
a r X i v :g r -q c /9910022v 1 6 O c t 1999
Collision of 1.4M ⊙Neutron Stars:Dynamical or Quasi-Equilibrium?
Mark Miller (1),Wai-Mo Suen (1,2)and Malcolm Tobias (1)
(1)
McDonnell Center for the Space Sciences,Department of Physics,Washington University,St.Louis,Missouri 63130
(2)
Physics Department,Chinese University of Hong Kong,Hong Kong
(February 7,2008)
Shapiro put forth a conjecture stating that neutron stars in head-on collisions (infalling from in?nity)will not collapse to black holes before neutrino cooling,independent of the mass of the neutron stars.In a previous paper we carried out a numerical simulation showing a counter example based on 1.4M ⊙neutron stars,and provided an analysis explaining why Shapiro’s argument was not applicable for this case.
A recent paper by Shapiro put forth an argument suggesting that numerical simulations of the 1.4M ⊙collisions could not disprove the conjecture with the accuracy that is presently attainable.We show in this paper that this argument is not applicable for the same reason that the Shapiro con-jecture is not applicable to the 1.4M ⊙neutron star collision,namely,the collision is too dynamical to be treated by quasi-equilibrium arguments.
Shapiro in [1]proposed an intriguing conjecture on head-on collisions of neutron stars (NSs)infalling from in?nity.It goes as follows:For two stable NSs that are described by a polytropic equation of state (EOS)P =KρΓ[K =K (s )is a function of the entropy s ,the polytropic index Γis a constant in space and time],it is conjectured that no prompt collapse can occur for an arbitrary Γand an arbitrary initial K ,independent of the mass of the neutron stars.The basic argument of [1]is that,with the polytropic EOS,there always exists a stable equilibrium TOV con?guration with the same total mass and total energy as the two initially isolated TOV stars.As the mass and energy are conserved to a good extent in the head-on collision process,Ref.[1]con-cluded that the merged object will be stable until energy is radiated away at a much longer timescale.
In [2],we present a counter example to the conjecture.We carried out a numerical simulation of the head-on collision of two 1.4M ⊙neutron stars,with polytropic index of 2and initial polytropic coe?cient K =1.16×
105cm
5
tice that with a strong shock,“thermalization”proceeds
much faster than the heat conduction time scale.How-ever the shock front is still not fast enough in its outward propagation;it gets trapped inside the apparent horizon before it can reach a good part of the infalling matter. The polytropic coe?cient K(s)is never a spatial con-stant,nor approximately constant,throughout the coa-lesced object.This implies that(B)must also be vio-lated:the collision process is so dynamical that although a stable equilibrium state exists(allowed by the energy and mass conservation laws),it is not attained in the col-lapse process.
One central message of
[2]and the present paper is that the head-on collision of1.4M⊙NSs is so dynamical
that one must not use any notion of quasi-equilibrium, on which both the original Shapiro conjecture and the “accuracy argument”are based.
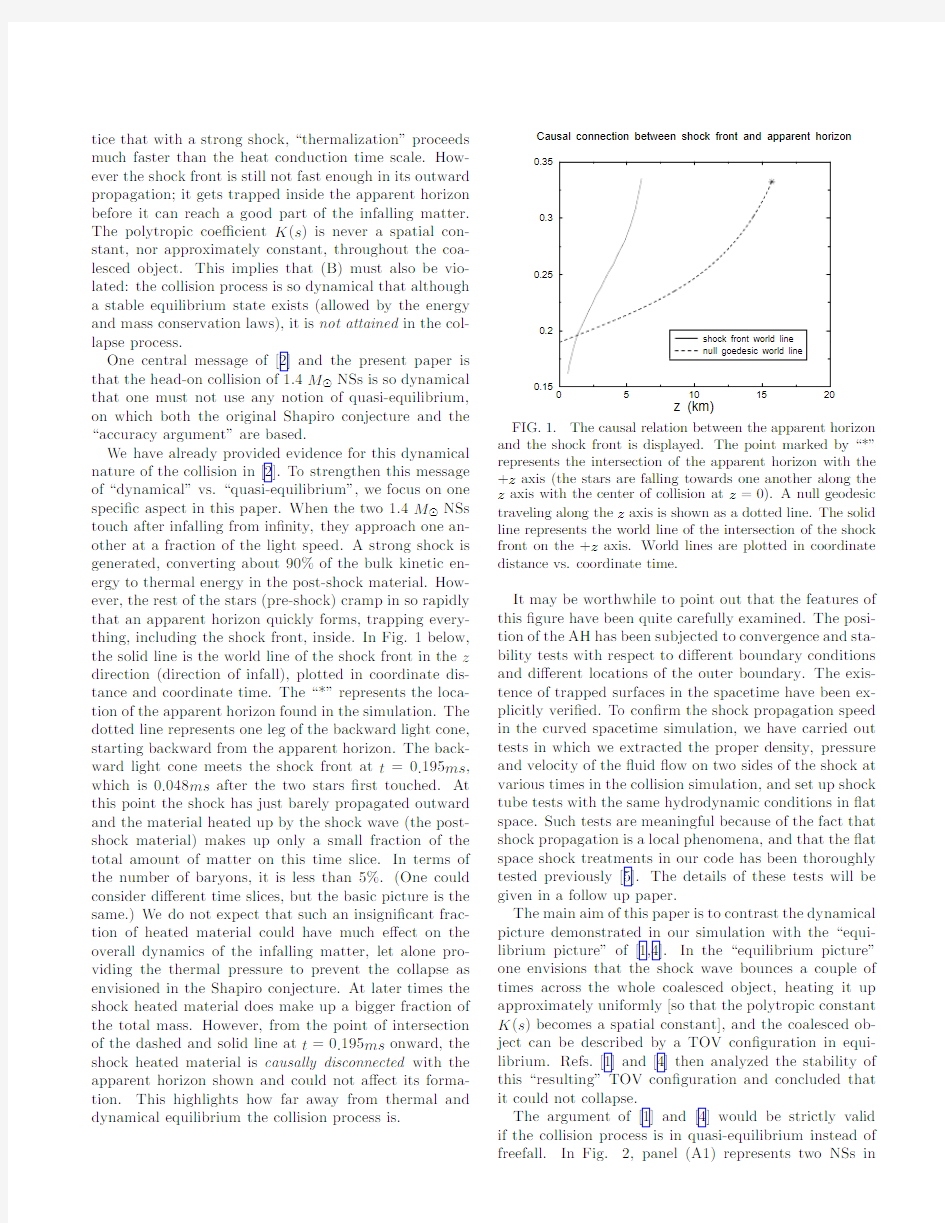
We have already provided evidence for this dynamical nature of the collision in[2].To strengthen this message of“dynamical”vs.“quasi-equilibrium”,we focus on one speci?c aspect in this paper.When the two1.4M⊙NSs touch after infalling from in?nity,they approach one an-other at a fraction of the light speed.A strong shock is generated,converting about90%of the bulk kinetic en-ergy to thermal energy in the post-shock material.How-ever,the rest of the stars(pre-shock)cramp in so rapidly that an apparent horizon quickly forms,trapping every-thing,including the shock front,inside.In Fig.1below, the solid line is the world line of the shock front in the z direction(direction of infall),plotted in coordinate dis-tance and coordinate time.The“*”represents the loca-tion of the apparent horizon found in the simulation.The dotted line represents one leg of the backward light cone, starting backward from the apparent horizon.The back-ward light cone meets the shock front at t=0.195ms, which is0.048ms after the two stars?rst touched.At this point the shock has just barely propagated outward and the material heated up by the shock wave(the post-shock material)makes up only a small fraction of the total amount of matter on this time slice.In terms of the number of baryons,it is less than5%.(One could consider di?erent time slices,but the basic picture is the same.)We do not expect that such an insigni?cant frac-tion of heated material could have much e?ect on the overall dynamics of the infalling matter,let alone pro-viding the thermal pressure to prevent the collapse as envisioned in the Shapiro conjecture.At later times the shock heated material does make up a bigger fraction of the total mass.However,from the point of intersection of the dashed and solid line at t=0.195ms onward,the shock heated material is causally disconnected with the apparent horizon shown and could not a?ect its forma-tion.This highlights how far away from thermal and dynamical equilibrium the collision process is.
z (km)
0.15
0.2
0.25
0.3
0.35
t
(
m
s
)
Causal connection between shock front and apparent horizon
FIG.1.The causal relation between the apparent horizon and the shock front is displayed.The point marked by“*”represents the intersection of the apparent horizon with the +z axis(the stars are falling towards one another along the z axis with the center of collision at z=0).A null geodesic traveling along the z axis is shown as a dotted line.The solid line represents the world line of the intersection of the shock front on the+z axis.World lines are plotted in coordinate distance vs.coordinate time.
