
12-11-20E xam pl e: C onf i gur i ng B FD on I nt er nal B G P P eer S essi ons - Techni cal D ocum ent at i on - S uppor t - Juni κ
1/5
w w w.j uni per
.net /t echpubs/en_U S /j unos12.2/t opi cs/exam pl e/bgp-bf d-i bgp.ht m l Example: Configuring BFD on Internal BGP Peer Sessions
This example shows how to configure internal BGP (IBGP) peer sessions with the Bidirectional Forwarding Detection (BFD) protocol to detect failures in a network.Requirements
Overview
Configuration Verification
Requirements
No special configuration beyond device initialization is required before you configure this example.
Overview
The minimum configuration to enable BFD on IBGP sessions is to include the b f d -l i v e n e s s -d e t e c t i o n m i n i m u m -i n t e r v a l statement in the BGP configuration of all neighbors participating in the BFD session. The m i n i m u m -i n t e r v a l statement specifies the minimum transmit and receive intervals for failure detection. Specifically, this value represents the minimum interval after which the local routing device transmits hello packets as well as the minimum interval that the routing device expects to receive a reply from a neighbor with which it has established a BFD session. You can configure a value from 1 through 255,000 milliseconds.
Optionally, you can specify the minimum transmit and receive intervals separately using the t r a n s m i t -i n t e r v a l m i n i m u m -i n t e r v a l and m i n i m u m -r e c e i v e -i n t e r v a l statements. For information about these and other optional BFD configuration statements, see b f d -l i v e n e s s -d e t e c t i o n .
Note: BFD is an intensive protocol that consumes system resources. Specifying a minimum interval for BFD less than 100 ms for Routing Engine-based
sessions and less than 10 ms for distributed BFD sessions can cause undesired BFD flapping.Depending on your network environment, these additional recommendations might apply:
For large-scale network deployments with a large number of BFD sessions, specify a minimum interval of 300 ms for Routing Engine-based sessions and 100 ms for distributed BFD sessions.
For very large-scale network deployments with a large number of BFD sessions, contact Juniper Networks customer support for more information.For BFD sessions to remain up during a Routing Engine switchover event when nonstop active routing (NSR) is configured, specify a minimum interval of 2500 ms for Routing Engine-based sessions. For distributed BFD sessions with NSR configured, the minimum interval recommendations are unchanged and depend only on your network deployment.
BFD is supported on the default routing instance (the main router), routing instances, and logical systems. This example shows BFD on logical systems.Figure 1 shows a typical network with internal peer sessions.Figure 1: Typical Network with IBGP Sessions
Configuration
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure this example, copy the following commands, paste them into a text file, remove any line breaks, change any details necessary to match your network configuration, and then copy and paste the commands into the CLI at the [e d i t ] hierarchy level.Device A
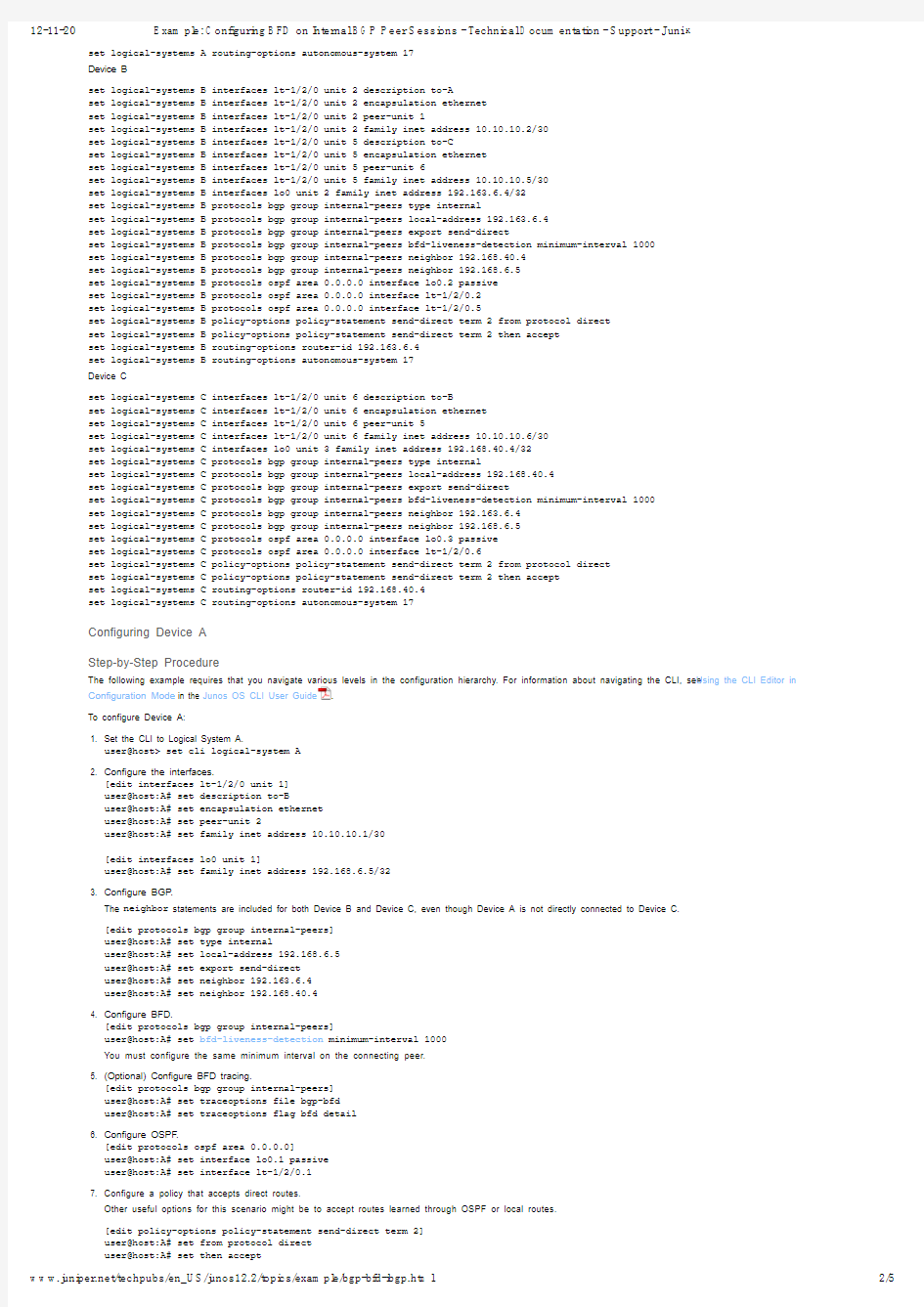
s e t l o g i c a l -s y s t e m s A i n t e r f a c e s l t -1/2/0 u n i t 1 d e s c r i p t i o n t o -B s e t l o g i c a l -s y s t e m s A i n t e r f a c e s l t -1/2/0 u n i t 1 e n c a p s u l a t i o n e t h e r n e t s e t l o g i c a l -s y s t e m s A i n t e r f a c e s l t -1/2/0 u n i t 1 p e e r -u n i t 2s e t l o g i c a l -s y s t e m s A i n t e r f a c e s l t -1/2/0 u n i t 1 f a m i l y i n e t a d d r e s s 10.10.10.1/30s e t l o g i c a l -s y s t e m s A i n t e r f a c e s l o 0 u n i t 1 f a m i l y i n e t a d d r e s s 192.168.6.5/32s e t l o g i c a l -s y s t e m s A p r o t o c o l s b g p g r o u p i n t e r n a l -p e e r s t y p e i n t e r n a l s e t l o g i c a l -s y s t e m s A p r o t o c o l s b g p g r o u p i n t e r n a l -p e e r s t r a c e o p t i o n s f i l e b g p -b f d s e t l o g i c a l -s y s t e m s A p r o t o c o l s b g p g r o u p i n t e r n a l -p e e r s t r a c e o p t i o n s f l a g b f d d e t a i l s e t l o g i c a l -s y s t e m s A p r o t o c o l s b g p g r o u p i n t e r n a l -p e e r s l o c a l -a d d r e s s 192.168.6.5s e t l o g i c a l -s y s t e m s A p r o t o c o l s b g p g r o u p i n t e r n a l -p e e r s e x p o r t s e n d -d i r e c t s e t l o g i c a l -s y s t e m s A p r o t o c o l s b g p g r o u p i n t e r n a l -p e e r s b f d -l i v e n e s s -d e t e c t i o n m i n i m u m -i n t e r v a l 1000s e t l o g i c a l -s y s t e m s A p r o t o c o l s b g p g r o u p i n t e r n a l -p e e r s n e i g h b o r 192.163.6.4s e t l o g i c a l -s y s t e m s A p r o t o c o l s b g p g r o u p i n t e r n a l -p e e r s n e i g h b o r 192.168.40.4s e t l o g i c a l -s y s t e m s A p r o t o c o l s o s p f a r e a 0.0.0.0 i n t e r f a c e l o 0.1 p a s s i v e s e t l o g i c a l -s y s t e m s A p r o t o c o l s o s p f a r e a 0.0.0.0 i n t e r f a c e l t -1/2/0.1s e t l o g i c a l -s y s t e m s A p o l i c y -o p t i o n s p o l i c y -s t a t e m e n t s e n d -d i r e c t t e r m 2 f r o m p r o t o c o l d i r e c t s e t l o g i c a l -s y s t e m s A p o l i c y -o p t i o n s p o l i c y -s t a t e m e n t s e n d -d i r e c t t e r m 2 t h e n a c c e p t s e t l o g i c a l -s y s t e m s A r o u t i n g -o p t i o n s r o u t e r -i d 192.168.6.5
