
Report on the 29th International Symposium on
Multiple-Valued Logic (ISMVL99)
Takahiro Hozumi*Yasunori Nagata? Noboru Takagi?Takao Waho§
* Department of Economics & Information Science
Hyogo University
2301, Shinzaike, Hiraoka, Kakogawa, Hyogo, 675-0101 Japan
? Department of Electrical & Electronics Engineering
University of the Ryukyus
1 Senbaru Nishihara, Okinawa, 903-0213 Japan
? Department of Electronics and Informatics
Toyama Prefectural University
Kosugi, Toyama, 939-0398 Japan
§ Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering
Sophia University
7-1, Kioicho, Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo, 102-8554 Japan
1. Introduction
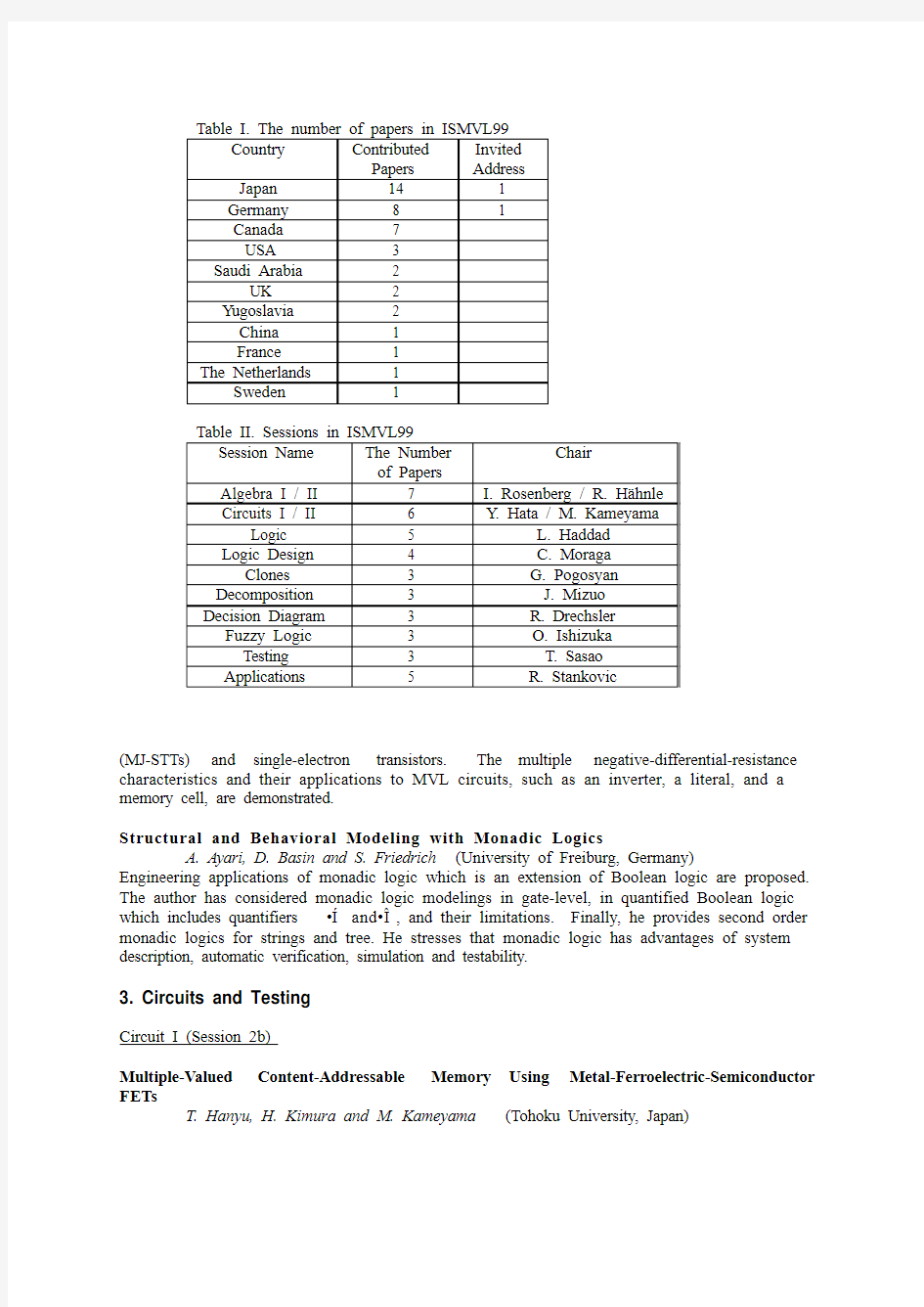
The 29th International Symposium on Multiple-Valued Logic (ISMVL99) was held in Freiburg im Breisgau, Germany, May 20-22, 1999. The Symposium was co-sponsored by the Albert-Ludwigs-Universit?t Freiburg (or University of Freiburg), and the IEEE Computer Society Technical Committee on Multiple-Valued Logic. Two invited addresses and 42 contributed papers were presented by MVL researchers from around the world (Table I). The number of attendees was around 60. This year, a panel session on Multiple-Valued Logic in the Next Millenium: Challenges and Perspectives was also included. In addition, the 8th International Workshop on Post-Binary ULSI Systems was held at the same conference cite on May 19.