It may be worthwhile to point out that the features of this?gure have been quite carefully examined.The posi-tion of the AH has been subjected to convergence and sta-bility tests with respect to di?erent boundary conditions and di?erent locations of the outer boundary.The exis-tence of trapped surfaces in the spacetime have been ex-plicitly veri?ed.To con?rm the shock propagation speed in the curved spacetime simulation,we have carried out tests in which we extracted the proper density,pressure and velocity of the?uid?ow on two sides of the shock at various times in the collision simulation,and set up shock tube tests with the same hydrodynamic conditions in?at space.Such tests are meaningful because of the fact that shock propagation is a local phenomena,and that the?at space shock treatments in our code has been thoroughly tested previously[5].The details of these tests will be given in a follow up paper.
The main aim of this paper is to contrast the dynamical picture demonstrated in our simulation with the“equi-librium picture”of[1,4].In the“equilibrium picture”one envisions that the shock wave bounces a couple of times across the whole coalesced object,heating it up approximately uniformly[so that the polytropic constant K(s)becomes a spatial constant],and the coalesced ob-ject can be described by a TOV con?guration in equi-librium.Refs.[1]and[4]then analyzed the stability of this“resulting”TOV con?guration and concluded that it could not collapse.
The argument of[1]and[4]would be strictly valid if the collision process is in quasi-equilibrium instead of freefall.In Fig.2,panel(A1)represents two NSs in
free fall towards each other.Panel(A2)represents the shock wave heating up the merging stars(with the dark grey area representing the material at higher temperature and hence higher K).However,at this point the ap-parent horizon pops into existence engul?ng most of the infalling matter.(A3)represents the black hole?nally formed.Fig.3represents a thought experiment in which the quasi-equilibrium analysis is valid.Panel(B1)repre-sents two NSs with ropes attached slowly lowered towards one another,with the potential energy extracted and re-deposited back into the stars.This makes the stars grad-ually heat up,maintaining quasi-equilibrium throughout the process.(To be precise,each?uid element has to be tied and arranged into its quasi-equilibrium position at each point in time.)This is represented in(B2).Darker grey is used to represent the uniformly heated object with the potential energy extracted and redistributed back to it through the ropes.One?nal equilibrium(hot)TOV star is formed,represented by(B3).The stability of
this TOV star is determined by the considerations in Refs.[1] and[4].
FIG.2.The freefall collision of two1.4M⊙NSs.In(A1) two NSs are in free fall towards each other.The grey region in panel(A2)represents the material heated by the shock wave. At this point,an apparent horizon forms,engul?ng most of the infalling matter.Panel(A3)represents the black hole ?nally formed.
FIG.3.The merging of two NSs in quasi-equilibrium. (B1)represents two NSs with ropes attached slowly lowered towards one another,with the potential energy extracted and re-deposited back into the stars.(The?uid elements are tied and arranged into their quasi-equilibrium position throughout the process.)Panel(B2)represents the uniformly heated,merging object with the potential energy extracted and redistributed back to it through the ropes.Panel(B3) represents the?nal equilibrium TOV star formed.In this quasi-equilibrium scenario the considerations in Refs.[1]and [4]would be strictly applicable.
Fig.4schematically represents the con?guration space of the coupled Einstein-GRHydro equations.The lower left dot denoted2TOV represents the state of two TOV con?gurations in?nitely separated.In free fall governed by the coupled Einstein-GRHydro equations,it evolves along the solid line towards the lower right hand dot denoted BH representing the solution of a black hole. The three stages A1,A2and A3in Fig.2are labeled. The dotted line represents the evolution of the Panels B in Fig.3(the Einstein-GRHydro equations with source terms including the ropes):The two TOV stars are tied and lowered towards one another.This leads to the state represented by the dot in upper right hand corner de-noted1TOV.The argument in Ref.[4]amounts to point-ing out that should one actually carry out a numerical simulation following this dotted line,one would have to maintain0.5%accuracy in order to determine whether the1TOV solution obtained at B3is stable or not.We see that this accuracy requirement is irrelevant to the head-on collision study:We are not carrying out a simulation along the quasi-equilibrium path(if such a simulation is at all possible).
the coupled Einstein-GRHydro equations.The lower left dot denoted2TOV represents the state of two TOV con?gura-tions in?nitely separated.In free fall governed by the cou-pled Einstein-GRHydro equations,it evolves along the solid line towards the lower right hand dot denoted BH represent-ing a black hole.The three stages A1,A2and A3in Fig. 2are labeled.The dotted line represents the evolution in quasi-equilibrium depicted in Panels B of Fig.3:The two TOV stars are tied and lowered towards one another.This leads to the state represented by the dot in upper right hand corner denoted1TOV.
How accurate do we have to get in following the evo-lution depicted by the solid line in Fig.4before we can be sure that a black hole is actually formed?We do not have an answer to this question presently.The ac-curacy we achieved can be monitored by the Hamilto-nian constraint violation at the point we found the AH (along the z-axis).The Hamiltonian constraint violation is0.146,0.096,0.062,0.040(in units of16πρ,withρbeing the maximum rest mass density at that time),for the sim-ulations carried out with grid sizes of403,963,1603,2563, respectively.The simulations are carried out with only one octant of the grid evolved.(Due to the symmetry of the problem,only one octant of the domain needs to be numerically calculated.The2563simulation corresponds to having about140points across the diameter of one star.)We note two points:1.the formation of a black hole can be obtained by a simulation with rather coarse resolution,and2.this feature of black hole formation is stable with respect to increasing resolution,i.e.,a long time scale convergence test.We emphasize that in nu-merical studies one must insist that the physical feature one is studying is subjected to,and passes convergence tests.We emphasize that here we are talking about not just the usual short time convergence code test.The con-vergence tests must be carried out for the speci?c system of physical interest,and maintained throughout the time of evolution up to the time the physical feature under consideration is extracted:a“long term”convergence test.Together with the consistency tests making sure that the?nite di?erence equations are faithful to the dif-ferential equations,one can then invoke the Lax theorem to give oneself a reasonable con?dence on the numerical result.This is a point that cannot be over-emphasized for all numerical studies.All simulations discussed in this paper and in[2]have gone through these consistency and long term convergence tests.
We further note that even though the simulations we carried out may be reliable and show the prompt forma-tion of a black hole,they still may not constitute counter examples to the Shapiro conjecture,subject to the fol-lowing consideration.In our numerical simulations,the initial data is set with the NSs at a?nite separation with an infall velocity.The initial data set we used may not be the same as what it would actually be falling in from in?nity.Indeed,setting initial data in numerical simu-lations to represent a given physical scenario is a major problem in numerical relativity.Fortunately,the prob-lem at hand is considerably easier than trying to set up initial data to,say,obtain a gravitational waveform to compare with observations.There,one has to deter-mine precisely the correct initial data corresponding to the physical scenario.Here,to establish a counter ex-ample to the Shapiro conjecture,our strategy is to con-struct reasonable initial data sets that one can consider as approximately representing the1.4M⊙head-on colli-sion problem.If all of them leads to the same dynamical picture of evolution with the same qualitative behavior, and all of them produce a black hole promptly,we are willing to conclude that a counter example is established, even though we might not be able to pin down precisely the exact initial data.
