
Corporate Finance, 3e (Berk/DeMarzo)
Chapter 13 Investor Behavior and Capital Market Efficiency
13.1 Competition and Capital Markets
Use the following information to answer the question(s) below.
Assume that the CAPM is a good description of stock price returns. The market expected return is 8% with 12% volatility and the risk-free rate is 3%. New news arrives that does not change any of these numbers, but it does change the expected returns of the following stocks:
1) The expected alpha for Taggart Transcontinental is closest to:
A) -3.00%
B) -1.00%
C) 1.00%
D) 3.00%
Answer: B
Explanation: B) αi = E[r s] - r f - βi(r m - r f), where r f - βi(r m - r f) is the CAPM return
Section: 13.1 Competition and Capital Markets
Skill: Analytical
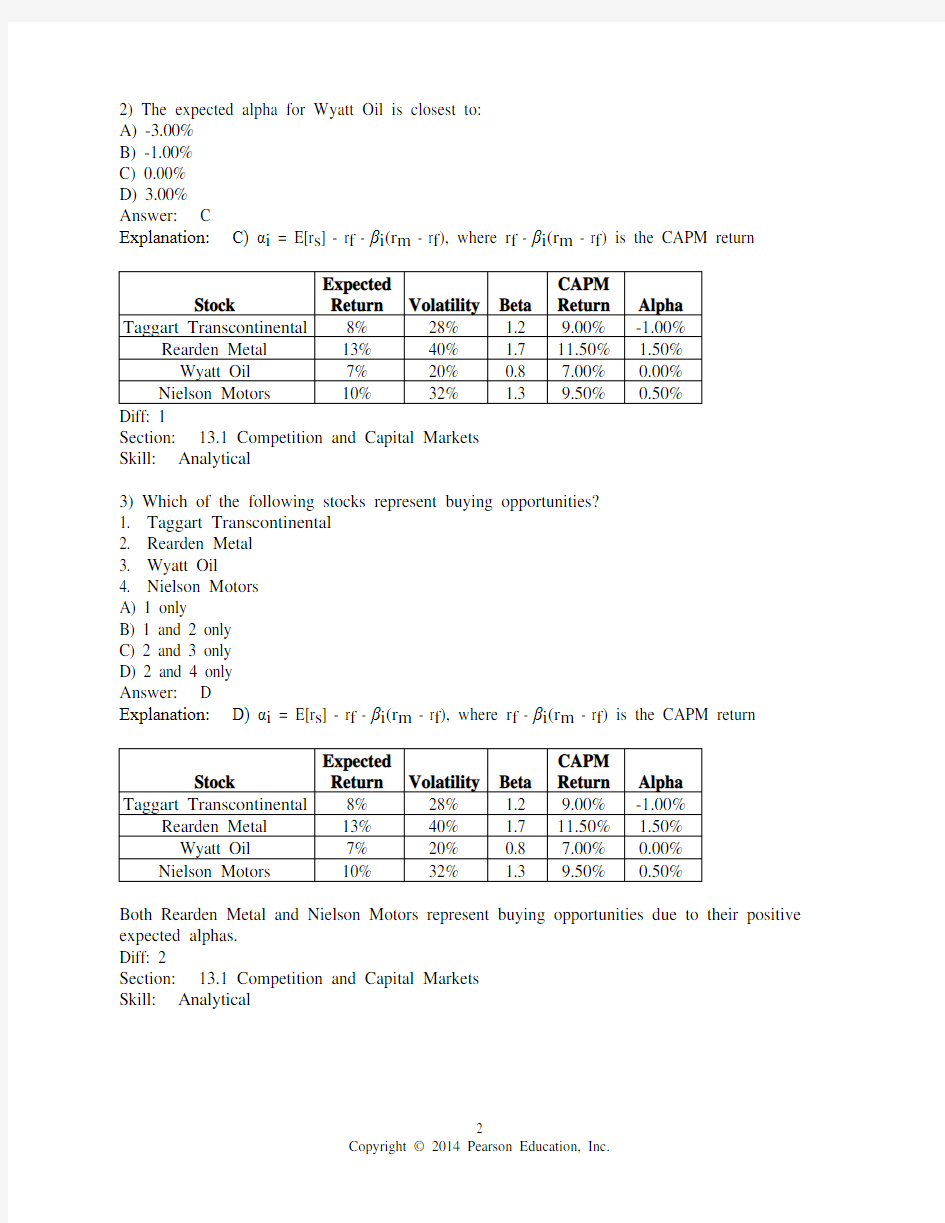
2) The expected alpha for Wyatt Oil is closest to:
A) -3.00%
B) -1.00%
C) 0.00%
D) 3.00%
Answer: C
Explanation: C) αi = E[r s] - r f - βi(r m - r f), where r f - βi(r m - r f) is the CAPM return
Section: 13.1 Competition and Capital Markets
Skill: Analytical
3) Which of the following stocks represent buying opportunities?
1. Taggart Transcontinental
2. Rearden Metal
3. Wyatt Oil
4. Nielson Motors
A) 1 only
B) 1 and 2 only
C) 2 and 3 only
D) 2 and 4 only
Answer: D
Explanation: D) αi = E[r s] - r f - βi(r m - r f), where r f - βi(r m - r f) is the CAPM return
Both Rearden Metal and Nielson Motors represent buying opportunities due to their positive expected alphas.