12-11-20
E xam pl e: C onf i gur i ng B FD on I nt er nal B G P P eer S essi ons - Techni cal D ocum ent at i on - S uppor t - Juni κ
2/5
w w w.j uni per .net /t echpubs/en_U S /j unos12.2/t opi cs/exam pl e/bgp-bf d-i bgp.ht m l s e t l o g i c a l -s y s t e m s A r o u t i n g -o p t i o n s a u t o n o m o u s -s y s t e m 17
Device B
s e t l o g i c a l -s y s t e m s B i n t e r f a c e s l t -1/2/0 u n i t 2 d e s c r i p t i o n t o -A
s e t l o g i c a l -s y s t e m s B i n t e r f a c e s l t -1/2/0 u n i t 2 e n c a p s u l a t i o n e t h e r n e t s e t l o g i c a l -s y s t e m s B i n t e r f a c e s l t -1/2/0 u n i t 2 p e e r -u n i t 1s e t l o g i c a l -s y s t e m s B i n t e r f a c e s l t -1/2/0 u n i t 2 f a m i l y i n e t a d d r e s s 10.10.10.2/30s e t l o g i c a l -s y s t e m s B i n t e r f a c e s l t -1/2/0 u n i t 5 d e s c r i p t i o n t o -C s e t l o g i c a l -s y s t e m s B i n t e r f a c e s l t -1/2/0 u n i t 5 e n c a p s u l a t i o n e t h e r n e t s e t l o g i c a l -s y s t e m s B i n t e r f a c e s l t -1/2/0 u n i t 5 p e e r -u n i t 6s e t l o g i c a l -s y s t e m s B i n t e r f a c e s l t -1/2/0 u n i t 5 f a m i l y i n e t a d d r e s s 10.10.10.5/30s e t l o g i c a l -s y s t e m s B i n t e r f a c e s l o 0 u n i t 2 f a m i l y i n e t a d d r e s s 192.163.6.4/32s e t l o g i c a l -s y s t e m s B p r o t o c o l s b g p g r o u p i n t e r n a l -p e e r s t y p e i n t e r n a l s e t l o g i c a l -s y s t e m s B p r o t o c o l s b g p g r o u p i n t e r n a l -p e e r s l o c a l -a d d r e s s 192.163.6.4s e t l o g i c a l -s y s t e m s B p r o t o c o l s b g p g r o u p i n t e r n a l -p e e r s e x p o r t s e n d -d i r e c t s e t l o g i c a l -s y s t e m s B p r o t o c o l s b g p g r o u p i n t e r n a l -p e e r s b f d -l i v e n e s s -d e t e c t i o n m i n i m u m -i n t e r v a l 1000s e t l o g i c a l -s y s t e m s B p r o t o c o l s b g p g r o u p i n t e r n a l -p e e r s n e i g h b o r 192.168.40.4s e t l o g i c a l -s y s t e m s B p r o t o c o l s b g p g r o u p i n t e r n a l -p e e r s n e i g h b o r 192.168.6.5s e t l o g i c a l -s y s t e m s B p r o t o c o l s o s p f a r e a 0.0.0.0 i n t e r f a c e l o 0.2 p a s s i v e s e t l o g i c a l -s y s t e m s B p r o t o c o l s o s p f a r e a 0.0.0.0 i n t e r f a c e l t -1/2/0.2s e t l o g i c a l -s y s t e m s B p r o t o c o l s o s p f a r e a 0.0.0.0 i n t e r f a c e l t -1/2/0.5s e t l o g i c a l -s y s t e m s B p o l i c y -o p t i o n s p o l i c y -s t a t e m e n t s e n d -d i r e c t t e r m 2 f r o m p r o t o c o l d i r e c t s e t l o g i c a l -s y s t e m s B p o l i c y -o p t i o n s p o l i c y -s t a t e m e n t s e n d -d i r e c t t e r m 2 t h e n a c c e p t s e t l o g i c a l -s y s t e m s B r o u t i n g -o p t i o n s r o u t e r -i d 192.163.6.4s e t l o g i c a l -s y s t e m s B r o u t i n g -o p t i o n s a u t o n o m o u s -s y s t e m 17Device C
s e t l o g i c a l -s y s t e m s C i n t e r f a c e s l t -1/2/0 u n i t 6 d e s c r i p t i o n t o -B s e t l o g i c a l -s y s t e m s C i n t e r f a c e s l t -1/2/0 u n i t 6 e n c a p s u l a t i o n e t h e r n e t s e t l o g i c a l -s y s t e m s C i n t e r f a c e s l t -1/2/0 u n i t 6 p e e r -u n i t 5s e t l o g i c a l -s y s t e m s C i n t e r f a c e s l t -1/2/0 u n i t 6 f a m i l y i n e t a d d r e s s 10.10.10.6/30s e t l o g i c a l -s y s t e m s C i n t e r f a c e s l o 0 u n i t 3 f a m i l y i n e t a d d r e s s 192.168.40.4/32s e t l o g i c a l -s y s t e m s C p r o t o c o l s b g p g r o u p i n t e r n a l -p e e r s t y p e i n t e r n a l s e t l o g i c a l -s y s t e m s C p r o t o c o l s b g p g r o u p i n t e r n a l -p e e r s l o c a l -a d d r e s s 192.168.40.4s e t l o g i c a l -s y s t e m s C p r o t o c o l s b g p g r o u p i n t e r n a l -p e e r s e x p o r t s e n d -d i r e c t s e t l o g i c a l -s y s t e m s C p r o t o c o l s b g p g r o u p i n t e r n a l -p e e r s b f d -l i v e n e s s -d e t e c t i o n m i n i m u m -i n t e r v a l 1000s e t l o g i c a l -s y s t e m s C p r o t o c o l s b g p g r o u p i n t e r n a l -p e e r s n e i g h b o r 192.163.6.4s e t l o g i c a l -s y s t e m s C p r o t o c o l s b g p g r o u p i n t e r n a l -p e e r s n e i g h b o r 192.168.6.5s e t l o g i c a l -s y s t e m s C p r o t o c o l s o s p f a r e a 0.0.0.0 i n t e r f a c e l o 0.3 p a s s i v e s e t l o g i c a l -s y s t e m s C p r o t o c o l s o s p f a r e a 0.0.0.0 i n t e r f a c e l t -1/2/0.6s e t l o g i c a l -s y s t e m s C p o l i c y -o p t i o n s p o l i c y -s t a t e m e n t s e n d -d i r e c t t e r m 2 f r o m p r o t o c o l d i r e c t s e t l o g i c a l -s y s t e m s C p o l i c y -o p t i o n s p o l i c y -s t a t e m e n t s e n d -d i r e c t t e r m 2 t h e n a c c e p t s e t l o g i c a l -s y s t e m s C r o u t i n g -o p t i o n s r o u t e r -i d 192.168.40.4s e t l o g i c a l -s y s t e m s C r o u t i n g -o p t i o n s a u t o n o m o u s -s y s t e m 17
Configuring Device A Step-by-Step Procedure
The following example requires that you navigate various levels in the configuration hierarchy. For information about navigating the CLI, see Using the CLI Editor in Configuration Mode in the Junos OS CLI User Guide .