In this report, the papers presented in the symposium, which covered almost all the topics on MVL (Table II), will be briefly described. Further information is available in the Symposium Proceedings published by IEEE Computer Society Press, and the web home page. 1) The next symposium will be held in Portland, Oregon, USA, May 23-25, 2000. Call for papers and other information are presented at the web page. 2)
2. Invited addresses
Development of Quantum Functional Devices for Multiple-Valued Logic Circuits Toshio Baba (NEC, Japan)
The author introduced the long-term MITI project on quantum functional devices (1991-2000). Then, he presented the experimental results on multi-junction surface tunneling transistors
(MJ-STTs) and single-electron transistors. The multiple negative-differential-resistance characteristics and their applications to MVL circuits, such as an inverter, a literal, and a memory cell, are demonstrated.
Structural and Behavioral Modeling with Monadic Logics
A. Ayari, D. Basin and S. Friedrich (University of Freiburg, Germany)
Engineering applications of monadic logic which is an extension of Boolean logic are proposed. The author has considered monadic logic modelings in gate-level, in quantified Boolean logic which includes quantifiers ?í and??, and their limitations. Finally, he provides second order monadic logics for strings and tree. He stresses that monadic logic has advantages of system description, automatic verification, simulation and testability.
3. Circuits and Testing
Circuit I (Session 2b)
Multiple-Valued Content-Addressable Memory Using Metal-Ferroelectric-Semiconductor FETs
T. Hanyu, H. Kimura and M. Kameyama (Tohoku University, Japan) Table I. The number of papers in ISMVL99
Country Contributed Papers Invited
Address
Japan 14 1
Germany 8 1
Canada 7
USA 3
Saudi Arabia 2
UK 2
Yugoslavia 2
China 1
France 1
The Netherlands 1
Sweden 1
Table II. Sessions in ISMVL99
Session Name The Number of Papers
Chair
Algebra I / II 7 I. Rosenberg / R. H?hnle
Circuits I / II 6 Y. Hata / M. Kameyama
Logic 5 L. Haddad
Logic Design 4 C. Moraga
Clones 3 G. Pogosyan
Decomposition 3 J. Mizuo
Decision Diagram 3 R. Drechsler
Fuzzy Logic 3 O. Ishizuka
Testing 3 T. Sasao
Applications 5 R. Stankovic
A design of novel non-volatile CAM with MFSFETs was presented. One-digit comparator consisting of only two MFSFETs results in a compact MVCAM cell. The bit density and access speed, as well as peripheral-circuit complexity, were evaluated. The performance was proved to be superior to those based on conventional technology.
“New Lamps for Old!” (Generalized multiple-valued neurons)
C. Moraga and R. Heider (University of Dortmund, Germany)
The authors tried t o develop artificial neural networks by using multiple-valued threshold logic investigated in 70’s. They found that by adapting design methods of feedforwards neural networks, any MV functions can be achieved.