Diff: 2
Section: 13.1 Competition and Capital Markets
Skill: Analytical
4) Which of the following stocks represent selling opportunities?
1. Taggart Transcontinental
2. Rearden Metal
3. Wyatt Oil
4. Nielson Motors
A) 1 only
B) 1 and 2 only
C) 2 and 3 only
D) 2 and 4 only
Answer: A
Explanation: A) αi = E[r s] - r f - βi(r m - r f), where r f - βi(r m - r f) is the CAPM return
Only Taggart Transcontinental represents a selling opportunities due to its negative expected alpha.
Diff: 2
Section: 13.1 Competition and Capital Markets
Skill: Analytical
5) A stock's alpha is defined as the stock's:
A) expected return minus its required return.
B) expected return minus its actual return.
C) nominal return minus its required return.
D) required return minus its actual return.
Answer: A
Diff: 1
Section: 13.1 Competition and Capital Markets
Skill: Definition
13.2 Information and Rational Expectations
1) When all investors correctly interpret and use their own information, as well as information that can be inferred from market prices or the trades of others, they are said to have:
A) sensation seeking expectations.
B) positive expectations.
C) rational expectations.
D) confident expectations.
Answer: C
Diff: 1
Section: 13.2 Information and Rational Expectations
Skill: Definition
2) The CAPM does not require investors have homogeneous expectations, but rather that they have:
A) rational biases.
B) no biases.
C) heterogenous expectations.
D) rational expectations.
Answer: D
Diff: 1
Section: 13.2 Information and Rational Expectations
Skill: Conceptual
13.3 The Behavior of Individual Investors
1) Investors that suffer from a familiarity bias:
A) prefer not to invest in companies they are familiar with.
B) favor investments in companies they are familiar with.
C) invest in the same stocks that their friends or family recommend.
D) tend to overestimate the precision of their knowledge.
Answer: B
Diff: 1
Section: 13.3 The Behavior of Individual Investors
Skill: Definition
2) The tendency of uninformed individuals to overestimate the precision of their knowledge is known as:
A) overconfidence bias.
B) herd behavior.
C) familiarity bias.
D) disposition bias.
Answer: A
Diff: 1
Section: 13.3 The Behavior of Individual Investors
Skill: Definition
3) If investors have relative wealth concerns, they care most about:
A) the return on their portfolio relative to their overall current wealth.
B) the performance of their portfolio relative to that of their peers.
C) their current portfolio performance relative to their past portfolio performance.
D) the performance of their current wealth relative to their past wealth.
Answer: B
Diff: 1
Section: 13.3 The Behavior of Individual Investors
Skill: Definition
4) An individual's desire for intense risk-taking experiences is known as:
A) phenomenon seeking.
B) herd seeking.
C) sensation seeking.
D) rational expectations seeking.
Answer: C
Diff: 1
Section: 13.3 The Behavior of Individual Investors
Skill: Definition
5) Which of the following is NOT true regarding individual investor behavior?
A) Individual investors fail to diversify their portfolios adequately.
B) A vast majority of individual investors hold fewer than 10 stocks in their portfolio.
C) Employees tend to overinvest in their company's own stock.
D) Individual investors' portfolios consistently outperform the market averages. Answer: D
Diff: 2
Section: 13.3 The Behavior of Individual Investors
Skill: Conceptual
13.4 Systematic Trading Biases
Use the following information to answer the question(s) below.
Consider the price paths of the following stocks over a six-month period:
None of these stocks pay dividends.
1) Assume that you are an investor with the disposition effect and you bought each of these stocks in January. Suppose that it is currently the end of March, which stocks are you most inclined to sell?
1. Taggart Transcontinental
2. Rearden Metal
3. Wyatt Oil
4. Nielson Motors
A) 1 only
B) 1 and 3 only
C) 2 only
D) 2 and 4 only
Answer: B
Explanation: B) With the disposition effect investors are likely to sell winners and hold on to losers, so they would sell the two winners Taggart and Wyatt.
Diff: 1
Section: 13.4 Systematic Trading Biases
Skill: Analytical
stocks in January. Suppose that it is currently the end of March, which stocks are you most inclined to hold?
1. Taggart Transcontinental
2. Rearden Metal
3. Wyatt Oil
4. Nielson Motors
A) 1 only
B) 1 and 3 only
C) 2 only
D) 2 and 4 only
Answer: D
Explanation: D) With the disposition effect investors are likely to sell winners and hold on to losers, so they would hold the two losers Rearden and Nielson.
Diff: 1
Section: 13.4 Systematic Trading Biases
Skill: Analytical
3) Assume that you are an investor with the disposition effect and you bought each of these stocks in January. Suppose that it is currently the end of June, which stocks are you most inclined to sell?
1. Taggart Transcontinental
2. Rearden Metal
3. Wyatt Oil
4. Nielson Motors
A) 1 only
B) 1 and 3 only
C) 2 only
D) 1, 2, and 3 only
Answer: D
Explanation: D) With the disposition effect investors are likely to sell winners and hold on to losers, so they would sell the three winners Taggart, Rearden, and Wyatt.
Diff: 1
Section: 13.4 Systematic Trading Biases
Skill: Analytical
stocks in January. Suppose that it is currently the end of June, which stocks are you most inclined to hold?