To configure Device A:
1. Set the CLI to Logical System A.
u s e r @h o s t > s e t c l i l o g i c a l -s y s t e m A
2. Configure the interfaces.[e d i t i n t e r f a c e s l t -1/2/0 u n i t 1]u s e r @h o s t :A # s e t d e s c r i p t i o n t o -B u s e r @h o s t :A # s e t e n c a p s u l a t i o n e t h e r n e t u s e r @h o s t :A # s e t p e e r -u n i t 2u s e r @h o s t :A # s e t f a m i l y i n e t a d d r e s s 10.10.10.1/30[e d i t i n t e r f a c e s l o 0 u n i t 1]u s e r @h o s t :A # s e t f a m i l y i n e t a d d r e s s 192.168.6.5/32
3. Configure BGP.
The n e i g h b o r statements are included for both Device B and Device C, even though Device A is not directly connected to Device C.[e d i t p r o t o c o l s b g p g r o u p i n t e r n a l -p e e r s ]u s e r @h o s t :A # s e t t y p e i n t e r n a l u s e r @h o s t :A # s e t l o c a l -a d d r e s s 192.168.6.5u s e r @h o s t :A # s e t e x p o r t s e n d -d i r e c t u s e r @h o s t :A # s e t n e i g h b o r 192.163.6.4u s e r @h o s t :A # s e t n e i g h b o r 192.168.40.4
4. Configure BFD.[e d i t p r o t o c o l s b g p g r o u p i n t e r n a l -p e e r s ]u s e r @h o s t :A # s e t b f d -l i v e n e s s -d e t e c t i o n m i n i m u m -i n t e r v a l 1000You must configure the same minimum interval on the connecting peer.
5. (Optional) Configure BFD tracing.[e d i t p r o t o c o l s b g p g r o u p i n t e r n a l -p e e r s ]u s e r @h o s t :A # s e t t r a c e o p t i o n s f i l e b g p -b f d u s e r @h o s t :A # s e t t r a c e o p t i o n s f l a g b f d d e t a i l
6. Configure OSPF.[e d i t p r o t o c o l s o s p f a r e a 0.0.0.0]u s e r @h o s t :A # s e t i n t e r f a c e l o 0.1 p a s s i v e u s e r @h o s t :A # s e t i n t e r f a c e l t -1/2/0.1
7. Configure a policy that accepts direct routes.
Other useful options for this scenario might be to accept routes learned through OSPF or local routes.[e d i t p o l i c y -o p t i o n s p o l i c y -s t a t e m e n t s e n d -d i r e c t t e r m 2]u s e r @h o s t :A # s e t f r o m p r o t o c o l d i r e c t u s e r @h o s t :A # s e t t h e n a c c e p t
12-11-20E xam pl e: C onf i gur i ng B FD on I nt er nal B G P P eer S essi ons - Techni cal D ocum ent at i on - S uppor t - Juni κ
3/5
w w w.j uni per .net /t echpubs/en_U S /j unos12.2/t opi cs/exam pl e/bgp-bf d-i bgp.ht m l 8. Configure the router ID and the autonomous system (AS) number.
[e d i t r o u t i n g -o p t i o n s ]u s e r @h o s t :A # s e t r o u t e r -i d 192.168.6.5u s e r @h o s t :A # s e t a u t o n o m o u s -s y s t e m 17
9. If you are done configuring the device, enter c o m m i t from configuration mode. Repeat these steps to configure Device B and Device C.
Results
From configuration mode, confirm your configuration by entering the s h o w i n t e r f a c e s , s h o w p o l i c y -o p t i o n s , s h o w p r o t o c o l s , and s h o w r o u t i n g -o p t i o n s commands. If the output does not display the intended configuration, repeat the instructions in this example to correct the configuration.u s e r @h o s t :A # s h o w i n t e r f a c e s l t -1/2/0 {
u n i t 1 {
d e s c r i p t i o n t o -B ;e n c a p s u l a t i o n e t h e r n e t ;p e e r -u n i t 2;f a m i l y i n e t {
a d d r e s s 10.10.10.1/30;
}
}
}l o 0 {
u n i t 1 {
f a m i l y i n e t {
a d d r e s s 192.168.6.5/32;
}
}
}u s e r @h o s t :A # s h o w p o l i c y -o p t i o n s p o l i c y -s t a t e m e n t s e n d -d i r e c t {
t e r m 2 {
f r o m p r o t o c o l d i r e c t ;t h e n a c c e p t ;
}
}u s e r @h o s t :A # s h o w p r o t o c o l s b g p {
g r o u p i n t e r n a l -p e e r s {
t y p e i n t e r n a l ;t r a c e o p t i o n s {
f i l e b
g p -b f d ;f l a g b f d d e t a i l ;
}l o c a l -a d d r e s s 192.168.6.5;e x p o r t s e n d -d i r e c t ;b f d -l i v e n e s s -d e t e c t i o n {
m i n i m u m -i n t e r v a l 1000;
}n e i g h b o r 192.163.6.4;n e i g h b o r 192.168.40.4;
}
}o s p f {
a r e a 0.0.0.0 {
i n t e r f a c e l o 0.1 {
p a s s i v e ;
}i n t e r f a c e l t -1/2/0.1;
}
}u s e r @h o s t :A # s h o w r o u t i n g -o p t i o n s r o u t e r -i d 192.168.6.5;a u t o n o m o u s -s y s t e m 17;
Verification
Confirm that the configuration is working properly.Verifying That BFD Is Enabled Verifying That BFD Sessions Are Up Viewing Detailed BFD Events
Viewing Detailed BFD Events After Deactivating and Reactivating a Loopback Interface
Verifying That BFD Is Enabled
Purpose
Verify that BFD is enabled between the IBGP peers.
A ction
From operational mode, enter the s h o w b g p n e i g h b o r command. You can use the | m a t c h b f d filter to narrow the output.u s e r @h o s t :A > s h o w b g p n e i g h b o r | m a t c h b f d O p t i o n s : B F D : e n a b l e d , u p T r a c e f i l e : /v a r /l o g /A /b g p -b f d s i z e 131072 f i l e s 10 O p t i o n s : B F D : e n a b l e d , u p T r a c e f i l e : /v a r /l o g /A /b g p -b f d s i z e 131072 f i l e s 10
Meaning
The output shows that Logical System A has two neighbors with BFD enabled. When BFD is not enabled, the output displays B F D : d i s a b l e d , d o w n , and the option is absent. If BFD is enabled and the session is down, the output displays B F D : e n a b l e d , d o w n . The output also shows that BFD-related events are being written to a log file because trace operations are configured.
12-11-20E xam pl e: C onf i gur i ng B FD on I nt er nal B G P P eer S essi ons - Techni cal D ocum ent at i on - S uppor t - Juni κ
4/5
w w w.j uni per .net /t echpubs/en_U S /j unos12.2/t opi cs/exam pl e/bgp-bf d-i bgp.ht m l Verifying That BFD Sessions Are Up
Purpose
Verify that the BFD sessions are up, and view details about the BFD sessions.
