表语、状语和动词原形: Child as(或though)he is, he knows a lot.[表语;名词] 她虽然是个孩子,但懂得很多。 ▲当表语是可数名词单数时,不能加不定冠词a (或an)。 Good as he is, he will never be top of his class.[表语;形容词] 她虽然很好,但她决不会成为班上的尖子。 Hard as(或though)he works, he makes little
同等学力英语比较状语从句 常用引导词:as(同级比较), than(不同程度的比较) 特殊引导词:the more …the more …; just as …, so…; A is to B what /as X is to Y; no …more than; not A so much as B She is as bad-tempered as her mother. 她和她妈一样脾气暴躁。 The house is three times as big as ours. 这所房子是我们的三倍大。 The more you exercise, the healthier you will be. 越锻炼你就越健康。 Food is to men what oil is to machine. 食物之于人,犹如油之于机器。 同等学力英语让步状语从句 引导让步状语从句的连词和词组:although, though(虽然);even if,even though(即使);as,while(尽管);whether…or(不论……还是);whoever,no matter who,however;(无论何时)whenever, no
matter when;(无论谁). no matter how(无论怎样);whatever,no matter what (无论什么)等。 (1)although和though都表示“虽然”,但although 比though正式,更多用于句首;二者都可与yet,still或nevertheless连用,但不能和but连用: He didn't stop working though(或although)he was ill. 他虽然病了,但未停止工作。 (2)as引导的让步状语从句要用倒装语序,可用though代替,但比though语气强,被倒装的部分可以是表语、状语和动词原形: Child as(或though)he is, he knows a lot.[表语;名词] 他虽然是个孩子,但懂得很多。 ▲当表语是可数名词单数时,不能加不定冠词a (或an)。 Good as he is, he will never be top of his class.[表语;形容词] 他虽然很好,但他决不会成为班上的尖子。Hard as(或though)he works, he makes little progress.[状语;副词]