1. Taggart Transcontinental
2. Rearden Metal
3. Wyatt Oil
4. Nielson Motors
A) 1 only
B) 4 only
C) 1 and 3 only
D) 2 and 4 only
Answer: B
Explanation: B) With the disposition effect investors are likely to sell winners and hold on to losers, so they would hold the only loser: Nielson Motors.
Diff: 1
Section: 13.4 Systematic Trading Biases
Skill: Analytical
5) If investors believe that others have superior information which they can take advantage of by copying their trades, this can lead to:
A) an informational cascade effect.
B) a disposition effect.
C) a sensation seeking effect.
D) an overconfidence bias.
Answer: A
Diff: 1
Section: 13.4 Systematic Trading Biases
Skill: Definition
6) The tendency to hang on to losers and sell winners is known as the:
A) cascade effect.
B) disposition effect.
C) overconfidence bias.
D) systematic behavior bias.
Answer: B
Diff: 1
Section: 13.4 Systematic Trading Biases
Skill: Definition
7) When investors imitate each other's actions, this is known as ________ behavior.
A) pack
B) flock
C) herd
D) shepherd
Answer: C
Diff: 1
Section: 13.4 Systematic Trading Biases
Skill: Definition
13.5 The Efficiency of the Market Portfolio
Use the following information to answer the question(s) below.
Assume that the economy has three types of people. 20% are fad followers, 75% are passive investors, and 5% are informed traders. The portfolio consisting of all informed traders has a beta of 1.4 and an expected return of 16%. The market has an expected return of 10% and the risk-free rate is 4%.
1) The alpha for the informed investors is closest to:
A) -2.4%
B) -0.9%
C) 0.0%
D) 3.6%
Answer: D
Explanation: D) αi = E[r s] - r f - βi(r m - r f) = 16% - 4% - 1.4(10% - 4%) = 3.6%
Diff: 1
Section: 13.5 The Efficiency of the Market Portfolio
Skill: Analytical
2) The alpha for the passive investors is closest to:
A) -2.4%
B) -0.9%
C) 0.0%
D) 3.6%
Answer: C
Explanation: C) αi = E[r s] - r f - βi(r m - r f) = 10% - 4% - 1.0(10% - 4%) = 0.0%
Diff: 1
Section: 13.5 The Efficiency of the Market Portfolio
Skill: Analytical
3) The expected return for the fad follower's portfolio is closest to:
A) 11.5%
B) 12.4%
C) 13.6%
D) 16.0%
Answer: A
Explanation: A) Since the passive investors are holding the market, the fad followers must be the counter parties to the informed investors. The predicted (by CAPM) return on the portfolio they are trading is:
r i = r f - βi(r m - r f) = 4% - 1.4(10% - 4%) = 12.4%
This return will be split between the informed traders and the fad followers. Therefore:
rp = w FF r FF + w IT r IT = 12.4% = r FF + 16% → r FF = 11.50%
Diff: 3
Section: 13.5 The Efficiency of the Market Portfolio
Skill: Analytical
4) The alpha for the fad follower's portfolio is closest to:
A) -0.9%
B) 0.0%
C) 3.6%
D) 6.0%
Answer: A
Explanation: A) Since the passive investors are holding the market, the fad followers must be the counter parties to the informed investors. The predicted (by CAPM) return on the portfolio they are trading is:
r i = r f - βi(r m - r f) = 4% - 1.4(10% - 4%) = 12.4%
This return will be split between the informed traders and the fad followers. Therefore:
rp = w FF r FF + w IT r IT = 12.4% = r FF + 16% → r FF = 11.50%
αi = E[r s] - r f - βi(r m - r f) = 11.5% - 4% - 1.4(10% - 4%) = -0.9%
Diff: 1
Section: 13.5 The Efficiency of the Market Portfolio
Skill: Analytical
Use the following information to answer the question(s) below.
John Galt is a mutual fund manager at Atlas Asset Management. He can generate an alpha of 2% a year up to $500 million of invested capital. After that amount his skills are spread too thin, so he cannot add value and his alpha is zero for all investments over $500 million. Atlas Asset Management charges a fee of 0.80% on the total amount of money under management. Assume that there are always investors looking for positive alpha investments and no investor would invest in a fund with a negative alpha. Assume that the fund is in equilibrium, meaning that no investor either takes out money or wishes to invest new money into the fund.
5) The alpha that investors in Galt's fund expect to receive is closest to:
A) -.80%
B) 0.0%
C) 0.80%
D) 1.8%
Answer: B
Explanation: B) At equilibrium investors will invest to the point where the alpha is driven down to zero. Any alpha that is greater than zero will force more investment.
Diff: 3
Section: 13.5 The Efficiency of the Market Portfolio
Skill: Analytical
6) The amount of money that Galt's fund will have under management is closest to:
A) $500 million
B) $600 million
C) $1,000 million
D) $1,250 million
Answer: D
Explanation: D) At equilibrium, alpha must equal zero. Therefore:
α = 0 = $500 × 2% - $X × 0.80% → $10 = 0.0080X → $X = $1,250 million
Diff: 2
Section: 13.5 The Efficiency of the Market Portfolio
Skill: Analytical
7) The amount of fee income that Galt's fund will generate is closest to:
A) $3.75 million
B) $8.00 million
C) $10.00 million
D) $25.00 million
Answer: C
Explanation: C) At equilibrium, alpha must equal zero. Therefore:
α = 0 = $500 × 2% - $X × 0.80%
→ $10 = 0.0080X → $X = $1,250 million under management
Total fees = 1,250 million × 0.0080 = $10 million
Diff: 2
Section: 13.5 The Efficiency of the Market Portfolio
Skill: Analytical
8) A stock's ________ measures the stock's return relative to that predicted based on its beta, at the time of some event.