For example,it is di?cult if at all possible to deter-mine the exact infalling velocity at the point we start the evolution(typically the initial separation is chosen to be around45km in our numerical study).We choose the initial velocity to be given by the Newtonian freefall velocity(M/r at45km separation is about0.05for1.4 M⊙and the EOS used;it is not too much out of the Newtonian regime).We have also carried out simula-tions with10%higher and lower initial velocities,and con?rmed that the prompt collapse result is not sensitive to the exact choice.Although we still cannot pin down the“correct”velocity,we believe that this inability to pin it down will not a?ect our conclusion of prompt collapse. For this reason we have also carried out simulations using di?erent constructions of the initial metric and matter distributions.There are di?erent ways to put two1.4M⊙TOV con?gurations together.One can di-rectly put the TOV density pro?le in and solve the four initial data constraints,or one can require the baryon number of the data to be held?xed before and after the solving of the initial data constraints,or the total ADM mass.While holding the total baryon number is arguably “preferable”,we have also carried out simulations of the other setups.The details of the evolutions with di?erent
initial data sets will be given in a follow up paper;but in all cases studied,we found the same qualitative behavior, and all of them produce a black hole promptly.It is with these tests we feel we have quite con?dently established a counter example to the Shapiro conjecture:Even though we cannot pin down the exact initial data,the dynamical nature of the problem and the prompt collapse to a black hole appear to be generic features and are insensitive to details in choosing initial data.
Ref.[4]also raised the point that we have not consid-ered tidal distortion of the two stars in the initial data, and that such an error could invalidate the prompt col-lapse result in view of the“0.5%accuracy requirement”. In the above we pointed out that the“0.5%accuracy re-quirement”is irrelevant to the present consideration,but it is true that we have not carried out studies of the tidal distortion e?ect.We note that we could have incorpo-rated tidal distortion with the same type of argument as above:Carry out simulations with di?erent distortions and verify that the qualitative behavior of the collapse is the same.Also,one can conceivably construct a tidally distorted initial con?guration using the“conformally?at quasi-equilibrium treatment”minimizing the energy(for review,see e.g.,Refs.[6,7]),although quasi-equilibrium for the head-on case would be less accurate compared to the inspiraling case at the same initial separation.We have not investigated along this line because of the fol-lowing consideration:The spherical symmetric density distribution of the individual star we used in starting o?the initial data calculation has more energy compared to the“correctly tidally distorted”con?guration that one would have obtained by tracking the stars all the way in from in?nity.The spherical symmetric density distribu-tion we used is in fact a“distorted con?guration”with respect to the correct density distribution the stars would have infalling from in?nity.By starting o?at a?nite dis-tance with spherical symmetric distributions we have put more potential energy in the system than it would actu-ally have.Hence,according to Shapiro’s argument,this should lead to more thermal energy upon coalescence and it should make it more di?cult to collapse,if it has any e?ect at all.But still it promptly collapses even in this case of more energy.With this consideration in mind, we felt that tidal distortion was not a major concern to-wards the goal of establishing a counter example to the Shapiro conjecture.(It would be an important concern if one were trying to determine the gravitational waveform for the collision.)
Conclusion.In the two recent papers[1]and[4], Shapiro provided useful insight to processes involving neutron stars.However,the arguments in these papers are not applicable to the head-on collision of1.4M⊙neu-tron stars in[2]and this paper.The crux of the problem is that such a collision is too dynamical to be studied using quasi-equilibrium analyses.