A ction
From operational mode, enter the s h o w b f d s e s s i o n e x t e n s i v e command.
u s e r @h o s t :A > s h o w b f d s e s s i o n e x t e n s i v e
D e t e c t T r a n s m i t A d d r e s s S t a t e I n t e r f a c e T i m e I n t e r v a l M u l t i p l i e r 192.163.6.4 U p 3.000 1.000 3 C l i e n t B G P , T X i n t e r v a l 1.000, R X i n t e r v a l 1.000 S e s s i o n u p t i m e 00:54:40 L o c a l d i a g n o s t i c N o n e , r e m o t e d i a g n o s t i c N o n e R e m o t e s t a t e U p , v e r s i o n 1 L o g i c a l s y s t e m 12, r o u t i n g t a b l e i n d e x 25 M i n a s y n c i n t e r v a l 1.000, m i n s l o w i n t e r v a l 1.000 A d a p t i v e a s y n c T X i n t e r v a l 1.000, R X i n t e r v a l 1.000 L o c a l m i n T X i n t e r v a l 1.000, m i n i m u m R X i n t e r v a l 1.000, m u l t i p l i e r 3 R e m o t e m i n T X i n t e r v a l 1.000, m i n R X i n t e r v a l 1.000, m u l t i p l i e r 3 L o c a l d i s c r i m i n a t o r 10, r e m o t e d i s c r i m i n a t o r 9
E c h o m o d e d i s a b l e d /i n a c t i v e M u l t i -h o p r o u t e t a b l e 25, l o c a l -a d d r e s s 192.168.6.5 D e t e c t T r a n s m i t A d d r e s s S t a t e I n t e r f a c e T i m e I n t e r v a l M u l t i p l i e r 192.168.40.4 U p 3.000 1.000 3 C l i e n t B G P , T X i n t e r v a l 1.000, R X i n t e r v a l 1.000 S e s s i o n u p t i m e 00:48:03 L o c a l d i a g n o s t i c N o n e , r e m o t e d i a g n o s t i c N o n e R e m o t e s t a t e U p , v e r s i o n 1 L o g i c a l s y s t e m 12, r o u t i n g t a b l e i n d e x 25 M i n a s y n c i n t e r v a l 1.000, m i n s l o w i n t e r v a l 1.000 A d a p t i v e a s y n c T X i n t e r v a l 1.000, R X i n t e r v a l 1.000 L o c a l m i n T X i n t e r v a l 1.000, m i n i m u m R X i n t e r v a l 1.000, m u l t i p l i e r 3 R e m o t e m i n T X i n t e r v a l 1.000, m i n R X i n t e r v a l 1.000, m u l t i p l i e r 3 L o c a l d i s c r i m i n a t o r 14, r e m o t e d i s c r i m i n a t o r 13 E c h o m o d e d i s a b l e d /i n a c t i v e M u l t i -h o p r o u t e t a b l e 25, l o c a l -a d d r e s s 192.168.6.52 s e s s i o n s , 2 c l i e n t s C u m u l a t i v e t r a n s m i t r a t e 2.0 p p s , c u m u l a t i v e r e c e i v e r a t e 2.0 p p s
Meaning
The T X i n t e r v a l 1.000, R X i n t e r v a l 1.000 output represents the setting configured with the m i n i m u m -i n t e r v a l statement. All of the other output represents the default settings for BFD. To modify the default settings, include the optional statements under the b f d -l i v e n e s s -d e t e c t i o n statement.
Viewing Detailed BFD Events
Purpose
View the contents of the BFD trace file to assist in troubleshooting, if needed.
A ction
From operational mode, enter the f i l e s h o w /v a r /l o g /A /b g p -b f d command.
u s e r @h o s t :A > f i l e s h o w /v a r /l o g /A /b g p -b f d A u g 15 17:07:25 t r a c e _o n : T r a c i n g t o "/v a r /l o g /A /b g p -b f d " s t a r t e d A u g 15 17:07:26.492190 b g p _p e e r _i n i t : B G P p e e r 192.163.6.4 (I n t e r n a l A S 17) l o c a l a d d r e s s 192.168.6.5 n o t f o u n d . L e a v i n g p e e r i d l e d A u g 15 17:07:26.493176 b g p _p e e r _i n i t : B G P p e e r 192.168.40.4 (I n t e r n a l A S 17) l o c a l a d d r e s s 192.168.6.5 n o t f o u n d . L e a v i n g p e e r i d l e d A u g 15 17:07:32.597979 t a s k _c o n n e c t : t a s k B G P _17.192.163.6.4+179 a d d r 192.163.6.4+179: N o r o u t e t o h o s t A u g 15 17:07:32.599623 b g p _c o n n e c t _s t a r t : c o n n e c t 192.163.6.4 (I n t e r n a l A S 17): N o r o u t e t o h o s t A u g 15 17:07:36.869394 t a s k _c o n n e c t : t a s k B G P _17.192.168.40.4+179 a d d r 192.168.40.4+179: N o r o u t e t o h o s t A u g 15 17:07:36.870624 b g p _c o n n e c t _s t a r t : c o n n e c t 192.168.40.4 (I n t e r n a l A S 17): N o r o u t e t o h o s t A u g 15 17:08:04.599220 t a s k _c o n n e c t : t a s k B G P _17.192.163.6.4+179 a d d r 192.163.6.4+179: N o r o u t e t o h o s t A u g 15 17:08:04.601135 b g p _c o n n e c t _s t a r t : c o n n e c t 192.163.6.4 (I n t e r n a l A S 17): N o r o u t e t o h o s t A u g 15 17:08:08.869717 t a s k _c o n n e c t : t a s k B G P _17.192.168.40.4+179 a d d r 192.168.40.4+179: N o r o u t e t o h o s t A u g 15 17:08:08.869934 b g p _c o n n e c t _s t a r t : c o n n e c t 192.168.40.4 (I n t e r n a l A S 17): N o r o u t e t o h o s t A u g 15 17:08:36.603544 a d v e r t i s i n g r e c e i v i n g -s p e a k e r o n l y c a p a b i l t y t o n e i g h b o r 192.163.6.4 (I n t e r n a l A S 17)A u g 15 17:08:36.606726 b g p _r e a d _m e s s a g e : 192.163.6.4 (I n t e r n a l A S 17): 0 b y t e s b u f f e r e d A u g 15 17:08:36.609119 I n i t i a t e d B F D s e s s i o n t o p e e r 192.163.6.4 (I n t e r n a l A S 17): a d d r e s s =192.163.6.4 i f i n d e x =0 i f n a m e =(n o n e ) t x i v l =1000 r x i v l =1000 m u l t =3 v e r =255A u g 15 17:08:36.734033 a d v e r t i s i n g r e c e i v i n g -s p e a k e r o n l y c a p a b i l t y t o n e i g h b o r 192.168.40.4 (I n t e r n a l A S 17)A u g 15 17:08:36.738436 I n i t i a t e d B F D s e s s i o n t o p e e r 192.168.40.4 (I n t e r n a l A S 17): a d d r e s s =192.168.40.4 i f i n d e x =0 i f n a m e =(n o n e ) t x i v l =1000 r x i v l =1000 m u l t =3 v e r =255A u g 15 17:08:40.537552 B F D s e s s i o n t o p e e r 192.163.6.4 (I n t e r n a l A S 17) u p A u g 15 17:08:40.694410 B F D s e s s i o n t o p e e r 192.168.40.4 (I n t e r n a l A S 17) u p
Meaning
Before the routes are established, the N o r o u t e t o h o s t message appears in the output. After the routes are established, the last two lines show that both BFD sessions come up.
Viewing Detailed BFD Events After Deactivating and Reactivating a Loopback Interface
Purpose
Check to see what happens after bringing down a router or switch and then bringing it back up. To simulate bringing down a router or switch, deactivate the loopback interface on Logical System B.