A) excessive abnormal return
B) cumulative average return
C) excessive predicted return
D) cumulative abnormal return
Answer: D
Diff: 1
Section: 13.5 The Efficiency of the Market Portfolio
Skill: Definition
13.6 Style-Based Anomalies and the Market Efficiency Debate
Use the following information to answer the question(s) below.
1) The correlation between the expected return and the market capitalization of these stocks is
A) negative.
B) positive.
C) zero.
D) Unable to determine with the information given
Answer: A
Explanation: A) As the size increases the return goes down indicating a negative correlation. Diff: 1
Section: 13.6 Style-Based Anomalies and the Market Efficiency Debate
Skill: Analytical
2) If the risk-free rate is 3% and the market risk premium is 5%, then the CAPM's predicted expected return for Wyatt Oil is closest to:
A) 7.0%
B) 8.5%
C) 9.0%
D) 9.5%
Answer: A
Explanation: A) r i = r f - βi(r m - r f) = 3% + 0.8(5%) = 7%
Diff: 1
Section: 13.6 Style-Based Anomalies and the Market Efficiency Debate
Skill: Analytical
3) If the risk-free rate is 3% and the market risk premium is 5%, then the CAPM's predicted expected return for Nielson Motors is closest to:
A) 8.5%
B) 9.0%
C) 9.5%
D) 10.0%
Answer: D
Explanation: D) r i = r f - βi(r m - r f) = 3% + 1.4(5%) = 10%
Diff: 1
Section: 13.6 Style-Based Anomalies and the Market Efficiency Debate
Skill: Analytical
4) Which of the following statements is FALSE?
A) If the market portfolio is efficient, then all securities and portfolios must plot on the SML, not just individual stocks.
B) For most stocks the standard errors of the alpha estimates are large, so it is impossible to conclude that the alphas are statistically different from zero.
C) It is not difficult to find individual stocks that, in the past have not plotted on the SML.
D) Small stocks (those with lower market capitalization) have lower average returns. Answer: D
Explanation: D) Small stocks (those with lower market capitalization) have higher average returns.
Diff: 1
Section: 13.6 Style-Based Anomalies and the Market Efficiency Debate
Skill: Conceptual
5) Which of the following statements is FALSE?
A) The size effect is the observation that small stocks have positive alphas.
B) When considering portfolios formed based on the book-to-market ratio, most of the portfolios plot below the security market line.
C) The largest alphas occur in the smallest size deciles.
D) When considering portfolios formed based on size, although the portfolios with the higher betas yield higher returns, most size portfolios plot above the security market line.
Answer: B
Explanation: B) When considering portfolios formed based on the market-to-book ratio, most of the portfolios plot above the security market line.
Diff: 2
Section: 13.6 Style-Based Anomalies and the Market Efficiency Debate
Skill: Conceptual
6) Which of the following statements is FALSE?
A) Portfolios with high market capitalizations must have positive alphas if the market portfolio is not efficient.
B) The book-to-market is the observation that firms with high book-to-market ratios have positive alphas.
C) If the market portfolio is not efficient, then a portfolio of high book-to-market stocks will likely have positive alphas.
D) Portfolios with low book-to-market ratios must have zero alphas if the market portfolio is efficient.
Answer: A
Explanation: A) Portfolios with low market capitalizations may have positive or negative alphas if the market portfolio is inefficient.
Diff: 2
Section: 13.6 Style-Based Anomalies and the Market Efficiency Debate
Skill: Conceptual
7) Which of the following statements is FALSE?
A) A momentum strategy is one where you buy stocks that have had low past returns and (short) sell stocks that have had high past returns.
B) Over the years since the discovery of the CAPM, it has become increasing clear to researchers and practitioners alike that forming portfolios based on market capitalization, book-to-market ratios, and past returns, one can construct trading strategies that have a positive alpha.
C) Portfolios containing firms with the highest realized returns over the previous six months have positive alphas over the next six months.
D) If the market portfolio is not efficient, then a portfolio of small stocks will likely have positive alphas.
Answer: A
Explanation: A) A momentum strategy is one where you buy stocks that have had high past returns and (short) sell stocks that have had low past returns.
Diff: 2
Section: 13.6 Style-Based Anomalies and the Market Efficiency Debate
Skill: Conceptual
Use the figure for the question(s) below.
Consider the following graph of the security market line:
8) Portfolio "B":
A) is less risky than the market portfolio.
B) is overpriced.
C) has a positive alpha.
D) falls above the SML.
Answer: B
Diff: 1
Section: 13.6 Style-Based Anomalies and the Market Efficiency Debate Skill: Conceptual
9) Portfolio "A":
A) has a relatively lower expected return than predicted.
B) has a positive alpha.
C) falls below the SML.
D) is overpriced.
Answer: B
Diff: 2
Section: 13.6 Style-Based Anomalies and the Market Efficiency Debate Skill: Conceptual
10) Portfolio "C":
A) is less risky than the market portfolio.
B) has a relatively lower expected return than predicted.