Acknowledgments.This research is supported by NASA NCS5-153,NSF NRAC MCA93S025,and NSF grants PHY96-00507,96-00049,and
99-79985.
人工智能在计算机网络技术的应 用 【摘要】近年来,计算机网络技术取得了极大的发展,与此同时其在多领域应用过程中所存在的问题也逐渐暴露并 引发人们的关注,比如计算机网络信息安全问题等。然而由于应用以往的数据运算等功能已然无法解决现阶段计算机 网络技术在实际应用中所出现的问题,因此便有了对人工智能应用的尝试。然而也正是在计算机网络技术发展日新月异的背景之下,人们对人工智能的应用优势也已然形成了较为成熟的认识,并于实际的计算机网络安全管理过程中扩大了对其的应用。本文首先从计算机网络安全管理技术与网络系统管理和评价技术两个角度介绍了人工智能的应用,接着对人工智能在计算机网络技术中的应用优势做了简要分析,以期能够推动人工智能应用的进一步发展。 【关键词】人工智能;计算机网络技术;应用 1人工智能在计算机网络安全管理技术中的具体应用 智能防火墙、智能反垃圾邮件系统以及智能化入侵检测是人工智能在计算机网络安全管理技术中的几个具体应用方面,在此主要对人工智能在入侵检测方面的应用进行介绍。第一,数据挖掘与数据融合技术。数据挖掘技术具有两大主
要功能,即学习与记忆功能。其在入侵检测过程中的具体应用为:首先应用审计程序提取和描述网络连接和主机会话的特征,接下来再利用数据挖掘技术这项人工智能来学习与记忆网络活动的正常轮廓等,如此一来,便可以在检测异常的情况发生时,对有害性的入侵进行准确的识别,从而使针对于入侵的实际检测效果获得大幅提升。而数据融合技术的应用原理则是,首先对数据进行组合,并在此基础上完成更多信息资源的获得。在计算机网络安全管理技术方面应用数据融合技术可以通过联合多个个体传感器共同发挥作用,从而有效降低其各自发挥作用时在检测范围方面所存在的局限性,最终实现传感器系统运行能力的大幅提升。第二,人工神经网络与人工免疫技术。人工神经网络的主要优势表现在其学习能力与容错能力等方面。将人工神经网络这项人工智能应用于计算机网络安全管理技术中不仅有利于提升对存 在噪声或畸变的输入模式的识别能力,而且还可以得益于并行模式从而有效提升入侵检测工作的效率。相较于传统的入侵检测技术而言,人工免疫技术的优势主要在于其自身所具备的三种机制,即基因库、否定选择、克隆选择,总得来说,这三种机制不仅有利于提升入侵检测系统的杀毒能力,而且有利于提升入侵检测系统对未知病毒的识别能力。而专就基因库这一项机制而言,其功能发挥原理在于:基因片段在发生突变或完成重组以后,可以储存在基因库中,如此一来,
高校网络出口解决方案 1.高校网络出口现状分析 随着高校信息化建设的开展,教学、科研、办公、生活对于校园网平台的依赖性越来越强。国内的高校经过多年持续不断的基础设施建设和应用提升,已经形成了较为稳定的校园网基础架构、相对丰富的校园网应用平台。但是,在讲究信息共享、资源整合的今天,有一块区域长期以来一直困扰着各大高校——这就是校园网出口区域。实践中会发现,众多高校都测试了多个厂商的设备,却未能获得很好的问题解决,无法取得理想的效果。 然而,几乎所有的高校信息化专家一致认为:“高校校园网不应该作为一个信息孤岛而存在。网络的价值更重要的是体现在信息的流通、资源的共享。”作为校园网络平台的“门户”——出口区域,承担着高校之间相互交流的窗口的重大作用。那么高校的校园网出口到底是怎样一个现状,都面临着哪些问题呢?为此,锐捷网络自2006年初对全国10个省进行了采样调查和分析。 1.1高校出口基本状况调研 高校网络出口调研的对象为10个省市的本科类非985院校(天津、辽宁、四川、重庆、湖南、湖北、广东、安徽、福建、江苏)。下面从学校规模,出口链路及带宽方面来介绍调研成果。 第一、从学校网络规模、信息点来看; 60%的高校拥有1000-10000这样的信息点数规模。仅仅有13%的高校信息点数在1000点以下。而超过10000点大规模的学校比例为27%。信息点数的多少基本上可以反映接入PC的数量(不是完全一一对应的关系),因此,我们通过结合网络规模和出口链路、出口设备状况可以来判断不同规模的学校所面临的共性和个性的问题。 一般来说:规模在1000点以下、出口带宽不是很低的情况下,出口区域的规划相对容易,对设备性能的要求相对较低,从而所采用的策略可以宽松一些。目前面临出口难题的主要为信息点数为1000-10000和10000以上的那些高校。 第二、从出口的链路条数和带宽情况来看; 一方面,网络规模较大的学校,出口带宽普遍较高;另一方面,根据学校所在区域有所差别,比如像在广州、武汉等全国网络的核心节点地区,高校的出口带宽普遍较高。同时,运营商在不同地区采取的收费标准也对高校出口带宽有着重要的影响。 具体来说:在广州、武汉,普通本科拥有千兆电信和千兆教育网带宽的比例最高,甚至有千兆电信/千兆网通的接入;而在大连,普通本科学校的出口带宽普遍在CERNET--100M,网通--10到50M不等。此外,由于一些特定因素,90%以上高校都有2个校园网出口,并且根据当地情况,相当比例的学校拥有三
xxx互联网出口负载均衡和流量分析 项 目 方 案 巴州浩展网络有限责任公司 2012年3月 目录 1项目背景.................................. 错误!未指定书签。2项目目标.................................. 错误!未指定书签。3项目原则.................................. 错误!未指定书签。4总体方案设计.............................. 错误!未指定书签。 4.1现状分析............................. 错误!未指定书签。 4.2方案论证............................. 错误!未指定书签。 4.3总体方案............................. 错误!未指定书签。5设计方案.................................. 错误!未指定书签。 5.1技术关键点........................... 错误!未指定书签。 5.2方案设计............................. 错误!未指定书签。6实施方案.................................. 错误!未指定书签。
6.1设备安装调试......................... 错误!未指定书签。 6.2设备上架、加电测试................... 错误!未指定书签。 6.3业务平滑迁移......................... 错误!未指定书签。 6.4链路跳接............................. 错误!未指定书签。 6.5策略调整、优化配置................... 错误!未指定书签。 6.6设备关机............................. 错误!未指定书签。7项目组织管理.............................. 错误!未指定书签。 7.1项目实施总体布署..................... 错误!未指定书签。 7.2项目实施准备工作..................... 错误!未指定书签。 7.3项目实施关键步骤说明................. 错误!未指定书签。 7.4项目文档管理......................... 错误!未指定书签。8项目实施进度计划.......................... 错误!未指定书签。9应急预案.................................. 错误!未指定书签。10培训计划................................. 错误!未指定书签。 10.1F5培训内容.......................... 错误!未指定书签。 10.2A llot 培训内容....................... 错误!未指定书签。11附件..................................... 错误!未指定书签。 11.1《F5-6400配置手册》................. 错误!未指定书签。 11.2《Allot管理服务器配置手册》......... 错误!未指定书签。 11.3《Allot-3040配置手册》.............. 错误!未指定书签。 11.4C3750G配置手册...................... 错误!未指定书签。