A ction
1. From configuration mode, enter the d e a c t i v a t e l o g i c a l -s y s t e m s B i n t e r f a c e s l o 0 u n i t 2 f a m i l y i n e t command.u s e r @h o s t :A # d e a c t i v a t e l o g i c a l -s y s t e m s B i n t e r f a c e s l o 0 u n i t 2 f a m i l y i n e t u s e r @h o s t :A # c o m m i t
2. From operational mode, enter the f i l e s h o w /v a r /l o g /A /b g p -b f d command.u s e r @h o s t :A > f i l e s h o w /v a r /l o g /A /b g p -b f d ...A u g 15 17:20:55.995648 b g p _r e a d _v 4_m e s s a g e :9747: N O T I F I C A T I O N r e c e i v e d f r o m 192.16
3.6.4 (I n t e r n a l A S 17): c o d e 6 (C e a s e ) s u b c o d e 6 (O t h e r C o n f i g u r a t i o n C h a n g e )A u g 15 17:20:56.004508 T e r m i n a t e d B F D s e s s i o n t o p e e r 192.163.6.4 (I n t e r n a l A S 17)
12-11-20
E xam pl e: C onf i gur i ng B FD on I nt er nal B G P P eer S essi ons - Techni cal D ocum ent at i on - S uppor t - Juni κ
5/5
w w w.j uni per .net /t echpubs/en_U S /j unos12.2/t opi cs/exam pl e/bgp-bf d-i bgp.ht m l
Site Map / RSS Feeds / Careers / Accessibility / Feedback / Privacy & Policy / Legal Notices
Copyright? 1999-2012 Juniper Networks, Inc. All rights
reserved.
A u g 15 17:21:28.007755 t a s k _c o n n e c t : t a s k
B G P _17.192.163.6.4+179 a d d r 192.163.6.4+179: N o r o u t e t o h o s t
A u g 15 17:21:28.008597 b g p _c o n n e c t _s t a r t : c o n n e c t 192.163.6.4 (I n t e r n a l A S 17): N o r o u t e t o h o s t
3. From configuration mode, enter the a c t i v a t e l o g i c a l -s y s t e m s B i n t e r f a c e s l o 0 u n i t 2 f a m i l y i n e t command.u s e r @h o s t :A # a c t i v a t e l o g i c a l -s y s t e m s B i n t e r f a c e s l o 0 u n i t 2 f a m i l y i n e t u s e r @h o s t :A # c o m m i t
4. From operational mode, enter the f i l e s h o w /v a r /l o g /A /b g p -b f d command.u s e r @h o s t :A > f i l e s h o w /v a r /l o g /A /b g p -b f d ...A u g 15 17:25:53.623743 a d v e r t i s i n g r e c e i v i n g -s p e a k e r o n l y c a p a b i l t y t o n e i g h b o r 192.163.6.4 (I n t e r n a l A S 17)A u g 15 17:25:53.631314 I n i t i a t e d B F D s e s s i o n t o p e e r 192.163.6.4 (I n t e r n a l A S 17): a d d r e s s =192.163.6.4 i f i n d e x =0 i f n a m e =(n o n e ) t x i v l =1000 r x i v l =1000 m u l t =3 v e r =255A u g 15 17:25:57.570932 B F D s e s s i o n t o p e e r 192.163.6.4 (I n t e r n a l A S 17) u p
Related Documentation
M Series
Understanding BFD Authentication for BGP PTX Series
Understanding BFD Authentication for BGP QFX Series
Understanding BFD Authentication for BGP T Series
Understanding BFD Authentication for BGP Additional Information
Junos OS Feature Support Reference for SRX Series and J Series Devices
Published: 2012-06-27
BFD技术白皮书 本文档介绍了双向转发检测(BFD)技术的原理及应用,BFD是一套用来快速检测的国际标准协议,提供了一种轻负荷,短周期的故障检测。迈普公司已在高端网络产品上实现了BFD技术,可以为用户提供完整的解决方案,从而能够大幅提高网络的服务质量。
目录 1概述 (3) 2 技术简介 (3) 2.1BFD技术原理 (3) 2.2 术语 (4) 3 关键技术 (4) 3.1 报文格式 (4) 3.2 协议状态机 (6) 3.3工作模式 (7) 3.4会话的建立 (8) 4 典型应用 (11) 4.1 BFD加快路由协议收敛 (11) 4.2 BFD加快VRRP协议收敛 (12)
1概述 众所周知,IP网络并不具备秒级以下的间歇性故障修复功能,而传统路由架构在对实时应用(如语音)进行准确故障检测方面能力有限。随着VoIP应用的激增,实现快速网络故障检测和修复越发显得必要。网络设备的一个日益重要的特色就是可以迅速的检测到临近系统之间的通信故障,以便更快的建立或切换到备用路径。在某些环境中由于数据链路硬件的作用可以使故障检测相当的迅速(例如SDH)。但是很多媒介并没有提供这种能力(例如以太),还有一些无法实现端到端的路径检测。 如果硬件不能够对故障检测提供帮助时,网络中将使用缓慢的Hello机制来进行故障检测,这一般是由路由协议来提供。而目前存在的路由协议所能够提供的可以检测到网络故障的最快时间基本都是秒级的,这对于某些应用来说实在是太长了,并且当网络业务达到吉比特时,秒级的故障检测速度将会导致大量数据的丢失。此外,路由协议所提供的Hello机制只有当该路由协议被使用时才有效,并且路由协议所提供的检测含义略有不同——它们检测的是两个路由协议引擎之间路径上的故障。 双向转发检测(Bidirectional Forwarding Detection ,BFD)能大大提高网络的故障检测速度。IETF草案标准BFD提供了一种简单、轻量和抽象的方法,对网络链接能力和系统通信转发功能进行检测。BFD的目标之一就是在临近的转发引擎之间的路径上提供低耗费、短周期的故障检测。而另一个目标则是提供一种专门的机制用于存活检测,适用于任何媒介、任何协议,并为检测周期和耗费提供较宽的选择范围,以避免不同检测方式的重叠。BFD协议的出现,为上述问题提出了一种解决方案,BFD能够在系统之间的任何类型通道上进行故障检测,这些通道包括直连的物理链路,虚电路,隧道,MPLS LSP,多跳路由通道,以及非直连的通道。同时正是由于BFD实现故障检测的简单、单一性,致使BFD能够专注于转发故障的快速检测,使故障检测时间提高到毫秒级。BFD功能实现简单,是针对通信转发故障检测的最好方案。 2 技术简介 2.1BFD技术原理 BFD是一种高速的独立Hello协议,可以用于检测一对邻近系统之间任何类型的路径故障。BFD在一对邻近系统间进行对等会话,一对邻近系统在它们之间建立会话的通道上周期性或间歇性的发送检测报文,如果某个系统在足够长的时间内没有收到对端的检测报文,则