C) is underpriced.
D) has a negative alpha.
Answer: A
Diff: 2
Section: 13.6 Style-Based Anomalies and the Market Efficiency Debate Skill: Conceptual
11) Portfolio "D":
A) falls below the SML.
B) has a negative alpha.
C) is overpriced.
D) offers an expected return equal to the risk-free rate.
Answer: D
Diff: 2
Section: 13.6 Style-Based Anomalies and the Market Efficiency Debate Skill: Conceptual
12) The market portfolio:
A) is underpriced.
B) has a positive alpha.
C) is overpriced.
D) falls on the SML.
Answer: D
Diff: 1
Section: 13.6 Style-Based Anomalies and the Market Efficiency Debate Skill: Conceptual
13) Which of the following statements regarding portfolio "A" is/are correct?
1. Portfolio "A" has a positive alpha.
2. Portfolio "A" is overpriced.
3. Portfolio "A" is less risky than the market portfolio.
4. Portfolio "A" should not exist if the market portfolio is efficient.
A) 1 and 2
B) 1, 3, and 4
C) 1 and 3
D) 1, 2, 3, and 4
Answer: B
Diff: 3
Section: 13.6 Style-Based Anomalies and the Market Efficiency Debate Skill: Conceptual
14) Which of the following statements regarding portfolio "B" is/are correct?
1. Portfolio "B" has a positive alpha.
2. Portfolio "B" is overpriced.
3. Portfolio "B" is less risky than the market portfolio.
4. Portfolio "B" should not exist if the market portfolio is efficient.
A) 2 and 4
B) 4 only
C) 1, 3, and 4
D) 1 and 4
Answer: A
Diff: 3
Section: 13.6 Style-Based Anomalies and the Market Efficiency Debate Skill: Conceptual
15) Which of the following statements regarding portfolio "C" is/are correct?
1. Portfolio "C" has a negative alpha.
2. Portfolio "C" is overpriced.
3. Portfolio "C" is less risky than the market portfolio.
4. Portfolio "C" should not exist if the market portfolio is efficient.
A) 1 and 3
B) 2 and 4
C) 1, 3, and 4
D) 3 only
Answer: D
Diff: 3
Section: 13.6 Style-Based Anomalies and the Market Efficiency Debate Skill: Conceptual
Use the information for the question(s) below.
Consider two firms, Chihuahua Corporation and Bernard Industries that are each expected to pay the same $1.5 million dollar dividend every year in perpetuity. Chihuahua Corporation is riskier and has an equity cost of capital of 15%. Bernard Industries is not as shaky as Chihuahua, so Bernard has an equity cost of capital of only 10%. Assume that the market portfolio is not efficient. Both stocks have the same beta and the CAPM would assign them both an expected return of 12% to both.
16) The market value for Chihuahua is closest to:
A) $10.0 million
B) $12.5 million
C) $12.0 million
D) $15 million
Answer: A
Explanation: A) MV = = = $10M
Diff: 1
Section: 13.6 Style-Based Anomalies and the Market Efficiency Debate
Skill: Analytical
17) The market value for Bernard is closest to:
A) $12.0 million
B) $10 million
C) $15.0 million
D) $12.5 million
Answer: C
Explanation: C) MV = = = $15M
Diff: 1
Section: 13.6 Style-Based Anomalies and the Market Efficiency Debate
Skill: Analytical
18) The alpha for Chihuahua is closest to:
A) +2%
B) -5%
C) -3%
D) +3%
Answer: D
Explanation: D) Alpha = expected return - predicted return (from CAPM) = .15 - .12 = .03 Diff: 2
Section: 13.6 Style-Based Anomalies and the Market Efficiency Debate
Skill: Analytical
19) The alpha for Bernard is closest to:
A) +5%
B) -2%
C) -3%
D) +2%
Answer: B
Explanation: B) Alpha = expected return - predicted return (from CAPM) = .10 - .12 = .-.02 Diff: 2
Section: 13.6 Style-Based Anomalies and the Market Efficiency Debate
Skill: Analytical
20) Various trading strategies appear to offer non-zero alphas when we examine real world data. If indeed these alphas are positive, it could be explained by any of the following EXCEPT:
A) Investors are systematically ignoring positive-NPV investment opportunities.
B) The market portfolio is inefficient, but the market portfolio proxy used to calculate the alphas is efficient.
C) A stock's beta with the market portfolio does not adequately measure a stock's systematic risk.
D) The positive alpha trading strategies contain risk that investors are unwilling to bear but the CAPM does not capture.
Answer: B
Diff: 2
Section: 13.6 Style-Based Anomalies and the Market Efficiency Debate
Skill: Conceptual
21) Which of the following is NOT an investment likely to be found in any proxy for the market portfolio?
A) Human capital
B) Stocks
C) Bonds
D) Precious metals
Answer: A
Diff: 1
Section: 13.6 Style-Based Anomalies and the Market Efficiency Debate
Skill: Conceptual
A) If the CAPM correctly computes the risk premium, investors would stop investing only when they expected the alpha of an investment strategy to be negative.
B) If the CAPM correctly computes the risk premium, an investment opportunity with a positive alpha is a positive NPV investment opportunity.
C) If the CAPM correctly computes the risk premium, investors should flock to invest in positive alpha stocks.
D) Anyone can implement a momentum trading strategy and therefore generate a positive investment opportunity.