人工智能与网络安全 【考点解析】 人工智能(Artificial Intelligence) , 英文缩写为AI 。人工智能是计算机科学的一个分支,它企图了解智能的实质,并生产出一种新的能以人类智能相似的方式作出反应的智能机器,该领域的研究包括机器人、语言识别、图像识别、自然语言处理和专家系统等。 人工智能的应用: ①模式识别:指纹识别、语音识别、光学字符识别、手写识别等 ②机器翻译:语言翻译 ③智能机器人、计算机博弈、智能代理 ④其它:机器证明、数据挖掘、无人驾驶飞机、专家系统等 ●例题1:下列不属于人工智能软件的是:( C ) A、语音汉字输入软件 B、金山译霸 C、在联众网与网友下棋 D、使用OCR汉字识别软件 ●例题2.下列运用了人工智能技术的是(C ) A.播放视频 B.播放音乐 C.手写板输入汉字 D.键盘输入汉字 ●例题3.以下不属于人工智能技术应用的( B ) A.超级国际象棋电脑“深蓝二代” B.office软件 C.医疗专家系统 D.于机器人对话 ●例题4.某公司为了加强考勤管理,购置了指纹打卡机,这体现信息技术的( C ) A.多元性 B.网络化 C.智能化 D.多媒体化 ●例题5. 指纹识别属于人工智能学科中的( B ) A.字迹识别研究范畴 B.模式识别研究范畴 C.语音识别研究范畴 D.字符识别研究范畴 【考点】了解信息的发布与交流的常用方式 【考点解析】 信息发布
?根据发布的方式:视觉:报纸、杂志、书籍听觉:广播视听:电影、电视、网络 ?根据发布主体分成三类:个人信息发布;行业信息发布;官方机构信息发布 ?因特网上信息发布的常用方式:E-mail(电子邮件)BBS(论坛公告板)QQ(同类的还有MSN等)博客(weblog) ?信息发布的效果与以下三个方面有关:发布的时间与地点、媒体的发布速度、信息的保存时间 ●例题6:以下关于电子邮件的说法不正确的是: ( C ) A、电子邮件的英文简称是E-mail。 B、所有的E-mail地址的通用格式是:用户名@邮件服务器名 C、在一台计算机上申请的“电子邮箱”,以后只有通过这台计算机上网才能收信 D、一个人可以申请多个电子邮箱 补充:网络常用术语 站点(网站):是一组网络资源的集合。便于维护和管理 超级链接:用超级链接可以实现从一个网页到另一个目标的连接,这个目标可以是一个网页,也可以是图像、动画、视频,甚至可以是一 个可执行程序 超文本:主要以文字的形式表示信息,建立链接关系主要是在文本间进行防火墙:是指一个或一组系统,用来在两个或多个网络间加强防问控制,限制入侵者进入,从而起以安全防护的作用。 BBS:就是我们平时所说的论坛,我们可以在里面就自己感兴趣的话题发布信息或提出看法 E-mail:就是我们平时所说的电子邮件,其特点P91 ●例题7.下列不属于在因特网上发布信息的是( A ) A.将数据保存在光盘中 B.发送E-mail邮件 C.发表博客文章 D.与同学通过QQ聊天 ●例题8.利用业余时间创作了一段flash动画,想与远方的朋友一起分享,下列可供他发表改作品的途径有( C ) ①在因特网以网页形式发布②在论坛公告板BBS上发布③通过电子邮件发送给朋友④通过固定电话告诉朋友⑤通过网络聊天工具QQ传送 A. ①②③④⑤ B. ①②③④ C. ①②③⑤ D.②③④⑤
2012— 2013学年第二学期期末考试 论文题目办公大楼网络综合布线设计方案 学号 110412137 姓名刘欢欢 系部电子通信工程系 专业通信网络与设备 班级通网111 日期:2013年6月1号
目录 第一章需求分析 1.1.1办公楼综合布线项目要求 (2) 1.1.2有关技术要求 (3) 1.2 项目设计目标 (3) 第二章综合布线系统整体设计 2.1 综合布线系统分析 (4) 2.2 综合布线的特点 (4) 2.3布线系统的结构 (5) 2.4 综合布线设计标准 (6) 2.5综合布线设计原则 (7) 2.6 综合布线目标功能 (7) 第三章综合布线系统详细设计 3.1工作区子系统 (8) 3.2水平子系统 (9) 3.3管理子系统 (9) 3.4设备间子系统 (11) 3.5.1水平子系统布线要求 (12)
3.5.2管理子系统设计建议 (13) 3.6综合布线系统拓扑图 (14) 3.7综合布线测试 (14) 3.8各种设备价格清单 (15)
办公大楼网络综合布线设计方案 第一章需求分析 在企业信息化建设过程中,网络综合布线是非常关键的一个环节,根据该集团信息化建设项目的要求,网络建设布线必须按照设计标准(SP-2840国际综合布线标准,EIA/TIA569电信服务商业布线标准)进行,达到1000M以太网距离要求。 1.1.1办公楼综合布线项目要求 基本情况:整个局域网采用以太网技术,主干带宽达1000Mbps,100Mbps到桌面。 1、满足集团公司本部各项业务的需求,且兼顾未来长远的发展; 2、符合当前信息传输的要求,并考虑未来发展的需求; 3、布线系统遵从国际(ISO/IEC 11801)标准和邮电部、建设部标准,布线系统采用国际标准建议的星型拓扑结构; 4、布线系统支持语音、图像、数据等综合信息的高质量传输,并能够适应集团公司内部各种不同类型不同厂家的电脑及网络产品; 5、布线的信息出口采用国际标准的RJ45插座,统一线路规格和设备接口,使任意信息点都能接插不同类型的终端设备,如电脑、打印机、网络终端、电话机、传真机等,以支持语音、图像、数据等信息及多媒体信息的传输; 6、采用目前流行,具有一定先进技术的超五类系列产品。 7、易于管理。面板、配线架有明显标识,机房线路管理、维护方便。
基于神经网络的人机对抗人工智能系统(理论) -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 基于神经网络的人机对抗人工智能系统 Harreke 摘要: 人工智能是一门科学名称。自电子计算机发明后不久,人工智能学科即宣布创立,其目的就是要模拟人类的智力活动机制来改进计算机的软件硬件构成,使他们掌握一种或多种人的智能,以便在各种领域内有效替代人的脑力劳动,特别是解决用传统软硬件方法难以解决的问题,如模式识别,复杂的控制行为或对海量的数据进行实时评估等。 所谓人工智能,就是由人工建立的硬件或软件系统的智能,是无生命系统的智能。智能是人类智力活动的能力,是一个抽象的概念。一个软件或硬件系统是否有智能,只能根据它所表现出来的行为是否和人类某些行为相类似来做判断。 人工智能在计算机上的实现,有两种不同的方式。一种是采用传统的编程技术,使系统呈现智能的效果,而不考虑所用方法是否与人或生物机体所用的方法相同。这种方法称为工程学方法,它的编程方式虽然简单,智能效果显著,可是算法和程序一旦固定下来,智能就很难再进一步提高。另一种是模拟法,它不仅要看智能效果,还要求实现方法和人类或生物机体所用的方法相同或类似。人工神经网络是模拟人类或生物大脑中神经元的活动方式,属于模拟法。 人工神经网络入门难度大,编程者需要为每一个对象设置一个智能系统来进行控制,新设置好的智能系统,虽然一开始什么都不懂,但它拥有学习的能力,可以通过学习,不断提升智能,不断适应环境、应付各种情况。通常来讲,使用人工神经网络虽然编程复杂,但编写完成后的维护工作,将比使用其他方式编程后的维护更加省力。 本文采用人工神经网络构建一个完整的人工智能系统,并将该人工神经网络理论应用于电脑领域的项目DOTA。 关键词:人机对抗,神经网络,人工智能,DOTA 目录 第一章神经网络系统概述 1.1生物学神经网络 1.2人工神经网络
第29卷第3期2019年9月 Vol.29.No.3 Sep.2019湖南工程学院学报 Journal of Hunan Institute of Engineering 基于策略路由部署的网络多出口设计研究 彭伟 (安徽工贸职业技术学院计算机信息工程系,淮南232001) 摘要:企业园区网络出口连接运营商网络以获取ISP服务,为了保障网络可靠性和稳定性,往往设计了多个出口,实现内网数据的流量均衡和链路备份.文中的园区网存在电信、联通、教育网3个网络出口,内网数据通过预先控制的方式沿着不同的路径访问不同的网络,并可以相互切换,实现了数据分流和负载均衡.在网络搭建过程中选用锐捷系列网络设备,使用了策略路由和路由选路部署,以及调整路由协议路径成本,使数据沿着多个出口加以实现.通过策略路由的部署,网络按照设定的方案实现了按不同路径进行转发,并且实现了故障切换.通过在网络出口设备上部署策略路由,有效地控制数据流量的转发和传输,使网络运行既快速又可靠. 关键词:策略路由;路由选路;链路切换;网络出口 中图分类号:TP393.1文献标识码:A文章编号:1671—119X(2019)03—0048—05 可靠、快速、安全、通畅是大中型园区网络的重要研究内容.在大园区网络组建过程中,使用OSPF、静态路由协议等实现网络的畅通,但是存在数据包传输路径的控制问题,路由协议依据度量标准选择最优的数据包转发路径,当数据需要按照自行设定的路径转发时便存在着问题.在复杂网络环境下不同类型的数据需要沿着不同的路径进行转发,内部网络通过不同的出口网关使用NAT访问外部网络.本文通过一个真实的网络环境构建了一个多出口的网络模型采用策略路由对网络中的数据进行路径选择,实现了网络流量的均衡和可靠,通过多个出口访问外部网络,实现了用户的需求,使网络数据能够更加可控.在具体实现过程中使用了策略路由进行数据包路径选择,当链路出现故障时能够进行快速切换,保障网络的可靠与稳定.同时,在出口网关部署NAT实现内部网络用户通过地址解析协议访问外部公共网络数据. 1网络模型立了研究院,为了实现网络的管理可控性,集团的所有数据都由总部进行控制,所有的无线用户都通过总部无线控制器统一管理.分校内网不同数据终端通过服务节点中转访问上海办事处和杭州办事处,当连接服务节点间链路失效时,可自动切换到其他服务节点进行转发,具体网络拓扑如图1所示. 宽带接入业务 图1网络拓扑结构图 专线(V ip)业务 VK教育集团社交网站在北京设立了总部,在全国多个重要城市设立了分校,并在上海和杭州设 收稿日期(019—02—28 基金金目:安安省高等学校质量工程项目(2015sjjd048). 作作者介:彭伟(1983-),男,硕士,讲师,研究方向: 计算机网络及应用.