Supplementary Symmetrical Logic Circuit Structure
E. D. Olson (USA)
The author obtained r-valued logic functions by combining MOSFETs with various threshold voltages. Demonstrating an experimental board equipped with the MV chip, he claimed that the circuit can be easily fabricated by binary LSI vendors without any special options.
Circuit II (Session 6b)
Ternary Multiplication Circuits Using 4-Input Adder Cells and Carry Look-Ahead
A. Herrfeld and S. Hentschke (University of Kassel, Germany)
A new ternary adder was introduced and applied to a ternary multiplier. The complexity of the multiplier can be reduced to one half that required for binary implementations. A ternary carry-look-ahead adder was also presented for a further reduction in the total delay time.
Down Literal Circuit with Neuron-MOS Transistors and Its Applications J. Shen, K. Tanno and O. Ishizuka (Miyazaki University, Japan)
Voltage-mode νMOS down-literal and T-gate circuits were presented. The noise margin and switching sensitivity were superior to those of conventional complementary νMOS circuits. Arithmetic with Signed Analog Digits
A. Saed, M. Ahmadi and G. A. Jullien (Notel Network, Canada)
A new method for binary arithmetic and digital signal processing was presented. This redundant representation of signals is based on analog residue digits, in contrast to binary or multiple-valued digit levels, which might open up a powerful approach to digital computing. Testing (Session 9a)
Fault Characterization and Testability Considerations in Multi-Valued Logic Circuits M. Abd-El-Barr, M. Al-Sherif and M. Osman (King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals, Saudi Arabia)
A CMOS functionally complete set of MVL operators was implemented by using existing standard binary CMOS technology in order to characterize faults in the MVL operators. Fault categories and recommendations for testability was also discussed..
Highly Testable Boolean Ring Logic Circuits
U. Kalay, M. A. Perkowski and D. V. Hall (Portland State University, USA)
The authors developed BR based expressions, called Boolean-Ring Sum-of-Product (BRSOP), to represent 2n-valued MVL functions, and discussed several advantages in terms of highly-testable circuit implementation.
Self-Checking Multiple-Valued Circuit Based on Dual-Rail Current-Mode Differential Logic T. Hanyu, T. Ike and M. Kameyama (Tohoku University, Japan)
A new self-checking circuit was proposed to achieve compact high-speed arithmetic system with a supply voltage of 1.5V. The authors showed the reduction in transistor counts, switching delay, and power dissipation by assuming a 0.5-μm standard CMOS technology.
4. Logic, Logic Design, and Related Topics
Decomposition (Session 3a)
Bi-Decompositions of Multi-Valued Functions for Circuit Design and Data Mining Applications
B. Steinbach, M. A. Perkowski and
C. Lang (University of Freiburg, Germany)
This paper presents efficient algorithms for the bi-decomposition of arbitrary incompletely specified functions in variable-valued logic. The algorithms are especially applicable for Data Mining applications and such decompositions lead to decision rules that are easier to understand by humans.
Totally Undecomposable Functions: Applications to Efficient Multiple-Valued Decompositions T. Sasao (Kyushu Institute of Technology, Japan)
In this paper, they define totally k-undecomposable logic functions, and show a systematic method to find the bipartitions that will not produce disjoint k-decompositions. In addition, they discuss generation of a set of k-undecomposable bipartitions from totally k-undecomposable subfunctions, representation of k-undecomposable bipartitions by an n-variable switching functions and enumeration of totally k-undecomposable functions.
A Generalization of Shestakov's Function Decomposition Method
J. J. Lou and J. A. Brzozowski (University of Waterloo, Canada)
This paper formalizes Shestakov's decomposition method using blanket algebra. They generalize it to multi-valued functions represented by cubes and relate it to the work of Luba and Selvaraj.
Logic Design (Session 4a)
Evaluation of m-Valued Fixed Pola rity Generalizations of Reed-Muller Canonical Form
E. Dubrova (Royal Institute of Technology, Sweden)
This paper compares the complexity of three different fixed polarity generalizations of Reed-Muller canonical form and shows that the Reed-Muller-Fourier form and expansion proposed by them require 40% less products on average than the expansion of Green and Taylor for the benchmark functions. It also shows that the Reed-Muller-Fourier form gives a compact representation for adders, while their expansion seems to be suitable for multipliers.