策略路由配置与BFD 38.1 理解策略路由 38.1.1 策略路由概述 策略路由 ( PBR :Policy-Based Routing )提供了一种比基于目的地址进行路由转发更加灵活的数据包路由转发机制。策略路由可以根据IP/IPv6 报文源地址、目的地址、端口、报文长度等内容灵活地进行路由选择。 现有用户网络,常常会出现使用到多个ISP ( Internet Server Provider ,Internet 服务提供商)资源的情形,不同ISP 申请到的带宽不一;同时,同一用户环境中需要对重点用户资源保证等目的,对这部分用户不能够再依据普通路由表进行转发,需要有选择的进行数据报文的转发控制,因此,策略路由技术即能够保证ISP 资源的充分利用,又能够很好的满足这种灵活、多样的应用。 IP/IPv6 策略路由只会对接口接收的报文进行策略路由,而对于从该接口转发出去的报文不受策略路由的控制;一个接口应用策略路由后,将对该接口接收到的所有包进行检查,不符合路由图任何策略的数据包将按照普通的路由转发 进行处理,符合路由图中某个策略的数据包就按照该策略中定义的操作进行转发。 一般情况下,策略路由的优先级高于普通路由,能够对IP/IPv6 报文依据定义的策略转发;即数据报文先按照IP/IPv6 策略路由进行转发,如果没有匹配任意一个的策略路由条件,那么再按照普通路由进行转发。用户也可以配置策略 路由的优先级比普通路由低,接口上收到的IP/IPv6 报文则先进行普通路由的转发,如果无法匹配普通路由,再进 行策略路由转发。 用户可以根据实际情况配置设备转发模式,如选择负载均衡或者冗余备份模式,前者设置的多个下一跳会进行负载均衡,还可以设定负载分担的比重;后者是应用多个下一跳处于冗余模式,即前面优先生效,只有前面的下一跳无效 时,后面次优的下一跳才会生效。用户可以同时配置多个下一跳信息。 策略路由可以分为两种类型:一、对接口收到的IP 报文进行策略路由。该类型的策略路由只会对从接口接收的报 文进行策略路由,而对于从该接口转发出去的报文不受策略路由的控制; 二、对本设备发出的IP 报文进行策略路由。该类型策略路由用于控制本机发往其它设备的IP 报文,对于外部设备 发送给本机的IP 报文则不受该策略路由控制。 38.1.2 策略路由基本概念/特性 38.1.2.1 策略路由应用过程 应用策略路由,必须先创建路由图,然后在接口上应用该路由图。一个路由图由很多条策略组成,每条策略都有对应的序号( Sequence ),序号越小,该条策略的优先级越高。 每条策略又由一条或者多条match 语句以及对应的一条或者多条set 语句组成。match 语句定义了IP/IPv6 报文的匹配规则,set 语句定义了对符合匹配规则的IP/IPv6 报文处理动作。在策略路由转发过程,报文依优先级从高到底依次匹配,只要匹配前面的策略,就执行该策略对应的动作,然后退出策略路由的执行。
故障检测的方法: 1.硬件检测: 通过SDH告警检测链路故障。硬件检测的优点是可以很快发现故障,但并不是所有介质都能提供硬件检测 2.慢Hello机制: 通常指路由协议的Hello机制。这种机制检测到故障所需时间为秒级。对于高速数据传输,例如吉比特速率级,超过1秒的检测时间将导致大量数据丢失;对于时延3敏感的业务,例如语音业务,超过1秒的延迟也是不能接受的。并且,这种机制依赖于路由协议 3.其他检测机制: 不同的协议或设备制造商有时会提供专用的检测机制,但在系统间互联互通时,这样的专用检测机制通常难以部署 BFD(Bidirectional Forwarding Detection):双向转发检测 提供了一个通用的标准化的介质无关和协议无关的快速故障检测机制,一种全网统一、检测迅速、监控网络中链路或者IP路由的双向转发连通状况,并为上层应用提供服务的技术 作用: 用于快速检测、监控网络中链路或者IP路由的转发连通状况 优点: 对相邻转发引擎之间的通道提供轻负荷、快速故障检测。这些故障包括接口、数据链路,甚至有可能是转发引擎本身 用单一的机制对任何介质、任何协议层进行实时检测 可以实现快速检测并监控网络中链路或IP路由的转发连通状态,改善网络性能 相邻系统之间通过快速检测发现通信故障,可以更快地帮助用户建立起备份通道以便恢复通信,保证网络可靠性
工作原理: BFD会话建立后周期性地快速发送BFD报文,若在检测时间内没有收到对端BFD报文则认为该双向转发路径发生了故障,通知被服务的相关层应用进行相应的处理 本身并没有邻居发现机制,而是靠被服务的上层应用通知其邻居信息以建立会话 不管是物理接口状态、二层链路状态、网络层地址可达性、还是传输层连接状态、应用层协议运行状态,都可以被BFD感知到 BFD会话建立方式和检测机制: BFD的标识符: 定义:BFD建立会话存在标识符的概念,类似于OSPF建立邻居需要一个路由器的Router ID 分类:1.本地标识符:用于表示本端设备 2.远端标识符:用于表示对端设备 BFD建立会话方式: 1.静态建立:通过命令行手工配置BFD会话参数,包括配置本地标识符和远端标识符等,然后手工下发BFD会话建立请求 2.动态建立:由应用程序触发创建BFD会话 当应用程序动态触发创建BFD会话时,系统分配属于动态会话标识符区域的值作为BFD会话的本地标识符 然后向对端发送Remote Discriminator的值为0的BFD控制报文,进行会话协商 当BFD会话的一端收到Remote Discriminator的值为0的BFD控制报文时,判断该报文是否与本地BFD会话匹配,如果匹配,则学习接收到的BFD报文中Local Discriminator的值,获取远端标识符 BFD的检测机制:
BFD技术原理及其应用 一、BFD简介 1.BFD(Bidirectional Forwarding Detection,双向转发检测)是一套全网统一的检测机制,用于快速检测、监控网络中链路或者IP 路由的转发连通状况 2.为了提升现有网络性能,邻居之间必须能快速检测到通信故障,从而更快的建立起备用通道恢复通信 二、常用的故障检测方法 1.硬件检测:例如通过SDH(Synchronous Digital Hierarchy,同步数字体系)告警检测链路 故障。硬件检测的优点是可以很快发现故障,但并不是所有介质都能提供硬件 检测 2.慢Hello机制:通常采用路由协议中的Hello 报文机制。这种机制检测到故障所需时间为 秒级。对于高速数据传输(例如吉比特速率级)超过1 秒的检测时间将 导致大量数据丢失;对于时延敏感的业务(例如语音业务)超过1 秒的 延迟也是不能接受的。并且,这种机制依赖于路由协议 3.其他检测机制:不同的协议有时会提供专用的检测机制,但在系统间互联互通时,这样 的专用检测机制通常难以部署 三、BFD的工作机制 1.概述: ①BFD 提供了一个通用的、标准化的、介质无关、协议无关的快速故障检测机制, 可以为各上层协议如路由协议、MPLS 等统一地快速检测两台路由器间双向转发 路径的故障 ②BFD 在两台路由器上建立会话,用来监测两台路由器间的双向转发路径,为上层 协议服务 ③BFD本身并没有发现机制,而是靠被服务的上层协议通知其与谁建立会话,会话 建立后如果在检测时间内没有收到对端的BFD 控制报文则认为发生故障,通知被 服务的上层协议,上层协议进行相应的处理 2.BFD的工作流程 ①流程图
2016-11-29 华为机密,未经许可不得扩散 第1页, 共47页 BFD 应用场景分析 华为技术有限公司 版权所有 侵权必究 (IPD-PTM / 仅供内部使用)
修订记录 2016-11-29 华为机密,未经许可不得扩散第2页, 共47页