湖南理工学院 人工智能课程论文 题目:模式识别及人工神经网络 课程名称:人工智能 院系:计算机学院 专业班级: 姓名: 学号: 课程论文成绩: 指导教师: 2016年 6 月 26 日 模式识别及人工神经网络 摘要:人工神经网络是指模拟人脑神经系统的结构和功能,运用大量的处理部件,由人工方式建立起来的网络系统。该文首先介绍了神经网络研究动向,然后介绍了近年来几种新型神经网络的基本模型及典型应用,包括模糊神经网络、神经网络与遗传算法的结合、进化神经网络、混沌神经网络和神经网络与小波分析的结合。最后,根据这几种新型神经网络的特点, 展望了它们今后的发展前景。[2] 关键词:模糊神经网络;神经网络与遗传算法的结合;进化神经网络;混沌神经网络;神经网络与小波分析。 Pattern recognition and artificial neural network
Abstract: Artificial neural network is the system that simulates the human brain’s structure and function, and uses a large number of processing elements, and is manually established by the network system. This paper firstly introduces the research trends of the neural network, and then introduces several new basic models of neural networks and typical applications in recent years, including of fuzzy neural network, the combine of neural network and genetic algorithm, evolutionary neural networks, chaotic neural networks and the combine of neural networks and wavelet analysis. Finally, their future prospects are predicted based on the characteristics of these new neural networks in the paper. Key words: Fuzzy neural network; Neural network and genetic algorithm; Evolutionary neural networks; Chaotic neural networks; Neural networks and wavelet analysis 1 什么是人工神经网络? 所谓人工神经网络就是模仿生物大脑的结构和功能而构成的一种信息系统计算机,人士地球上具有最高智慧的动物,而人的指均来自大脑,人类靠大脑进行思考,联想,记忆和推理判断等,这些功能是任何被称为“电脑”的一般计算机所无法取代的,长期以来,许多科学家一直致力于人脑内部结构和功能的探讨和研究,并试图建立模拟人脑的计算机,虽然到目前对大脑的内部工作机理还不是完全清楚,但对其结构有所了解。粗略地讲,大脑是由大量神经细胞或者神经元组成的,每个神经元可看作是一个小的处理单元,这些神经元按某种方式连接起来,形成大脑内部的生理神经元网络。这种神经元网络中各神经元之间联结的强弱,按外部的激励信号做自适应变化,而每个神经元又随着所接收到的多个信号的综合大小而呈现兴奋或抑制状态。 1.1 人工智能网络的发展 (1)初期(萌发)期---MP模型的提出和人工升级网络的兴起 --1943年,美国神经生理学家Warren Mcculloch和数学家Walter Pitts 合写了一篇关于神经元如何工作的开拓性文章:“A Logical Calculus of Ideas Immanent in Nervous Activity”。该文指出,脑细胞的活动就像各种逻辑运算。
多ISP出口接入的设计与实现 【摘要】提出了多出口校园网环境下路由器的多种配置,即地址转换、默认路由、静态路由、策略路由。旨在合理利用现有CERNET网络及当地多个ISP 提供的网络出口,提高校园网的出口带宽和利用率,优化了网络配置。 【关键词】校园网络;ISP;设计与实现 0.引言 目前国内大多数非省会城市高校普遍采用多出口方式实现其高速对外访问,即一个通过中国教育科研网(CERNET)的低带宽出口(地址列表可以参考地址:http://https://www.doczj.com/doc/243236132.html,)和另一个或多个通过本地电信运营商的高带宽出口,由于电信ISP和铁通ISP(internet service provider网络服务商)具有较高的接入带宽且接入费用较低,可以极大的提高校园网网络出口带宽,于是我院选择电信和铁通作为第二、第三网络出口,以达到既使用教育科研网的IP地址和域名解析,又能够实现校内用户通过ISP运营商访问外部资源和校外用户高速访问学校的www等服务器的目的。 1.校园网络出口现状分析 在校园网中使用两个或多个网络出口后,一般会有如下需求: (1)在有限的本地ISP服务商提供的几个合法公网IP地址情况下,不对任何客户端做任何修改,就能使所有用户正常访问外网,使得校园网能够正常工作。 (2)要求校园网客户端用户访问CERNET的免费地址时,客户端网络出口能够自动选择为CERNET;而访问其他网站(非CERNET站点)时,走当地ISP 提供的网络出口。 (3)要求校外的用户通过网络服务商能够快速访问校园网的Web、教务管理系统、Mail、DNS等服务器,即要求相关服务器使用ISP提供的合法IP地址。 2.目前我院网络设备主要有 一台华为NE20-4路由器、一台清华得实NetST防火墙、一台华三S9508核心交换机及若干台H3CE352(48口)和H3CE328(24口)以太网交换机。 校园网络结构图如下: 保山学院校园网拓扑图 综合以上需求,要求校园网的核心网络设备必须能够根据客户端源、目的IP
人工智能在计算机网络中的运用-计算机网络论文-计算机论文 ——文章均为WORD文档,下载后可直接编辑使用亦可打印—— [摘要]近年来,人工智能作为信息化时代的典型代表,其应用领域越发广泛,也备受社会各界人士关注,并开始应用在生理学、电子学、计算机科学以及生物学等领域。随着互联网技术和信息技术的不断更新,对于计算机网络技术来说,实现人性化、智能化的服务已经成为一个必然的发展趋势。基于此,本文首先介绍了人工智能技术中的基本概念,然后结合人工智能的主要优势,探讨了其在计算机网络技术当中的应用。 [关键词]人工智能;计算机网络技术;安全隐患 1人工智能的优势
人工智能的概念在20世纪60年代被提出,经历了多年的发展,开始应用在很多领域。人工智能技术体现了综合性的特征,涵盖了心理学、计算机科学以及语言学等多种理论体系,就现阶段人工智能的发展趋势来讲,其功能也越发多样,主要包括模式识别、自动设计程序以及语言理解等,随着时间的推移,以及学者对于人工智能的研究不断深入,必然会拓宽其应用范围,同时其优势也将越发显著。人工智能的优势主要体现在以下几个层面。 1.1拥有巨大的潜力 人工智能沿袭了计算机网络技术强大的运算功能,同时与计算机网络技术相比,拥有巨大的潜力。但是,人工智能的运作过程中更加依赖内部运行结构的支撑,不会消耗过多的能量,同时也将减少外界环境的影响。因此,应用人工智能符合可持续发展的要求,也体现了高效与低耗运作的特征。
1.2拥有强大的运算功能 人工智能的运算功能较为强大,可解决模型不确定以及信息模糊等诸多问题。在大数据时代,人们提高了对于大数据技术的重视程度,而人工智能同样有效应用了大数据的相关理念,能够通过数据建模预测事物的发展方向,已成为网络管理重点。值得一提的是,传统的运算模式在处理海量信息时仍然存在诸多问题,但人工智能却可以避免该问题,可对海量数据信息进行精准判断,在处理模糊信息时更加高效,能够有效提高网络运行的效率。 1.3人工智能的学习能力相对较强 传统的计算机网络技术具有提前预设的功能,而人工智能则在此基础上具有严谨而详细的逻辑推理,拥有较强的学习能力,解决问题