Multiple-Valued Minimization to Optimize PLAs with Output EXOR Gates
D. Debnath and T. Sasao (Kyushu Institute of Technology, Japan)
This paper considers an optimization method of programmable logic arrays (PLAs), which realize an EXOR of-two sum-of-products expressions (EX-SOP) for multiple-valued input two-valued output functions. They present techniques to minimize the expression and show that the technique produces better EX-SOPs than existing methods.
The Output P ermutation for the Multiple-Valued Logic Minimization with Universal Literals T. Hozumi, O. Kakusho and Y. Hata (Hyogo University, Japan)
This paper shows that a combination of an output permutation and a logic circuit can realize a logic circuits of the s ame function with lower costs. They compare the combination with direct implementation and show that about 70% of four-valued two-variable functions can reduce the costs and their reduction ratio is about 12% on average.
Logic Model for Representing Uncertain Statuses of Multiple-Valued Logic Systems Realized by Min, Max and Literals
N. Takagi, A. Hon-nami and K. Nakashima (Toyama Prefectural University, Japan) This paper discusses an extension of Kleene's regularity into V r, where V r is set of all nonempty subset of r-valued set {0, ..., r-1}. They prove that a necessary and sufficient condition for a function on V r to be realized by ∧, ∨, x{a} and the constants {0}, ..., {r-1}. Decision Diagrams (Session 6a)
Matrix-Valued EXOR-TDDs in Decomposition of Switching Functions
R. S. Stankovic (University of Nis, Yugoslavia)
This paper introduces the matrix-valued EXOR-TDDs and shows that decomposition or bi-decomposition with respect to r variables can be obtained by building an EXOR-TDD for a matrix-valued function of (n-r) variables.
Synthesis of Multiple-Valued Decision Diagrams using Current-Mode CMOS Circuits M. Abd-El-Barr and H. Fernandes (King Fahd University of Dhahran, Saudi Aravia) This paper discusses Ordered Multiple Decision Diagrams (OMDDs) and their implementation using Current-Mode CMOS Logic (CMCL) circuits. The paper shows complete layout for OMDD basic cells using CMOS3DLM design rules and their performance for some benchmark circuits from the LGSynth93.
Shared Multiple-Valued Decision Diagrams for Multiple-Output Functions
H. Md. H. Babu and T. Sasao (Kyushu Institute of Technology, Japan)
This paper proposes a shared multiple-valued decision diagrams (SMDDs) and shows an algorithm for pairing the input variables of BDDs and a method t o find good orderings of the pairs. Their experimental results for general functions and symmetric functions show that the sizes of the SMDDs are almost a half those of the SBDDs.
Logic (Session 7b)
Information Relationships and Measures in Application to Logic Design L. Jozwiak (Eindhoven University of Technology, The Netherlands)
In this paper, the theory of information relationships and relationship measures is considered. The paper shows how to apply the relationships and measures to input support minimization, parallel decomposition and serial functional decompositions. The experimental results demonstrate the high potential in solving the problems.
Probabilistic and Truth-Functional Many-Valued Logic Programming
T. Lukasiewicz (University of Gie?en, Germany)
This paper introduces probabilistic many-valued logic programs in which the implication connectives are interpreted as material implication. The paper discusses some properties on the probabilistic many-valued logic programming and classical logic programming. Representation Theorems and Theorem Proving in Non-Classical Logics V. Sofronie-Stokkermans (Max-Planck-Institute Saarbrücken, Germany)
This paper shows that the Priestly duality for distributive lattices with operators provides a theoretical tool for clarifying the link between algebraic and Kripke-style models for certain classes of non-classical logics. Based on these results, they gave a method for translation to clause form and automated theorem proving for some of these classes of non-classical logics.
Transformations between Signed and Classical Clause Logic
B. Beckert, R. Hahnle and F. Manya (University of Karlsruhe, Germany)
In this paper, they relate signed logic and classical logic more closely than before by defining two new transformations between them. As a byproduct they obtain a number of new complexity results and proof procedures for signed logics.