目录 BFD应用场景分析 (1) 1概述 (5) 2BFD协议基本原理介绍 (5) 3BFD for LSP应用场景分析 (7) 3.1BFD + TE HSB应用场景 (7) 3.2BFD + TE FRR应用场景 (13) 3.3BFD + TE Tunnel 1:1保护场景 (22) 3.4BFD + LDP FRR应用场景 (25) 3.5BFD + VPN FRR 应用场景 (28) 4BFD for 路由应用场景分析 (33) 4.1BFD For OSPF邻居 (33) 4.2BFD For ISIS邻居 (33) 4.3BFD For BGP邻居 (34) 4.4BFD For 静态路由 (36) 4.5BFD For VRRP (37) 4.6BFD For IP FRR (42) 5BFD for 接口状态联动分析 (44) 5.1物理接口应用场景 (44) 5.2Trunk接口应用场景 (44) 5.3物理子接口应用场景 (46) 6附录 (47) 2016-11-29 华为机密,未经许可不得扩散第3页, 共47页
BFD 应用场景分析 关键词:BFD,PST,PIS 快速检测,保护 摘 要:本文从应用的角度着重介绍了不同BFD session 和不同应用APP 的结合应用场景 缩略语清单: 参考资料清单:
BFD原理
介绍 网络设备一个越来越重要的特征是,要求对相邻系统之间通信故障进行快速检测,这样可以更快的建立起替代通道。当前,在特定的环境下,当数据链路硬件上出现故障可以相当快的检测到。而在某些媒介却不能检测通道上的一些特定故障,例如,接口或者转发引擎部件的故障。 在路由协议网络中,当故障不能通过硬件信号检测出来时,网络采用相对较慢“Hello”机制。在目前的协议中,采用“Hello”机制检测到故障的时间要超过1秒钟,这对某些应用来说时间太长了,当数据速率到吉比特时,这么长时间代表了大量的数据丢失。而且,在没有使用路由协议的地方,“Hello”机制是没有用处的,并且,对两个路由协议引擎之间通道故障的检测的语义也是稍微有点差别的。 BFD的目标是对相邻转发引擎之间通道故障提供轻负荷、持续时间短的检测。这些故障包括接口,数据链路,甚至可能是转发引擎本身。 BFD另外一个目标是提供一个单一的机制,它能够用来对任何媒介、任何协议层进行实时地检测,并且检测的时间与开销范围比较宽,这样防止产生一些其他的方法。这篇文档给出了基本协议的详细情况,对一些机制的使用是与应用相关的,将在单独的应用系列文档中描述。
设计 BFD设计用来检测相邻两个转发引擎之间的通信故障。在转发引擎与控制引擎分离的情况下,BFD是打算在实施在系统转发引擎的某些部件上。这不但将协议更多的绑定到转发平面,而且将协议从路由协议引擎中分离出来。BFD也可以实施在控制平面,尽管这样做可能会导致一些故障检测不到。 BFD运行在任何数据协议的顶层,这个数据协议用于两个系统之间进行数据转发。BFD总是运行在单播、P2P模式。BFD净荷可以作为任何媒介或者网络的封装协议净荷在网络中传输。BFD可以运行在一个系统的多个协议层上。任何特定BFD会话的操作上下文都是与它的封装相关的。 BFD能够在系统之间的任何类型通道上进行故障检测,这些通道包括直接的物理链路,虚电路,隧道,MPLS LSPs,多跳路由通道,以及非直接的通道。在同一对系统之间,如果存在多条通道,至少在一个方向上有多条通道也行,则可以在这对系统之间建立多个BFD会话。 在建立一个BFD会话,或者在拆除一个BFD会话时,BFD状态机实施一个三向握手,保证两个系统都能知道状态的改变。 BFD可以抽象成一个简单的服务,它提供的服务原语包括,在给定目的地址以及其他参数前提下,创建、删除、修改一个BFD会话。BFD最终提供一个信号给它的客户层,表示BFD会话开始或者结束。
基本原理的掌握和应用 一、选择题 例题:意识是客观存在的反映说明:(?? ) A、意识的感性形式是客观存在的反映; B、意识的理性形式是客观存在的反映; C、意识的正确内容是客观存在的反映; D、意识的错误内容是客观存在的反映; E、意识的任何变动都是对客观存在的反映。 答案:(A、B、C、D)。 题解说明:意识是客观存在的反映,说明意识的感性形式和理性形式、正确内容和错误内容都是对客观存在的反映,区别只在于现象的反映和本质的反映,符合客观实际的反映和歪曲客观实际的反映。意识的变动则不一定都是客观实际的反映,它可以是主观的设想和虚构,也可以是各种意识之间的相互影响和相互作用所引起的。 (一)单项选择题 1、在人的意识产生过程中起决定作用的是:(?? ) A、直立行走; B、生产劳动; C、语言的产生; D、人脑的完善。 2、科学证明人脑是:(?? ) A、思维的源泉; B、思维的产物; C、思维的器官; D、思维的对象。 3、反射的第二信号系统是:(?? ) A、所有生物都有的; B、人和动物共有的; C、动物所特有的; D、人所特有的。 4、正确发挥意识能动性的前提条件是:(?? ) A、遵循物质运动的客观规律; B、充分发挥个人的积极主动性; C、坚持以正确的理论原则为指导; D、排除错误思想的干扰。 5、人工智能的思维模拟:(?? ) A、能完全代替人类思维; B、能部分代替人类思维; C、能超过人类思维并主宰人类; D、与人类思维无关。 答案:1、(B);2、(C);3、(D);4、(A);5、(B)。 (二)双项选择题 1、就起源来说,意识是:(?? ) A、自然界长期发展的产物; B、社会劳动的产物; C、上帝创人时,“嵌入”人脑中的; D、天才头脑中创造的; E、动物进化的产物。 2、就其本质来说,意识是:(?? ) A、大脑的机能; B、人脑的机能; C、客观存在的反映; D、物质的分泌物; E、自我感觉。 3、割裂物质和意识的辩证关系在理论上会导致:(?? ) A、机械唯物论; B、庸俗进化论; C、庸俗唯物论; D、各种唯心论; E、折衷主义。 4、下列哪些说法反映了意识的能动性(?? ) A、不可无根据地胡思乱想; B、巧妇难为无米之炊; C、一个好主意救活一个厂; D、找出优势,扬长避短; E、看菜吃饭,量体裁衣。 5、意识能动性的主要表现有:(?? ) A、能动地认识客观世界; B、能动地改造客观规律; C、直接反映事物的本质; D、无条件地创造奇迹; E、指导实践活动、改造客观世界。 答案:1、(A、B);2、(B、C);3、(A、D);4、(C、D);5、(A、E); (三)多项选择题 1、劳动在人的意识产生中起了决定性作用,因为:(?? ) A、劳动使人和动物从本质上区别开来; B、劳动为意识的产生提供了生理基础; C、劳动为意
KCPSM6 PicoBlaze 的原理与应用 引言PicoBlaze 8 位嵌入式处理器是Xilinx 公司为Virtex、Spartan 系列FPGA 和CoolRunnerII 系列CPLD 设计的嵌入式处理器软核。针对不同的器件,Xilinx 公司共推出了3 个版本的PicoBlaze,包括KCPSM3(目标器件为Spartan 3、Virtex II、Virtex II PRO、Virtex 4 和Virtex 5)CPLD 版(目标器件为CoolRunnerII)和最新推出的KCPSM6(目标器件为Spartan 6、Virtex 6 和7 系列FPGA)。KCPSM6 针对Spartan 6、Virtex 6 和7 系列FPGA 进行了特殊优化,增加了一些新特性,在开发和调试方法上也与KCPSM3 有所不同。本文分析对 比了其异同,对KCPSM6 在开发调试中的注意事项进行总结,并在Avnet Spartan 6 MicroBoard 上进行了实例验证。1 KCPSM6 PicoBlaze 的体系结构KCPSM6 PicoBlaze(以下简称KCPSM6)8 位嵌入式处理器是Xilinx 公司为Spartan 6、Virtex 6 和7 系列FPGA 设计的嵌入式处理器软核,它具有效率高、占用资源少等优点,可以方便地嵌入到硬件系统设计中,实现与其他功能模块 的无缝连接。它仅占用26 个Slice 和1 个BRAM,占XC6SLX4 器件4.3%的 资源、XC6SLX150T 器件不到0.11%的资源。KCPSM6 嵌入式处理器具有高 达52~120 MIPS 的指令执行速度,具体速度取决于所选用的FPGA 所属系列和器件速度等级。KCPSM6 微处理器主要由以下几个单元组成:◆两组16 个8 位通用寄存器;◆最高支持4 KB 的程序存储单元;◆8 位算术逻辑单元, 带有CARRY 和ZERO 标志位;◆64、128 或256 字节内部暂存RAM;◆256 个输入和256 个输出端口,方便扩展应用;◆中断控制单元;◆休眠模式,进一步降低系统功耗。KCPSM6 嵌入式处理器的原理框图如图1 所示。 KCPSM6 新增的特性和功能总结如下:(1)新增引脚sleep 引脚。当sleep 引