网络时代人工智能的发展 摘要:五十多年来,人工智能在模式识别、知识工程、机器人等领域已经取得重大成就,但是离真正的人类智能还相差甚远。本文强调在当今的网络时代,作为信息技术的先导,人工智能科学有着非常值得关注的研究方向,要在科学交叉研究中实现人工智能的发展与创新。要关注认知科学、脑科学、生物智能、物理学、复杂网络、计算机科学与人工智能间的交叉渗透,尤其是重视认知物理学的研究;自然语言是人类思维活动的载体,是人工智能研究知识表示无法回避的直接对象,要对语言中的概念建立起能够定量表示的不确定性转换模型,发展不确定性人工智能;要利用现实生活中复杂网络的小世界模型和无尺度特性,把网络拓扑作为知识表示的一种新方法,研究网络拓扑的演化与网络动力学行为,研究网络化了的智能,从而适应信息时代数据挖掘的普遍要求,迎接人工智能科学与应用新的辉煌。 关键词;人工智能;认知物理学;数据场;云模型;网络化智能 从1956年著名的达特茅斯(Dartmouth)会议算起,人工智能学科诞生已有半个世纪的历史,先后出现有逻辑学派(符号主义)、控制论学派(联结主义)和仿生学派(行为主义)。符号主义方法以物理符号系统假设和有限合理性原理为基础,联结主义方法以人工神经网络和进化计算为核心,行为主义方法则侧重研究感知和行动之间的关系。这些理论和方法在模式识别、知识工程、机器人等领域取得伟大成就,极大地推动了科技进步和社会发展。专家 系统、智能控制、数据挖掘、智能机器人、智能社区随处可见,改变了我们的生活。 人工智能自诞生之日起就引发了人们无限美丽的想象和憧憬,但人工智能的
发展过程也存在着不少争议和困惑:什么才算是真正的“智能”?为什么再高级的电脑、再智能的机器与人类的智能相比仍然那么幼稚?为什么人工智能与人们最初的想象和期望仍然相距甚远?在网络时代人工智能的发展会有什么样新的特征? 最近十几年来,我们在国家自然科学基金项目、国家863计划、973计划的支持下,把网络拓扑作为知识表示手段,围绕不确定性人工智能做了一些研究工作。这些研究正走向一个有机的整体,把许多重要的、但又是局部的结果,统一到一个令人满意的框架内。这些研究也让我们深深陷入了对人工智能未来发展方向的思考。 1在交叉学科研究中实现人工智能的创新 人工智能虽然常常被划分为计算机或自动化学科的一个分支,但它的研究范畴一直是很宽泛的,涉及到哲学、认知科学、行为科学、脑科学、生理学、心理学、语言学、逻辑学、物理学、数学以及信息论、控制论和系统论等许多学科领域。人工智能这种综合性、交叉渗透性早在它诞生之日起就得到充分地体现。在达特茅斯会议上,有包括数学、神经生理学、精神病学、心理学、信息论和计算机科学等多领域的 学者参加,科学家们从各自学科的角度出发,根据不同的学科背景,强调了各自的重点,产生了激烈的碰撞。尽管各自的出发点有所不同,它们都汇聚到研究人类智能活动的表现形式和认知规律,借用数理逻辑来形式化,用计算机作为载体,提供关于形式化计算和符号处理的理论,模拟人类某些智能行为和方法,构造具有一定智能的人工系统,让计算机去完成以往需要人的智力才能胜任的工作,从而诞生了“人工智能”这一新的学科。 当前,网络科学和技术无所不在,网络中的节点,可以是形形色色的行为主体,本质上说,网络科学是研究网络中节点相互作用的理论和方法。回首人工智
网络系统组建项目设计方案 第一章项目概述 1.1项目背景 随着互联网的不断发展,XXXX的壮大。随着用户的增多,上网、共享网络资源越来越慢,总经理要求网络工程师对基地网络进行整改规划。要求基地的所有机器都能连接互联网。为防止网络通信出现故障,要对网络进行冗余。考虑到网络通信的速度,要求对网络进行负载均衡。考虑到网络通信的质量,要缩短广播域的围。 1.2项目目标 在一个月,各网络小组分段组建小型局域网,最后将XXXX建成。 第二章总体技术设计 2.1网络新建或者改造目标
2.1.1改造情况描述 结构整齐,层次清晰,便于管理。 采用静态路由协议,维护简单,扩展性好; 2.1.2新增设备列表 第三章详细技术设计 3.1设备使用部署规划 3.1.1设备命名规划
3.1.2软件版本规划 3.1.3端口描述规划
3.2IP地址规划 3.2.1管理地址规划 3.2.2互联地址规划
3.2.3业务地址规划 3.3VLAN和端口规划 3.3.1VLAN规划 VLAN 10 作为用户主机的所在VLAN; VLAN 20 作为服务器区域VLAN。 3.4路由协议规划 3.4.1路由协议选择 该区域网络仅选择静态路由即可,快捷、方便、易搭建。 3.4.2路由协议部署 在核心层交换机上配置一条指向出口路由的静态路由,使网络数据能传输到外网; 在出口路由上配置一条指向用户主机跟服务器区域的静态路由,使网络数据能回到主机端。
3.5网络安全规划 3.5.1Telnet 远程控制核心交换机 3.5.2登录口令 enable secret 5 $1$mERr$v8N22LDv5Ra7uI3pi/Td50 (加密后的口令)第四章关键设备详细配置 4.1出口路由区设备配置实现 TSG-ck-RSR20-1#show running-config Building configuration... Current configuration : 773 bytes ! version 12.4 no service timestamps log datetime msec no service timestamps debug datetime msec no service password-encryption
移动LTE出口解决方案之防火墙设计 移动LTE背景介绍 LTE(Long Term Evolution,长期演进)是3G的演进,被视为3G到4G演进的主要技术。LTE并非人们普遍误解的4G技术,而是3G与4G技术的一个过渡,是3.9G的全球标准。它改进并增强了3G的空中接入技术,采用OFDM和MIMO 作为其无线网络演进的唯一标准。在20MHz的频谱带宽下能提供下行100Mbps 和上行50Mbps峰值速率。 中国移动TD-LTE核心网局点目前承载基本只有分组域业务,电路域业务依旧由原2G/TD网络承载。 LTE拟承载业务包括: ?中高速承类载数据业务; ?现网PS域业务:WAP、无线游戏、音乐下载等; ? TD-LTE高宽带演示业务:即摄即传、标清视频监控等。 移动LTE流量模型介绍 中国移动TD-LTE核心网中流量主要分为Gn和Gi两种。对于两种流量一般分别设置两组防火墙分别承载接入CMNET出口路由器。
其中,Gn流量主要为本地SGSN访问其他局点SGSN流量,用于请求漫游客户终端注册信息,由Gn防火墙做NAT后经CMNET至其他局点。 Gi流量主要分为两个部分,一部分为直接访问CMNET的流量,一部分为访问LTE 业务的流量,两种流量通过手机终端的APN接入点不同,分别分配不同地址池的私网地址。 访问CMNET流量在Gi防火墙上做NAT后访问CMNET,访问LTE流量在GGSN上封装入GRE隧道,Gi防火墙直接转发,通过CMNET至LTEGRE路由器上解封装后访问WAP业务服务器。
在TD-LTE网络中,基本流量走向有两种,本地用户和漫游用户。 本地用户上网流量由终端至eNodeB(LTE无线基站)经PTN网络至SGSN,通过Gn链路到达GGSN,在GGSN上分为WAP流量和CMNET流量,WAP流量封装GRE隧道经防火墙、CMNET至LTE系统经过解封装至WAP服务器。CMNET流量由防火墙做NAT访问CMNET。 漫游用户上网流量在SGSN之前与本地用户一样,但由于本地SGSN没有漫游用户终端注册信息,需要通过Gn链路经Gn防火墙、CMNET访问其他局点SGSN请求此漫游用户的终端注册信息,当本地SGSN收到漫游用户终端注册信息后,上网流量在到达GGSN,后续访问过程则与本地用户一致。 Gi防火墙与Gn防火墙相比,Gi由于主要是访问CMNET,域间策略相对简单但业务量较大;Gn防火墙需要放通对于其他局点包括国际局点Gn地址,策略较为复杂,在几千条数量级,但业务量相对Gi防火墙较少。 LTE出口防火墙设计 H3C公司提供的防火墙方案,采用vrrp技术,实现双机框高可靠性的部署。同时采用NAT业务单板插卡的方式,实现整机容量的灵活扩容。 因整机容量和商务的不同,目前可以选择的机框有S75E、S95E,以95E为主;目前可以选择的NAT业务插卡有Secblade II、SecbladeIII板卡。 防火墙采用串接方式接入CMNET,下联核心网交换机。