Answer: A
Diff: 2
Section: 13.6 Style-Based Anomalies and the Market Efficiency Debate
Skill: Conceptual
23) Which of the following statements is FALSE?
A) If indeed alphas are positive, it is possible that the positive alpha trading strategies contain risk that investors are unwilling to bear but the CAPM does not capture.
B) If indeed alphas are positive, it is possible that the costs of implementing investment strategies are larger than the NPVs of undertaking them.
C) If indeed alphas are positive, then investors have to be systematically ignoring negative-NPV investments opportunities.
D) The only way a positive NPV investment opportunity can exist in a market is if some barrier to entry restricts competition.
Answer: C
Diff: 2
Section: 13.6 Style-Based Anomalies and the Market Efficiency Debate
Skill: Conceptual
24) Which of the following statements is FALSE?
A) The existence of the momentum trading strategy has been widely known for at least ten years.
B) The information required to implement a momentum strategy is not readily available to investors.
C) If the market portfolio is not efficient, then a stock's beta with the market is not an adequate measure of its systematic risk.
D) If the market portfolio is not efficient, then the so-called profits from a positive alpha trading strategy are really returns for bearing risk that investors are averse to and the CAPM doesn't capture.
Answer: B
Explanation: B) The information required to implement a momentum strategy is readily available to investors.
Diff: 2
Section: 13.6 Style-Based Anomalies and the Market Efficiency Debate
Skill: Conceptual
上财经济学考研参考书及考试科目 为了方便广大考研学子更好的了解上财经济学考研,凯程艾老师为大家整理总结了上海财经大学考试科目及参考书,希望能帮到广大考研学子。祝愿2019考研学子顺利考上研究生。 考试科目:801经济学 一、适用专业: 人文学院:马克思主义哲学/伦理学/科学技术哲学/经济哲学/马克思主义基本原理/马克思主义中国化研究/思想政治教育 经济学院:政治经济学/经济思想史/经济史/西方经济学/人口、资源与环境经济学/劳动经济学/数量经济学(要求硕博连读) 公共经济与管理学院:国民经济学/财政学/投资经济/税收学/公共经济政策学/房地产经济学/技术经济及管理/行政管理/社会医学与卫生事业管理/教育经济与管理/社会保障/土地资源管理 财经研究所:区域经济学/国防经济/城市经济与管理/能源经济与环境政策/农业经济管理/林业经济管理 金融学院:金融学/保险学/金融数学与金融工程/信用管理(要求硕博连读) 国际工商管理学院:世界经济/世界经济/国际贸易学/企业管理/旅游管理/市场营销学/体育经营管理 会计学院:会计学/财务管理 二、参考书目: 范里安版《微观经济学:现代观点》、曼昆版《宏观经济学》、巴罗版《宏观经济学:现代观点》 三、试卷构成: 微观经济学(75分) 宏观经济学(75分) 四、考试题型: 判断题(每小题1分,共20分) 单项选择题(每小题1分,共40分) 问答(计算)题(每题15分,共90分)
五、招生概括: 近几年,上海财大考研报考人数日益增多,复试分数持续攀升,竞争日趋白热化。这一方面是由于随着大批海归的加盟,学科发展很快,另一方面依托上海国际金融中心的加快建设,吸引了越来越多的考生选择上海财大。