RACE 的简介 目前,全长基因的获得是生物工程及分子生物学研究的一个重点。尽管已经有多种方法可以获得基因的全长序列,但在很多生物研究中,由于所研究的目的基因丰度较低,从而使得由低丰度mRNA 通过转录获得全长cDNA 很困难。近年来发展成熟的cDNA 末端快速扩增(RACE)技术为从低丰度转录快速获得全长cDNA 提供了一个便捷的途径。 cDNA 末端快速扩增(rapid amplification of cDNA ends,RACE)技术是一种基于mRNA 反转录和PCR 技术建立起来的、以部分的已知区域序列为起点,扩增基因转录本的未知区域,从而获得mRNA(cDNA)完整序列的方法。简单的说就是一种从低丰度转录本中快速增长cDNA5’和cDNA3’末端,进而获得获得全长cDNA 简单而有效的方法,该方法具有快捷、方便、高效等优点,可同时获得多个转录本。因此近年来RACE 技术已逐渐取代了经典的cDNA 文库筛选技术,成为克隆全长cDNA 序列的常用手段。 第二RACE 的原理 RACE 是采用PCR 技术由已知的部分cDNA 顺序来扩增出完整cD NA5’和3’ 末端,是一种简便而有效的方法,又被称为锚定PCR (anchoredPCR)和单边PCR(one2side PCR)。 3’RACE 的原理 一)加入oligo(dT)17 和反转录酶对mRNA 进行反转录得到(-)cDNA; 二)以oligo(dT)l7 和一个35bp 的接头(dT17-adaptor)为引物,其中在引物的接头中有一在基因组DNA 中罕见的限制酶的酶切位点。这样就在未知cDNA 末端接上了一段特殊的接头序列。再用一个基因特异性引物(3 amp)与少量第一链(-)cDNA 退火并延伸,产生互补的第二链(+)cDNA。 三)利用3amp 和接头引物进行PCR 循环即可扩增得到cDNA 双链。扩增的特异性取决于3amp 的碱基只与目的cDNA 分子互补.而用接头引物来取代dT17 一adaptor 则可阻止长(dT)碱基引起的错配。
大数据技术原理及应用 大数据处理架构—Hadoop简介 Hadoop项目包括了很多子项目,结构如下图 Common 原名:Core,包含HDFS,MapReduce和其他公共项目,从Hadoop0.21版本后,HDFS和MapReduce分离出去,其余部分内容构成HadoopCommon。Common为其他子项目提供支持的常用工具,主要包括文件系统、RPC(Remoteprocedurecall)和串行化库。 Avro Avro是用于数据序列化的系统。它提供了丰富的数据结构类型、快速可压缩的二进制数据格式、存储持久性数据的文件集、远程调用RPC的功能和简单的动态语言集成功能。其中,代码生成器既不需要读写文件数据,也不需要使用或实现RPC协议,它只是一个可选的对静态类型语言的实现。Avro系统依赖于模式(Schema),Avro数据的读和写是在模式之下完成的。这样就可以减少写入数据的开销,提高序列化的速度并缩减其大小。 Avro可以将数据结构或对象转化成便于存储和传输的格式,节约数据存储空间和网络传输带宽,Hadoop的其他子项目(如HBase和Hive)的客户端和服务端之间的数据传输。 HDFS
HDFS:是一个分布式文件系统,为Hadoop项目两大核心之一,是Googlefilesystem(GFS)的开源实现。由于HDFS具有高容错性(fault-tolerant)的特点,所以可以设计部署在低廉(low-cost)的硬件上。它可以通过提供高吞吐率(highthroughput)来访问应用程序的数据,适合那些有着超大数据集的应用程序。HDFS放宽了可移植操作系统接口(POSIX,PortableOperatingSystemInterface)的要求,这样就可以实现以流的形式访问文件系统中的数据。MapReduce HadoopMapReduce是针对谷歌MapReduce的开源实现,它是一种编程模型,用于大规模数据集(大于1TB)的并行运算。“映射”(map)、“化简”(reduce)等概念和它们的主要思想都是从函数式编程语言中借来的。它使得编程人员在不了解分布式并行编程的情况下也能方便地将自己的程序运行在分布式系统上。MapReduce在执行时先指定一个map(映射)函数,把输入键值对映射成一组新的键值对,经过一定的处理后交给reduce,reduce对相同key下的所有value进行处理后再输出键值对作为最终的结果。核心思想就是“分而治之”。HBase HBase是一个分布式的、面向列的开源数据库,该技术来源于Google 的论文“Bigtable:一个结构化数据的分布式存储系统”。如同Bigtable利用了Google文件系统(GoogleFileSystem)提供的分布式数据存储方式一样,HBase在Hadoop之上提供了类似于Bigtable 的能力。HBase不同于一般的关系数据库,其一,HBase是一个适合
B F D技术原理及其应用 Document number【AA80KGB-AA98YT-AAT8CB-2A6UT-A18GG】
BFD技术原理及其应用 一、BFD简介 1.BFD(Bidirectional Forwarding Detection,双向转发检测)是一套全网统一的检测机制,用于快速检测、监控网络中链路或者IP 路由的转发连通状况 2.为了提升现有网络性能,邻居之间必须能快速检测到通信故障,从而更快的建立起备用通道恢复通信 二、常用的故障检测方法 1.硬件检测:例如通过SDH(Synchronous Digital Hierarchy,同步数字体系)告警检测链路 故障。硬件检测的优点是可以很快发现故障,但并不是所有介质都能提供硬件 检测 2.慢Hello机制:通常采用路由协议中的Hello 报文机制。这种机制检测到故障所需时间为 秒级。对于高速数据传输(例如吉比特速率级)超过1 秒的检测时间将 导致大量数据丢失;对于时延敏感的业务(例如语音业务)超过1 秒的 延迟也是不能接受的。并且,这种机制依赖于路由协议 3.其他检测机制:不同的协议有时会提供专用的检测机制,但在系统间互联互通时,这样 的专用检测机制通常难以部署 三、BFD的工作机制 1.概述: ①BFD 提供了一个通用的、标准化的、介质无关、协议无关的快速故障检测机制, 可以为各上层协议如路由协议、MPLS 等统一地快速检测两台路由器间双向转发 路径的故障 ②BFD 在两台路由器上建立会话,用来监测两台路由器间的双向转发路径,为上层 协议服务 ③BFD本身并没有发现机制,而是靠被服务的上层协议通知其与谁建立会话,会话 建立后如果在检测时间内没有收到对端的BFD 控制报文则认为发生故障,通知被 服务的上层协议,上层协议进行相应的处理 2.BFD的工作流程 ①流程图
B F D技术原理及其应用 The latest revision on November 22, 2020
BFD技术原理及其应用 一、BFD简介 1.BFD(Bidirectional Forwarding Detection,双向转发检测)是一套全网统一的检测机制,用于快速检测、监控网络中链路或者IP 路由的转发连通状况 2.为了提升现有网络性能,邻居之间必须能快速检测到通信故障,从而更快的建立起备用通道恢复通信 二、常用的故障检测方法 1.硬件检测:例如通过SDH(Synchronous Digital Hierarchy,同步数字体系)告警检测链路 故障。硬件检测的优点是可以很快发现故障,但并不是所有介质都能提供硬件 检测 2.慢Hello机制:通常采用路由协议中的Hello 报文机制。这种机制检测到故障所需时间为 秒级。对于高速数据传输(例如吉比特速率级)超过1 秒的检测时间将 导致大量数据丢失;对于时延敏感的业务(例如语音业务)超过1 秒的
延迟也是不能接受的。并且,这种机制依赖于路由协议 3.其他检测机制:不同的协议有时会提供专用的检测机制,但在系统间互联互通时,这样 的专用检测机制通常难以部署 三、BFD的工作机制 1.概述: ①BFD 提供了一个通用的、标准化的、介质无关、协议无关的快速故障检测机制, 可以为各上层协议如路由协议、MPLS 等统一地快速检测两台路由器间双向转发 路径的故障 ②BFD 在两台路由器上建立会话,用来监测两台路由器间的双向转发路径,为上层 协议服务 ③BFD本身并没有发现机制,而是靠被服务的上层协议通知其与谁建立会话,会话