人工智能的应用领域和发展方向 …………………….. 摘要 人工智能是一门极富挑战性的科学,但也是一门边沿学科。它属于自然科学和社会科学的交叉。涉及的学科主要有哲学、认知科学、数学、神经生理学、心理学、计算机科学、信息论、控制论、不定性论、仿生学等。 人工智能(Artificial Intelligence) ,英文缩写为AI。。它是研究、开发用于模拟、延伸和扩展人的智能的理论、方法、技术及应用系统的一门新的技术科学。人工智能是计算机科学的一个分支,它企图了解智能的实质,并生产出一种新的能以人类智能相似的方式做出反应的智能机器,该领域的研究包括机器人、语言识别、图像识别、自然语言处理和专家系统等。 关键词:人工智能;应用领域;发展方向;人工检索;
目录 人工智能的应用领域和发展方向 (1) 摘要 (1) 一、有关人工智能 (3) 二、人工智能的二种实现方式及其比较 (3) 三、人工智能的应用领域 (3) 3.1在管理系统中的应用。 (3) 3.2在工程领域中应用。 (3) 3.3在技术研究中应用 (4) 四、人工智能的发展方向 (4) 4.1专家系统。 (4) 4.2智能信息检索技术 (4) 4.3 SOAr (4) 4.4未来人工智能的研究方向 (5) 结论 (5) 参考文献 (5)
一、有关人工智能 人工智能也称机器智能,它是计算机科学、控制论、信息论、神经生理学、心理学、语言学等多种学科互相渗透而发展起来的一门综合性学科。从计算机应用系统的角度出发,人工智能是研究如何制造出人造的智能机器或智能系统,来模拟人类智能活动的能力,以延伸人们智能的科学。 人工智能没有社会性,没有人类的意识所特有的能动的创造能力,纯系无意识的机械的物理的过程。正因为如此它一直处在计算机技术的前沿,同时它的理论和发现在很大程度上将决定计算机技术的发展方向。 二、人工智能的二种实现方式及其比较 第一种叫做工程学方法(Engineering approach),是采用传统的编程技术,使系统呈现智能的效果,而不考虑所用方法是否与人或动物机体所用的方法相同。它已在一些领域内作出了成果,如文字识别、电脑下棋等。第二种是模拟法(Modeling approach),它不仅要看效果,还要求实现方法也和人类或生物机体所用的方法相同或相类似。第一种方法,需要人工详细规定程序逻辑,如果游戏简单,还是方便的。如果游戏复杂,角色数量和活动空间增加,相应的逻辑就会很复杂(按指数式增长),人工编程就非常繁琐,容易出错。而一旦出错,就必须修改原程序,重新编译、调试,最后为用户提供一个新的版本或提供一个新补丁, 非常麻烦。采用第二种方法时,编程者要为每一角色设计一个智能系统(一个模块)来进行控制,这个智能系统(模块)开始什么也不懂,就像初生婴儿那样,但它能够学习,能渐渐地适应环境,应付各种复杂情况。 三、人工智能的应用领域 3.1在管理系统中的应用。 (1)人工智能应用于企业管理的意义不在于提高效率,而是用计算机实现人们非常需要做,但工业工程信息却做不了或很难做到的事。 (2)智能教学系统(ITS)是人工智能与教育结合的主要形式。也是今后教学系统的发展方向。信息技术的飞速发展和新的教学体系开发模式的提出和不断完善,推动人们综合运用媒体技术、网络基础和人工智能技术开发新的教学体系。计算机智能教学体系就是其中的代表。 3.2在工程领域中应用。
人工智能在计算机网络技术中的运用 随着科技的不断发展,在当前社会中,计算机技术、信息技术等逐渐得到了广泛的应用。而与此同时,用户的实际使用需求也在不断提高,过去简单的词义解释、数据运算等功能已经难以满足用户的实际使用需要。随着互联网技术和信息技术的不断更新,对于计算机网络技术来说,实现人性化、智能化的服务已经成为了一个必然的发展趋势。基于此,该文首先介绍了人工智能技术中的基本概念,然后结合人工智能的主要优势,探讨了其在计算机网络技术当中的应用。 在当前的社会当中,人工智能是一项应用前景十分广阔的技术, 在社会各个领域中,都得到了极为广泛的应用。在人们的日常娱乐、工作、生活当中,人工智能发挥了很大的作用,例如专家系统、智能电器等。智能化科技的出现和应用,使得人们的生活得到了极大的丰富。同时,人工智能的出现,是现代社会中一种全新的科学产业,它的出现对当下社会生活和生产等诸多方面都带来看非常深远的影响。随着人工智能的逐渐深入,促进社会发展的生产工厂机器开始步入到半智能化半人工的状态。这种状况在当下的社会生产和计算机网络技术发展中起到了有效促进作用。本文通过对人工智能进行简要概述,在此基础上探讨了其在计算机网络技术中的具体运用,希望能够为我国人工智能和计算机网络技术的发展带来一定帮助。 人工智能是一项集合了众多学科的综合型应用技术,涉及的学科有语言学、生理学、心理学等。人工智能技术以模仿和超越人类的智能为主要目标,采用各种高科技手段,让机器具有人的基本能力、思
维方式、行为方式等。智能化产品是人工智能技术的直接载体,智能化产品让人们的生活变得丰富多彩。人工智能研究的内容非常广泛,包括自动设计、机器学习、专家系统。 人工智能的发展历史并不长,在上世纪五十年代美国科学家首次提出了人工智能这一概念。在人工智能的发展历史进程中,有三次跨越式发展。第一次是机器实现代替人类进行计算推理,对问题进行求解,如机器定理证明和专家系统(ES);第二阶段发展中,发明了机器人,它能在变化的环境中找到有用的资料信息,与外界环境进行交流,代替人类完成一部分思维分析工作;在第三阶段,研究出了智能化的数据挖掘系统,这个系统将大量数据进行自动化智能分析,提取出有用的信息,最终完成出货、数据分析、可视化技术和识别功能。这种数据挖掘系统的研发提高机器的自主学习能力,有利于扩大适用领域和范围。在人工智能的整个发展过程中,都依赖于计算机网络技术。计算机网络技术对人工智能的发展具有决定性作用。 2 人工智能技术的优势 现在的计算机网络系统具有一些明显的特点,比如动态性、高速性、瞬变性。由于网络系统的这些特点,对网络管理技术提出了更高的要求。要想使网络系统能够安全高效的运行,就必需提高网络管理技术,包括管理方法和手段。人工智能技术是提高网络管理技术的重要工具,具有一定的优势,主要表现在以下几方面。 2.1 具有处理模糊信息能力和协作能力
人工智能在计算机网络技术中的应用 摘要:当前我们生活在信息化发展的大时代之中,计算机网络技术在不断的发展,并且与人们的生活息息相关。进你那俩,人工智能技术的发展越来越趋于成熟,其不仅能够帮助人类对计算机数据进行良好的管理,还能够促使计算机网络不断趋于智能化,使人们的工作和生活越来越便利。接下来在本文中,笔者将对人工智能的定义、特点以及其在网络中的应用进行简要的分析。 关键词:人工智能;计算机网络技术;应用 随着计算机技术的不断发展,我们对计算机的依赖性越来越强,这种依赖性也对计算机的进一步发展起到了促进的作用,至今已经达到了一个质的上升[1]。但是就目前的情况来看,人们的工作和生活对计算机的要求已经大大提高,计算机不能够再单纯的作为一个计算和储存的工具,而是需要人工智能的出现使人们的工作和生活提高效率,并且增强人们的用户体验[2]。 一、人工智能的定义及特点 (一)人工智能的定义 人工智能首次被提出大约是在上个世纪的60年代,该技术与计算机、心理学、语言学等多个学科具有紧密的联系,
内容十分丰富并且具有挑战性,具有人性化与智能化的双重特征。对人工智能进行研发,其主要的目的是使用机器替代人类完成复杂的、难度较大的工作,在提升工作质量的同时提升工作效率,以节约时间与人力资源[3]。 人工智能能够对多种知识范围进行探索,例如智能控制、模式识别、自动程序设计、自然语言理解都在其能够进行探索的范围之内,并且,人工智能的发展也是需要各个学科为其打下坚实的基础,尤其是计算机这一学科,对人工智能的出现与发展都起到了至关重要的作用。 (二)人工智能的特点 人工智能的特点主要可以从三个方面进行体现:①人工智能能够对不具有确定性的问题进行解决:例如,某些问题需要使用计算机进行计算,但是又无法得知具体的模型,此时采用人工智能,其能够应用自身较强的运算能力从模糊的信息中分析其关键的内容,最后将与关键内容相关的数据完整、全面的呈现出来,有效的保障了网络管理的流畅性与高效性[4];②人工智能具有学习新知识的能力:在过去的很多年里,学习新知识的能力都是只有具有生命特征的动物才具有的能力,但是随着科学技术的发展,人工智能已经成功的突破了多年的界限,做到了对输入的数据进行具有较强逻辑性的计算和推理,并且能够得到层次更高的数据,大大缩短了网络运行所需的时间,有效的提高了工作质量与效率;③