一、单项选择题 1、在得出某种商品的厂商供给曲线时,不保持常数的因素是()(答题答案:) A、消费者收入 B、其余商品的价格 C、所考虑商品的价格 D、消费者偏好 2、导致需求曲线发生位移的原因是()(答题答案:) A、因价格变动,引起了需求量的变动 B、因供给曲线发生位移,引起了需求量的变动 C、因影响需求量的非价格因素改变,从而引起需求的变动 D、因社会经济因素发生变动引起产品价格的变动 3、在某一时期内彩色电视机的需求曲线向左平移的原因是()(答题答案:) A、彩色电视机的价格上升 B、消费者对彩色电视机的预期价格上升 C、消费者对彩色电视机的预期价格下降 D、黑白电视机的价格上升 4、下列变化中,哪种变化不会导致需求曲线的位移?()(答题答案:) A、人们的偏好和爱好 B、产品的价格 C、消费者的收入 D、相关产品的价格 5、已知市场需求方程为Qd=5000-10P,市场供给方程为Qs=500+5P。则()(答题答案:) A、均衡价格为300元,均衡购销量为2000单位 B、均衡价格为100元,均衡购销量为6000单位 C、均衡价格为600元,均衡购销量为4000单位 D、均衡价格为900元,均衡购销量为5000单位 6、生产者预期某产品未来价格要下降,则该产品当前的生产()(答题答案:) A、增加 B、减少 C、不变 D、不增加 7、影响需求量的主要因素中不包括()(答题答案:) A、产品价格 B、消费者收入 C、广告费用 D、产品成本 8、如果某产品需求曲线是一条垂直的直线,则该需求曲线上每一点的价格弹性()(答题答案:) A、都等于1 B、都大于1 C、都等于0 D、不等 9、下面哪种情况将导致供给的增加()(答题答案:) A、消费者收入的增加 B、采用更加先进的技术 C、消费者收入的减少 D、生产成本的上升 10、收入和偏好是()(答题答案:) A、影响供给的因素 B、影响需求的因素 C、在经济分析中可以忽略 D、上述都不准确 11、需求和供给同时减少的情况下()(答题答案:) A、均衡价格的变化无法确定,均衡交易量将下降 B、均衡价格将下降,均衡交易量的变化无法确定 C、均衡价格和均衡交易量都将下降 D、均衡价格将上升,均衡交易量将下降
广西财经学院学生网上选课指南 我院从2007年秋季学期开始全面启用新的教务管理系统,以下是新系统的学生网上选课步骤, 一、打开IE,在“地址”栏中输入:“210.36.136.11/jwweb”后回车,IE加载系统,如图一示: 图一 二、点击“用户登录”选项卡,系统加载用户认证窗口,身份默认为“学生” 人学号及个人密码(注:学生初始密码即为个人学号,请及时修改个人密码 按钮,如图二、图三示
三、输入正确学号及密码后,系统进入图三界面 图三 注:“”为返回到主菜单,“”按钮为隐藏主菜单(图三红色部分为主菜单)择相应功能菜单进行选课操作:
五、在图四中,点击“正选”菜单,系统加载图五界面窗口,在“课程范围”下拉框中选择相应课程范围: 图五 课程范围注解: 1、“主修(本年级/专业)”:为本年级/专业所开设的专业任选课程。(根据各年级各专业人才培养方案,有小部分专业的专业选修课程全部为限选课程,该部分专业学生检索后将无相关内容显示。) 2、“辅修”:为专业辅修课程,目前我院学生不需在此进行选择。 3、“主修(公共任选)”:为全校公选课,在此进行公共任选课课程选择,每位学生都必须在此项进行选课。 4、“主修(可跨年级/专业)”:为可跨年级/专业课程选择,目前我院学生不需在此进行选择。 六、在图五中的“课程范围”中选择相应类别,点击“检索”按钮,系统即可检索出相关课程范围内的所有课程,学生可根据本人实际情况在图六中课程名称前方框中打“√”选取课程,然后点“提交”按钮即可完成预选操作。
图六 图七 根据本人实际情况选择课程在其前方框中打“√”后,点“提交”铵钮即可完成操作 “提交”后,系统在此提示课程提交成功与否,系统会显示正选成功的课程和正选未成功的课程及其原因
一、单项选择题(每小题1分) 1、A; 2、C; 3、A; 4、B; 5、D; 6、C; 7、D; 8、B; 9、C;10、D;11、C;12、A 一、单项选择题 1、信息资源的无限性是指()。 A.信息的来源是无限的B.信息的获得是无限的 C.信息的应用是无限的D.信息的作用是无限的 2、信息资源的稀缺性是指()。 A.信息的来源是稀缺的B.获得信息的渠道是稀缺的 C.信息的应用能力是稀缺的D.有价值的信息是稀缺的 3、将信息定义为信息是经过加工过的数据,属于()。 A.狭义的信息概念B.广义的信息概念C.信息学的信息概念D.经济学的信息概念 4、将信息定义为信息是经过传播的消息,属于()。 A.狭义的信息概念B.广义的信息概念C.信息学的信息概念D.经济学的信息概念 5、按照信息的经济涵义,信息是认识主体接收到的新内容和新知识,它可以消除对事物认识的()。 A.随意性B.主观性C.不完全性D.不确定性 6、计算机软件信息产品中的属于()。 A.内容性产品B.应用性产品C.工具性产品D.服务性产品7、搜索引擎属于信息产品中的()。 A.内容性产品B.应用性产品C.工具性产品D.服务性产品8、信息产品消费者偏好的特征之一是()。 A.信息产品效用增量的饱和性B.信息产品效用增量的非饱和性 C.信息产品消费者偏好的确定性D.信息产品消费者偏好的不确定性 9、信息产品消费者偏好的特征之一是()。 A.信息产品消费者偏好的确定性B.信息产品消费者偏好的不确定性 C.信息产品消费者偏好增强的自发性D.信息产品消费者偏好增强的强制性 10、信息产品的无差异曲线与一般产品不同,其形状为()。 A.左下方凹进B.向右下方凹进C.向左上方凸起D.向右上方凸起11、信息产品的无差异曲线与一般产品不同的原因是()。
上财经济学真题 Document serial number【NL89WT-NY98YT-NC8CB-NNUUT-NUT108】