Semirigidity Problems in k-Valued Logic
M. Miyakawa (Tsukuba College of Technology, Japan)
This paper overviews the semirigidity problems. They discuss whether autodual clones are rigid to each other for k prime and listed some open questions
Fuzzy Logic (Session 9b)
On the Concept of Qualitative Fuzzy Set
H. Thiele (University of Dortmund, Germany)
This paper introduces a sensible concept of a qualitative fuzzy set and sensible algebraic operations with such sets using Kripke-style semantics approach. The paper shows that the concept of multi-fuzzy set introduced by LIN is a special case of the concept of context-depending fuzzy set.
On Some Classes of Fuzzy Information Granularity and Their Representations Y. Hata and M. Mukaidono (Himeji Institute of Technology, Japan)
This paper shows three classes of fuzzy information granularity structures, which are called Kleene class, Lukasiewics class and probabilisticlike class. The paper discusses their meaning and representation methods and their examples are demonstrated.
From a Fuzzy Flip-Flop to a MVL Flip-Flop
L. P. Maguire, T. M. McGinnity and L. J. McDaid (University of Ulster, UK)
The paper describes the MOS implementation of a fuzzy flip-flop which is appropriate for VLSI implementations and demonstrates that this fuzzy flip-flop can also be interpreted as a MVL flip-flop.
5. Applications (Session 7a)
Quaternary Coded Genetic Algorithms
K. Freitag, L. Hildebrand and C. Moraga (University of Dortmund, Germany)
In this article, quaternary coded genetic algorithms are proposed. These algorithms provides solutions as good as their corresponding binary versions for problems with low dimensions and achieves very fast an acceptable good fitness, if not the best, for high dimensional problems. Moreover, the performance of genetic algorithms under a Gray code is considered.
Redundant Complex Arithmetic and Its Application to Complex Multiplier Design Takafumi Aoki, Ken-ichi Hoshi and Tatsuo Higuchi (Tohoku University, Japan)
This article presents a class of complex number representations, redundant complex number systems(RCNS). RCNS is useful for designing DSP, because of its possibility of constructions of high-speed complex arithmetic circuits. As experiments, a complex-number parallel adder
with no-carry propagation chain, and a complex-number multiplier exploiting fast binary-tree
adder structure. Practically, an e xperimental fabrication of the RCNS c omplex multiplier in 0.5?êm CMOS rule is provided.
On the number of Multilinear Partitions and the Computing Capacity of Multiple-Valued
Multiple-Threshold Perceptrons
Alioune Ngom, Ivan Stojmenovic and Jovisa Zunic (Lakehead University, Canada)
This paper introduces multilinear partition of point set and multilinear separability of a function. From this, for real number input - multiple valued output function (n-input,
k-valued logic function), (n, k, s)-perceptrons are proposed where s is the number of threshold
values. The authors consider the (n, k, s)-perceptron for pattern recognition application, and
also consider partitioning and separability mathematically.
B-ternary Logic Based Asynchronous Micropipeline
Y. Nagata, D. M. Miller and M. Mukaidono (University of the Ryukyus, Japan)
B-ternary logic oriented asynchronous micropipeline system is presented. The system
processes binary data asynchronously, and the process can be done in parallel and in elastic.
It has high-speed operation potential in spite of having an idle phase. The mechanism for
correct pipeline behavior and the designed circuits are provided.
State Assignment Techniques in Multiple-Valued Logic
K. J. Adams, J. G. Campbell, L. P. Maguire and J.A.C. Webb (University of Ulster,
UK)
This article considers a design method for FPGA like circuits including universal literal by
state assignment. The authors propose a module suitable to GF(23) and applying to functions consists of NOT, AND and XOR. Also they consider transforms to GF(22).
6. Algebra and Clones
Algebra I (Session 2a)
Multivalued binary relations and Post algebras
Michel Serfati (L.I.A.F.A, Université Paris VII and CNRS, France)
This paper deals with a multi-valued extension of the concept of a binary relation on a set E. The set of all r-valued binary relations on E is employed an order relation so that the set will become a Post algebra of order r. This paper studies multi-valued product of binary relations as well as multi-valued reflexivity, symmetry, antisymmetry and transitivity.
(Not Presented) Quaternion groups versus dyadic groups in representations and processing of switching functions
R. S. Stankovic, D. Milenovic and D. Jankovic (University of Nis, Yugoslavia)
This paper compares effects of two different domain groups for switching functions to the efficiency of calculation of spectral transforms representations and the complexity of decision diagrams representations. Dyadic groups and quaternion groups are assumed for domain groups for switching functions. This paper concludes that the quaternion groups have advantages in processing of large switching functions. When the number of variables grows, these advantages increase.
On axiomatization of conditional entropy of functions between finite sets S. Jaroszewicz and D. A. Simonici (University of Massachusetts at Boston, USA)
This paper presents a new axiomatization of the notion of entropy of functions between finite sets, and introduces and axiomatizes the notion of conditional entropy between functions.
Algebra II (Session 4b)
A super switch algebra for quantum device based systems
G. W. Dueck, M. Hu and B. Fraser (St. Francis Xavier University, Canada)
In this paper, a new type of multiple-valued algebra (called super switch algebra) is presented. This algebra is well suited for the design of quantum device based multiple-valued systems. A minimization algorithm based on this algebra is proposed.
Clarifying the axioms of Kleene algebra based on the method of indeterminate coefficients T. Ninomiya and M. Mukaidono (Meiji University, Japan)
This paper shows all of the Kleene algebras with 8 elements by using indeterminate coefficient method. There are 6 such Kleene algebras in total. Furthermore, the indeterminate coefficient method can also generate a set of independent and complete axioms of a given algebra. So, some examples of a set of independent and complete axioms of Kleene algebras are presented.
The number of cascade functions
G. Pogosyan (International Christian University, Japan)
An n-input cascade network is a circuit built with n-1 two-input-one-output gates such that at least one input of each gate except for one is a network input. A cascade function is a Boolean function which can be implemented by a cascade network. This paper presents the number of cascade functions with n-input.
(Not Presented) Research on the similarity among precomplete sets preserving m-ary relations in partial k-valued logic
R. Liu (Xiangtan University, China)
Let P k* be a set of all partially specified functions on the set {0, 1, … , k-1}. T his paper presents some relationships between subsets of P k*preserving m-ary relations on P k*.
Clones (Session 3b)
Gigantic pairs of minimal clones
I. G. Rosenberg and H. Machida (Université de Montréal, Canada)
A pair (f, g) of operations on {0, 1, … , k-1} is called gigantic if each of f and g generates a minimal clone and the set (f, g) generates a clone of all functions on {0, 1, … , k-1}. One of results of the paper is that it gives a general theorem to characterize a gigantic pair. For k=2, there are exactly 2 gigantic pairs (?, ∨) and (?, ∧), for example. It is well known that each of the gigantic pair (?, ∨) and (?, ∧) can generate all of the Boolean functions.
Maximal chains of partial clones containing all idempotent partial functions L. Haddad and J. Fugère (Collége militaire royal du Canada, Canada)
The following are presented in this paper: every partial clone containing all idempotent partial functions on the set {0, 1, … , k-1} is finitely generated; the method for constructing maximal chains of length 2k of such partial clones.
Partial clones and their generating sets
L. Haddad and D. Lau (Collége militaire royal du Canada, Canada)
For ever maximal clone C on {0, 1, … , k-1}, this paper shows the maximal partial clone on {0, 1, … , k-1} that contains the C. Furthermore, it discusses on families of finitely generated
maximal partial clones as well as a family of not finitely generated maximal partial clones. The papers whose numbers are 2, 3, 4 and 6 are closely relating to logic design. The paper no. 4 is interesting because it proposes a new type of multiple-valued logic functions whose operations are motivated by quantum devices based on multiple-valued systems. The paper
no. 3 is also interesting since one would find its applications in decomposition of MVL functions. In the paper no. 5, the indeterminate coefficients method is applied to derive all Kleene algebras with 8 elements. This method is not only derive models of a given algebra, but also can generate its independent and complete axioms.
The author thinks that some of readers are not familiar with clones. So, a short note concerning clones will be given below.