一、判断题(每小题1分) 1、给定消费者偏好,如果两种商品之间满足边际替代率递减,那么这两种商品的边际效用一定递减。 2、在垄断市场上,一种商品需求的价格弹性越大,垄断定价中成本加成系数减少。 3、如果一种商品的收入效应为正,那么当价格下降时,消费者剩余的变化(△CS)、补偿变差(CV)和等价变差(EV)大小满足:∣EV∣>∣△CS∣>∣CV ∣。 4、如果李三的偏好可以用函数Max{x,y}表示,那么他的偏好是凸的。 5、如果消费者偏好可以用C-D效用函数表示,那么,消费者在一种商品上的支出占总支出的比例不随价格或收入改变而变化 6、对于一个公平的赌博,即期望的净收益为零,此时判断一个人是否是风险爱好,取决于他是否会接受公平的赌博。 7、在博弈情形中,如果扩大一个参与者的策略集,那么至少该参与者的福利不会下降。 8、福利经济学第二定理告诉我们,只要所有交易者具有理性、严格递增偏好,那么每一个帕累托有效的配置都是某一竞争均衡的结果。 9、在外部性问题中,如果每个消费者具有拟线性偏好,那么帕累托有效配置独立于产权分配。 10.、道德风险问题是由于交易一方不能观察另一方类型或质量导致的。 11、新古典经济增长模型与内生经济增长模型的主要区别是,前者没有考虑技术进步,,后者包含了技术进步。 12、货币中性主要是指货币供给变动只影响名义变量,而不影响实际变量。 13、对汇率固定、资本只有流动的小国开放经济,财政政策比货币政策更有效。 14、货币需求交易理论注重货币收益,货币需求资产组合理论注重货币成本。 15.、与政策相关的“时间不一致性”是指当政者宣布政策的目的在于麻痹公众,以达到自己的党派利益。 16、在计算GDP时,企业购买的新厂房及办公用房应当计入投资,而个人购买的新住房应计入消费。 17、在物价为黏性的时间范围内,古典二分法不再成立,并且经济会背离古典模型所预言的均衡。 18、根据货币需求的资产组合理论,股票的实际预期收益不影响货币需求。 19、正如凯恩斯一样,许多经济学家相信在经济衰退时,投资相对无弹性,因此,利益的降低对投资和国民收入几乎没有什么影响。 20、资本与劳动在生产上是可以相互替换的,这是新古典增长模型的假设条件。 二、单项选择题(每小题1分) 21、在两商品经济中,王四觉得商品1越来越好,商品2越多越糟,那么__. A、无差异曲线一定是凸向原点的; B、无差异曲线一定向右上方倾斜; C、无差异曲线可能是呈椭圆形; D、以上都不是 22、在下列效用函数中,哪一个具有风险规避(risk-aversion)倾向,这里x 代表财富水平。 A、u(x)=100+3x B、u(x)=lnx C、u(x)=x2 D、以上都不是
上海财经大学历年博士真题 经济学试题(一) (上海财经大学博士研究生入学考试试题) (2005 年 04 月) (三道微观经济学题目,两道宏观经济学题目,每题20分,共5题) 1. 什么是马歇尔需求,希克斯需求,并请用斯卢滋矩阵解释说明。 2. 简述利润函数的性质,若生产函数为y=x i“xJ “,求其利润函数并验证利润函数的性质。 3. 什么是占优策略,纳什均衡,给定如图的策略,哪些是重复删除占劣策略所不能删除的,求纯策略纳什均 衡,混合策略的纳什均衡。 4. 关于拉姆齐模型:个人消费为C,效用为u(J,u为凹函数,生产函数F(K, L)为规模报酬 不变,资本成本为r,工资为w,效用贴现率为B,人口增长率为n,折旧为S,请说明修 正的黄金率水平,人均资本的变化方程K/L,人均产量的变化方程 Y/L,说明趋向C/L,K/L的 均衡状态为鞍点路径 5. 说明价格、工资刚性的模型。 {回忆者留言:就是书中的五个模型,以前曾考过} 经济学试题(一) (2004 年 10 月 上海财经大学博士研究生入学考试试题) (三道微观经济学题目,两道宏观经济学,每题20分,共5题) 1 .效用函数U=AX「1X2a 2 X3“3, a 1+a 2+a 3=1,P=(P1, P 2, P 3),求马歇尔需求函数,间接效用函 数,希克斯需求函数,支岀函数。 2. 用埃奇渥斯盒式图说明福利经济学第一、第二定理及其经济含义。 3. 证明:在古诺模型中,纳什均衡时的每个厂商生产的产量是市场容量的1/ (n+1),给定有n 个 厂商。 4. 推导IS、LM曲线的斜率,给定的条件有l=l(r,Y), I r<0, I Y>0,政府采购为G,真实货币需求 m=m (r,Y), m r<0, m Y>0,消费为 C. 5. 给岀生产函数为 Y=K“(AL)1-“,请推导索洛模型基本方程,说明稳定增长,说明黄金率水平;如果 Y=AK,稳定增长的情况又如何。 经济学试题(一) (2004年4月博士研究生入学考试试题) 答案请用另纸,并请在各题的答案前标明相应的题号 注意:需要用公式和图形表示的,请注明所使用符号的意义 每题25分 1. 若消费者偏好满足完备性、传递性、连续性、严格单调性、严格凸性五个公理,预算集为 B= {x | x € R:px < y} (x 、p为商品和价格向量,y为给定收入)。试证明这一消费者问题若有解x* ,则 a) x*是唯一的, b)相应于x*,消费者收入将用尽,即有y = p x* 。 2 ?在为本考试科目所列的参考书中,阿罗不可能定理是用四个条件来规定的。请对阿罗不可能定理作出定义,并解释这四个条件中每一个条件都是不可缺少的。 (在其他国际流行的高水平的经济学教科书或者专著中,阿罗不可能定理需要的条件可能和为 本考试科目所列的参考书中所提出的四个条件不同。你当然可以用那些书籍中的说法,但你必须 选择某一种说法,而不能够混用不同说法) 3 ?考虑一个生产函数 y t = k a t A b t, 0 南 京 财 经 大 学 经济数学基础课程习题参考答案 (一) 一、填空题 1.0 2.)(2x f '- 3.14-=x y 4.1±=x 5. )2,2(- 6. c x +cos 7. 10<南京财经大学继续教育经济数学基础题1参考答案