Let k be a finite set with k (>1) elements. Let O k(n) be the set of all n-ary operations from A n
into k, and let O k =U∞
=1
n O k(n). A projection p i n (i = 1, …, n) is an n-ary operation on k such that
p i n (x1, …, x n) = x i for every (x1, …, x n) in A n. Denote by I k the set of all projections. A subset C of O k is a clone on k if (1) C contains I k, i.e., I k?C; (2) C is closed under (functional) composition. The set of all clones on k is a lattice with respect to the inclusion relation. O k is the maximum in the lattice of clones, while I k is the minimum. A clone on k is said to be maximal if (1) C≠O k and (2) C?C’?O k implies C’ = C for any clone C’ on k. A set A of functions on k is called complete if it is possible to define any function on A as a composition of functions on A with the
possible identification of variables. The following are basic and important results concerning clones: A necessary and sufficient condition for a set A of functions on k to be complete is that A is not contained by any maximal clone on k; Maximal clones have been completely determined in terms of relations by I. G. Rosenberg.
Recently, studies on clones are focusing on minimal clones and partial clones. Minimal clones C are a dual concept of maximal clones. That is, a minimal clone C on k is a clone on k such that (1) C≠I k and (2) I k?C’ ?C implies C ' = C for any clone C ' on k. A partial clone C on k is a set of partially specified functions on k such that (1) C contains I k and (2) C is closed under (functional) compositions. The papers in Session Clone deal with minimal clones and partial clones on k.
7. ULSI Workshop
This workshop was held annually in conjunction with ISMVL since 1992. The purpose of the workshop is to provide an opportunity to discuss latest topics in an informal atmosphere. This year, a special focus was on the challenge of intelligent systems and the role of quantum circuits. The program was as follows:
Invited Talks: (Chair: G. Gulak)
Innovation of Intelligent Integrated Systems Architecture -Future Challenge
Michitaka Kamayama (Japan) Quantum Electronic Circuit Concepts by Nanometric Technology
Hans Hartnagel (Germany) Session 1: Nanoelectronics (Chair: T. Waho)
High-Speed Single-Electron Memory and Logic
H. Mizuta, K. Tsukagoshi, K. Nakazato and H. Ahmed (UK)
Programmable HBT-Quantum Dot Structures for Arithmetic MVL
Lutz Micheel (USA), A. Sigurdardottir, H. Hartnagel and K. Mutamba (Germany) GaAs- and InP-based Technologies of Resonant Tunneling Devices
O. Dupuis, P. Mounaix, F. Mollot, O. Vanbesien and D. Lippens (France) Nano-Fabrication Technology and Silicon Nano-Devices
Toshio Baba (Japan) Session 2: BDD and MDD (Chair: C. Scholl)
Nonapproximability Results for OBDD- and FBDD-Minimization
Detlef Sieling (Germany) Improving Reachability Analysis by means of Activity Profiles
Gianpiero Cabodi, Paolo Camurati and Stefano Quer (Italy)
A Word-Level Graph Representation Package
Stefan Hoereth (Germany) Interval Diagram Techniques and Their Applications
Karsten Strehl and Lothar Thiele (Switzerland) Session 3: Logic Design Using Information Theory (Chair: S. Yanushkevich) Information Theory Approach in Logic Design: Results, Trends and Non-Solved Problems
S. Yanushkevich (Poland/Belarus) and D. Simovici (USA) Some Remarks on Information Entropy, Vitality and Information Engine
H. Watanabe (Japan)
Information Theoretical Approach in Evolutionary Circuit Design
C. Moraga (Germany), J. Kolodziejczyk (Poland), M. Opoka (Poland)
and S. Yanushkevich (Poland/Belarus) Information Theoretical Approach in Reed-Muller Expansion Minimization
D. Popel (Belarus), Shmerko (Poland/Belarus), S.Yanushkevich (Poland/Belarus)
References:
1) https://www.doczj.com/doc/3911275242.html,rmatik.uni-freiburg.de/~drechsle/ismvl99/index.html.
2) https://www.doczj.com/doc/3911275242.html,/~mperkows/ISMVL/=index2000.html.